
|
|
Lecture notes, cheat sheets
Anesthesiology and resuscitation. Assessment of patient severity and monitoring (lecture notes)
Directory / Lecture notes, cheat sheets Table of contents (expand) Lecture No. 14. Assessment of the severity of the patient and monitoring Assessment of the somatic condition of the patient. 1 point - patients whose disease is localized and, as a rule, does not cause systemic disorders, i.e. practically healthy people. 2 points - this includes patients with unexpressed disorders that moderately disrupt the vital activity of the body without pronounced shifts in homeostasis. 3 points - patients with vital systemic disorders that significantly disrupt the functioning of the body, but do not lead to disability. 4 points - patients with severe systemic disorders that pose a high danger to human life and lead to disability. 5 points - patients whose condition is considered critical, the risk of death within 24 hours is high. The volume and nature of the surgical intervention: 1 point - small operations for: removal of superficially located and localized tumors, opening of small abscesses, amputation of fingers and toes, ligation and removal of hemorrhoids, uncomplicated appendectomy and herniotomy. 2 points - operations of moderate severity: removal of superficially located malignant tumors requiring extended intervention; opening of abscesses localized in cavities; amputation and disarticulation of the upper and lower extremities; operations on peripheral vessels; complicated appendectomy and herniotomy requiring extensive intervention; trial thoracotomy and laparotomy; others similar in complexity and scope of intervention. 3 points - extensive surgical interventions: radical operations on the abdominal organs (except those listed above); radical operations on the organs of the chest cavity; extended limb amputations, such as transiliosacral amputation; brain surgery. 4 points - operations on the heart, large vessels and other complex interventions performed under special conditions (artificial circulation, hypothermia, etc.). Emergency surgical interventions are evaluated, as well as planned ones, according to the physical condition and volume of the operation, but they are included in a separate group or denoted in addition to the figure by the index "C". Note Operational and anesthetic risk is designated as follows: the numerator indicates the severity of the initial condition in points, the denominator indicates the volume of the operation, also in points. Classification of the objective status of the patient, developed by the American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA). 1. There are no systemic disorders. 2. Mild systemic disorders without functional impairment. 3. Moderate and severe systemic diseases with dysfunction. 4. Severe systemic disease that constantly poses a threat to life and leads to failure of functions. 5. Terminal state, high risk of death during the day, regardless of the operation. 6. Brain death, organ donation for transplantation. If the intervention is carried out on an emergency basis, the assessment of the state is supplemented by the letter "E". The assessment of the patient's condition and the possible lethality of each case are shown in Table 7. Table 7 Assessment of the patient's condition and perioperative mortality
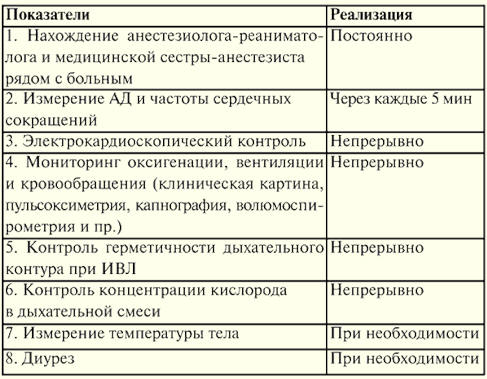
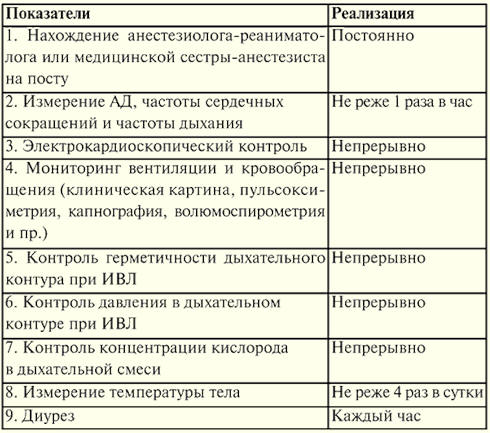
Monitoring (Table 7) is the control of functions and processes, the identification of their dangerous deviations in order to prevent complications, in particular, during anesthesia and intensive care. Monitoring is carried out to control: 1) for the functions of the patient (electrocardiography, pulse oximetry, capnography, etc.); 2) therapeutic actions (control of the neuromuscular block); 3) environment (gas composition of the inhaled mixture); 4) operation of technical means (ventilator, etc.). Monitoring of functions by degree of complexity can be carried out by: 1) continuous monitoring of parameters; 2) control with signaling when a parameter fails beyond the established limits; 3) continuous monitoring with notification when the parameter goes beyond the established limits, and additionally a hint for the solution; 4) the same with the implementation of measures to normalize the function. The relevance of monitoring is due to: 1) the ever-increasing complexity and duration of surgical interventions; 2) an increase in the severity of functional disorders in patients; 3) the complication of technical means used in