
|
|
Lecture notes, cheat sheets
Anesthesiology and resuscitation. Infusion therapy (lecture notes)
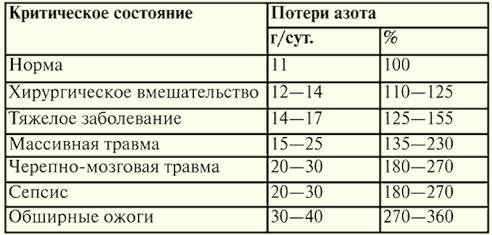
Directory / Lecture notes, cheat sheets Table of contents (expand) Lecture No. 16. Infusion therapy Infusion therapy is a drip injection or infusion intravenously or under the skin of drugs and biological fluids in order to normalize the water-electrolyte, acid-base balance of the body, as well as for forced diuresis (in combination with diuretics). Indications for infusion therapy: all types of shock, blood loss, hypovolemia, loss of fluid, electrolytes and proteins as a result of indomitable vomiting, intense diarrhea, refusal to take fluids, burns, kidney disease; violations of the content of basic ions (sodium, potassium, chlorine, etc.), acidosis, alkalosis and poisoning. The main signs of dehydration of the body: retraction of the eyeballs into the orbits, dull cornea, dry, inelastic skin, characteristic palpitations, oliguria, urine becomes concentrated and dark yellow, the general condition is depressed. Contraindications to infusion therapy are acute cardiovascular failure, pulmonary edema and anuria. Crystalloid solutions are able to compensate for the deficiency of water and electrolytes. Apply 0,85% sodium chloride solution, Ringer and Ringer-Locke solutions, 5% sodium chloride solution, 5-40% glucose solutions and other solutions. They are administered intravenously and subcutaneously, by stream (with severe dehydration) and drip, in a volume of 10-50 ml/kg or more. These solutions do not cause complications, except for overdose. The goals of infusion therapy are: restoration of BCC, elimination of hypovolemia, ensuring adequate cardiac output, maintaining and restoring normal plasma osmolarity, ensuring adequate microcirculation, preventing aggregation of blood cells, normalizing the oxygen transport function of blood. Colloidal solutions are solutions of macromolecular substances. They contribute to the retention of fluid in the vascular bed. Hemodez, polyglucin, reopoliglyukin, reogluman are used. With their introduction, complications are possible, which manifest themselves in the form of an allergic or pyrogenic reaction. Routes of administration - intravenously, less often subcutaneously and drip. The daily dose does not exceed 30-40 ml/kg. They have a detoxifying quality. As a source of parenteral nutrition, they are used in case of prolonged refusal to eat or inability to feed by mouth. Blood and casein hydrolysins are used (alvezin-neo, polyamine, lipofundin, etc.). They contain amino acids, lipids and glucose. Sometimes there is an allergic reaction to the introduction. Rate and volume of infusion. All infusions in terms of volumetric infusion rate can be divided into two categories: requiring and not requiring rapid correction of the BCC deficiency. The main problem may be patients who need rapid elimination of hypovolemia. i.e., the rate of infusion and its volume must ensure the performance of the heart in order to properly supply regional perfusion of organs and tissues without significant centralization of blood circulation. In patients with an initially healthy heart, three clinical landmarks are most informative: mean BP > 60 mm Hg. Art.; central venous pressure - CVP> 2 cm of water. Art.; diuresis 50 ml/h. In doubtful cases, a test with a load in volume is carried out: 15-20 ml of a crystalloid solution is poured over 400-500 minutes and the dynamics of CVP and diuresis are observed. A significant rise in CVP without an increase in diuresis may indicate heart failure, which suggests the need for more complex and informative methods for assessing hemodynamics. Keeping both values low suggests hypovolemia, then a high infusion rate is maintained with repeated step-by-step assessment. An increase in diuresis indicates prerenal oliguria (hypoperfusion of the kidneys of hypovolemic origin). Infusion therapy in patients with circulatory insufficiency requires a clear knowledge of hemodynamics, large and special monitoring monitoring. Dextrans are colloidal plasma substitutes, which makes them highly effective in the rapid recovery of BCC. Dextrans have specific protective properties against ischemic diseases and reperfusion, the risk of which is always present during major surgical interventions. The negative aspects of dextrans include the risk of bleeding due to platelet disaggregation (especially characteristic of rheopolyglucin), when it becomes necessary to use significant doses of the drug (> 20 ml / kg), and a temporary change in the antigenic properties of the blood. Dextrans are dangerous because of their ability to cause a "burn" of the epithelium of the tubules of the kidneys and therefore are contraindicated in renal ischemia and renal failure. They often cause anaphylactic reactions, which can be quite severe. Of particular interest is a solution of human albumin, as it is a natural colloid of a plasma substitute. In many critical conditions accompanied by damage to the endothelium (primarily in all types of systemic inflammatory diseases), albumin is able to pass into the intercellular space of the extravascular bed, attracting water and worsening interstitial tissue edema, primarily the lungs. Fresh frozen plasma is a product taken from a single donor. FFP is separated from whole blood and frozen immediately within 6 hours of blood sampling. Stored at 30°C in plastic bags for 1 year. Given the lability of clotting factors, FFP should be infused within the first 2 hours after rapid thawing at 37°C. Transfusion of fresh frozen plasma (FFP) gives a high risk of contracting dangerous infections, such as HIV, hepatitis B and C, etc. The frequency of anaphylactic and pyrogenic reactions during transfusion of FFP is very high, so compatibility according to the ABO system should be taken into account. And for young women, Rh-compatibility must be considered. Currently, the only absolute indication for the use of FFP is the prevention and treatment of coagulopathic bleeding. FFP performs two important functions at once - hemostatic and maintaining oncotic pressure. FFP is also transfused with hypocoagulation, with an overdose of indirect anticoagulants, with therapeutic plasmapheresis, with acute DIC, and with hereditary diseases associated with a deficiency of blood coagulation factors. Indicators of adequate therapy are a clear consciousness of the patient, warm skin, stable hemodynamics, the absence of severe tachycardia and shortness of breath, sufficient diuresis - within 30-40 ml/h. 1. Blood transfusion Complications of blood transfusion: post-transfusion disorders of the blood coagulation system, severe pyrogenic reactions with the presence of hyperthermic syndrome and cardiovascular decompensation, anaphylactic reactions, erythrocyte hemolysis, acute renal failure, etc. The basis of most complications is the reaction of rejection by the body of foreign tissue. There are no indications for transfusion of canned whole blood, because the risk of post-transfusion reactions and complications is significant, but the most dangerous is the high risk of infection of the recipient. In case of acute blood loss during surgical intervention and adequate replenishment of the BCC deficiency, even a sharp decrease in hemoglobin and hematocrit does not threaten the life of the patient, since oxygen consumption under anesthesia is significantly reduced, additional oxygenation is acceptable, hemodilution helps prevent the occurrence of microthrombosis and mobilization of erythrocytes from the depot, increase blood flow velocity and etc. The "reserves" of erythrocytes that a person has by nature significantly exceed the real needs, especially in a state of rest, in which the patient is at this time. Recommendations for the appointment of transfusion of donor blood and erythrocytes during surgery. 1. Transfusion of erythrocyte mass is carried out after the restoration of the BCC. 2. In the presence of severe concomitant pathology, which can lead to death (for example, severe anemia is poorly tolerated in severe coronary heart disease). 3. In the presence of the following indicators of the patient's red blood: 70-80 g / l for hemoglobin and 25% for hematocrit, and the number of red blood cells is 2,5 million. Indications for blood transfusion are: bleeding and correction of hemostasis. Types of erythrocytes: whole blood, erythrocyte mass, EMOLT (erythrocyte mass separated from leukocytes, platelets with saline). Blood is administered intravenously by drip, using a disposable system at a rate of 60-100 drops per minute, in a volume of 30-50 ml/kg. Before blood transfusion, it is necessary to determine the blood type and Rh factor of the recipient and donor, conduct a test for their compatibility, and a biological test for compatibility is performed at the patient's bedside. When an anaphylactic reaction occurs, the transfusion is stopped and measures to eliminate shock begin. Standard platelet concentrate is a suspension of twice centrifuged platelets. The minimum platelet count is 0,5 x 1012 per liter, leukocytes - 0,2 x 109 per liter. Hemostatic characteristics and survival are most pronounced in the next 12-24 hours of preparation, but the drug can be used within 3-5 days from the moment of blood sampling. Platelet concentrate is used for thrombocytopenia (leukemia, bone marrow aplasia), thrombopathy with hemorrhagic syndrome. 2. Parenteral nutrition In severe diseases accompanied by severe disturbances of homeostasis, it is necessary to provide the body with energy and plastic material. Therefore, when nutrition through the mouth is impaired or completely impossible for some reason, it is necessary to transfer the patient to parenteral nutrition. In critical conditions of various etiologies, the most significant changes occur in protein metabolism - intensive proteolysis is observed, especially in striated muscles. Depending on the severity of the ongoing process, body proteins are catabolized in the amount of 75-150 g per day (daily protein losses are shown in Table 11). This leads to a deficiency of essential amino acids, which are used as an energy source during gluconeogenesis, resulting in a negative nitrogen balance. Table 11 Daily protein loss in critical conditions
The loss of nitrogen leads to a decrease in body weight, since: 1 g of nitrogen \u6,25d 25 g of protein (amino acids) \uXNUMXd XNUMX g of muscle tissue. Within a day from the onset of a critical condition, without adequate therapy with the introduction of a sufficient amount of essential nutrients, its own reserves of carbohydrates are exhausted, and the body receives energy from proteins and fats. In this regard, not only quantitative, but also qualitative changes in metabolic processes are carried out. The main indications for parenteral nutrition are: 1) anomalies in the development of the gastrointestinal tract (esophageal atresia, pyloric stenosis, and others, pre- and postoperative period); 2) burns and injuries of the oral cavity and pharynx; 3) extensive body burns; 4) peritonitis; 5) paralytic ileus; 6) high intestinal fistulas; 7) indomitable vomiting; 8) coma; 9) severe diseases accompanied by increased catabolic processes and decompensated metabolic disorders (sepsis, severe forms of pneumonia); 10) atrophy and dystrophy; 11) anorexia due to neuroses. Parenteral nutrition should be carried out in conditions of compensation for volemic, water-electrolyte disorders, elimination of microcirculation disorders, hypoxemia, metabolic acidosis. The basic principle of parenteral nutrition is to provide the body with an adequate amount of energy and protein. For the purpose of parenteral nutrition, the following solutions are used. Carbohydrates: The most acceptable drug used at any age is glucose. The ratio of carbohydrates in the daily diet should be at least 50-60%. For complete utilization, it is required to maintain the rate of administration, glucose should be supplied with ingredients - insulin 1 unit per 4 g, potassium, coenzymes involved in energy utilization: pyridoxal phosphate, cocarboxylase, lipoic acid, and ATP - 0,5-1 mg / kg per day intravenously. When properly administered, highly concentrated glucose does not cause osmotic diuresis and a significant increase in blood sugar levels. For nitrogen nutrition, either high-quality protein hydrolysates (aminosol, aminone) or solutions of crystalline amino acids are used. These drugs successfully combine essential and non-essential amino acids, they are low toxic and rarely cause an allergic reaction. Doses of administered protein preparations depend on the degree of violation of protein metabolism. With compensated disorders, the dose of protein administered is 1 g/kg of body weight per day. Decompensation of protein metabolism, manifested by hypoproteinemia, a decrease in the albumin-globulin ratio, an increase in urea in daily urine, requires the introduction of increased doses of protein (3-4 g/kg per day) and anti-catabolic therapy. This includes anabolic hormones (retabolil, nerabolil - 25 mg intramuscularly 1 time in 5-7 days), building a parenteral nutrition program in the hyperalimentation mode (140-150 kcal / kg of body weight per day), protease inhibitors (kontrykal, trasylol 1000 U / kg per day for 5-7 days). For adequate assimilation of plastic material, each gram of introduced nitrogen must be provided with 200-220 kcal. Amino acid solutions should not be administered with concentrated glucose solutions, as they form toxic mixtures. Relative contraindications to the introduction of amino acids: renal and hepatic failure, shock and hypoxia. Fat emulsions containing polyunsaturated fatty acids are used to correct fat metabolism and increase the caloric content of parenteral nutrition. Fat is the most high-calorie product, however, for its utilization, it is necessary to maintain optimal doses and the rate of administration. Fat emulsions should not be administered together with concentrated polyionic glucose solutions, as well as before and after them. Contraindications for the introduction of fat emulsions: liver failure, lipemia, hypoxemia, shock conditions, thrombohemorrhagic syndrome, microcirculation disorders, cerebral edema, hemorrhagic diathesis. The required data of the main ingredients for parenteral nutrition are given in Table 12 and Table 13. Table 12 Doses, rates, calorie content of the main ingredients for parenteral nutrition
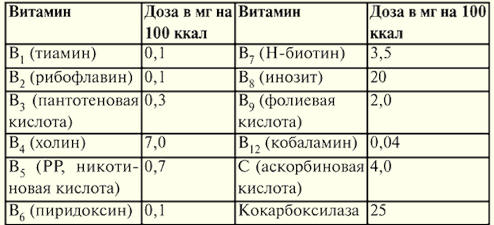
When prescribing parenteral nutrition, it is necessary to introduce optimal doses of vitamins that are involved in many metabolic processes, being coenzymes in energy utilization reactions. Table 13 Doses of vitamins (in mg per 100 kcal) required during parenteral nutrition
The program of parenteral nutrition, carried out in any mode, should be drawn up in terms of a balanced ratio of ingredients. The optimal ratio of proteins, fats, carbohydrates is 1: 1,8: 5,6. For the breakdown and inclusion of proteins, fats and carbohydrates in the process of synthesis, a certain amount of water is necessary. The ratio between the need for water and the calorie content of food is 1 ml H2O - 1 kcal (1: 1). Calculation of the need for resting energy consumption (ERP) according to Harris-Benedict: Men - EZP = 66,5 + 13,7 x weight, kg + 5 x height, cm - 6,8 x age (years). Women - EZP = 66,5 + 9,6 x weight, kg + 1,8 x height, cm - 4,7 x age (years). The EZP value, determined by the Harris-Benedict formula, averages 25 kcal/kg per day. After the calculation, the patient's physical activity factor (PFA), the metabolic activity factor (FMA) based on the clinical status, and the temperature factor (TF) are selected, with the help of which the energy requirement (E) of a particular patient will be determined. The coefficient for calculating FFA, FMA and TF are shown in Table 14. Table 14 Coefficient for calculating FFA, FMA and TF
To determine the daily PE, the EZP value is multiplied by FFA, FMA and TF. 3. Detoxification therapy In severe intoxication, active detoxification therapy is necessary, aimed at binding and removing toxins from the body. For this purpose, solutions of polyvinylpyrrolidone (neocompensan, gemodez) and gelatinol are most often used, adsorbing and neutralizing toxins, which are then excreted by the kidneys. These solutions are administered dropwise in an amount of 5-10 ml/kg of the patient's weight, adding vitamin C and potassium chloride solution in a minimum amount of 1 mmol/kg of body weight. Mafusol, which is an effective antihypoxant and antioxidant, also has a pronounced detoxifying property. In addition, it improves microcirculation and rheological properties of blood, which also contributes to the detoxification effect. With various poisonings, one of the most effective methods of detoxification is forced diuresis. Intravenous fluids for the purpose of forced diuresis are prescribed for severe degrees of poisoning and for milder ones, when the patient refuses to drink. Contraindications to forced diuresis are: acute cardiovascular failure and acute renal failure (anuria). Carrying out forced diuresis requires strict accounting of the volume and quantitative composition of the injected fluid, the timely appointment of diuretics, clear clinical and biochemical control. As the main solution for water load, it is proposed: glucose 14,5 g; sodium chloride 1,2 g; sodium bicarbonate 2,0 g; potassium chloride 2,2 g; distilled water up to 1000 ml. This solution is isotonic, contains the required amount of sodium bicarbonate, the concentration of potassium in it does not exceed the permissible one, and the ratio of the osmotic concentration of glucose and salts is 2: 1. At the initial stage of forced diuresis, it is also advisable to introduce plasma-substituting and any detoxification solutions: albumin 8-10 ml / kg, gemodez or neocompensan 15-20 ml / kg, mafusol 8-10 ml / kg, refortan or infucol 6-8 ml / kg kg, reopoliglyukin 15-20 ml/kg. The total amount of injected solutions should approximately exceed the daily requirement by 1,5 times. Author: Kolesnikova M.A. << Back: Artificial lung ventilation
▪ Commercial activity. Lecture notes
The existence of an entropy rule for quantum entanglement has been proven
09.05.2024 Mini air conditioner Sony Reon Pocket 5
09.05.2024 Energy from space for Starship
08.05.2024
▪ Smart material based on shark skin ▪ By 2025, HDD capacity will grow to 100 TB ▪ American scientists have developed a new filter
▪ section of the site Labor protection. Selection of articles ▪ article Noosphere. History and essence of scientific discovery ▪ How long do earthworms reach? Detailed answer ▪ article Head of department of insurance department. Job description ▪ article Knots of amateur radio equipment. Directory ▪ article Altai proverbs and sayings. Large selection
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese



 See other articles Section
See other articles Section 