critical medicine. Significance of monitoring: 1) timely diagnosis of disorders and prevention of severe complications, including cardiac and respiratory arrest; 2) more adequate tactics of intensive care and high efficiency of treatment. Monitoring indications: 1) minimal monitoring - always mandatory during anesthesia and intensive care; 2) in-depth monitoring (non-invasive and invasive methods) in case of significant violations of the body's functions, especially when a patient develops multiple organ failure; 3) preventive monitoring - at the risk of developing a critical condition. Monitoring standards. In 1978, the Dutch Board of Health introduced the first operating room monitoring standard, which listed the equipment needed for monitoring. In 1985, at the suggestion of insurance companies, the Harvard monitoring standard for anesthesiology was proposed, which provides parameters for monitoring patients during anesthesia during surgery and the mode of such monitoring. Its introduction into practice reduced the risk of anesthetic complications and made it safer for the patient. In Russia, in 1997, the MORF system outlined standards for minimal monitoring of anesthesia, resuscitation and intensive care (No. 161/DM-2 of February 24, 1997 “On measures to ensure the safety of patients during anesthesia, resuscitation and intensive care "). The data is shown in table 8, table 9. Table 8 Anesthesia
Table 9 Conducting resuscitation and intensive care
To conduct effective intensive care, it is necessary to monitor the cardiovascular, respiratory and nervous systems, the functions of the liver, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, hematopoiesis, hemostasis, as well as energy, water-electrolyte, acid-base and onco-osmotic balance. Equally important is the intensive monitoring of ongoing therapeutic interventions and their results. An important role is played by monitoring the external and internal microbiological status, as well as the use of prognostic criteria and outcome assessment. First of all, it is necessary to use a clinical assessment of the patient's status and non-invasive monitoring methods. Clinical monitoring, i.e. the observation of clinical signs and symptoms, qualitative data, is no less important than quantitative indicators obtained using sophisticated technology. System function monitoring Monitoring of the circulatory system Circulation monitoring provides timely detection of cardiac arrhythmias and myocardial ischemia through the use of electrocardiography. Cardiac arrhythmias can be identified by the P wave and the ORS complex on the electrocardiomonitor in leads V1 and V2 of the standard lead from the limbs or their modifications. Myocardial ischemia can be identified by the resulting depression of the ST segment on the ECG: 1) in the chest lead V5, as well as on one of its modifications - ischemia of the septum of the left side wall; 2) standard 2 lead from the extremities - ischemia of the basal zone of the myocardium in the basin of the right coronary artery. Downsloping ST depression (elevation) is an indicator of stress-induced ischemia. Monitoring of hemodynamics is carried out by: 1) blood pressure measurements; 2) CVP measurements in combination with volumetric stress tests (this is information about vascular filling); 3) determination of pulmonary artery pressure and wedge pressure (PWP) using a floating pulmonary artery catheter is a more accurate method for assessing intravascular volume than CVP, and can also serve as a measure of left ventricular preload; 4) determination of cardiac output using a thermodilution technique, the Fick method (CO = VCO2 /CaCO2), various modifications of the Doppler technique (esophageal Doppler echocardiography), ultrasound of the heart. Breath monitoring Respiratory monitoring is carried out according to clinical symptoms and data of capnography, pulse oximetry, volume spirometry and periodic blood gas examination. During mechanical ventilation, the pressure in the "ventilator - patient" system and the oxygen concentration in the inhaled mixture (FiO2). Clinical signs of respiratory failure: frequent (more than 24-30 per minute for adults) shallow breathing, participation in breathing of additional muscles (sternocleidomastoid, abdominal and others, which is manifested by retraction of the intercostal spaces, swelling of the wings of the nose, forced half-sitting position), sweating, cyanosis, a change in heart rate (first increase, and then there may be arrhythmia) and blood pressure (increase, and with severe hypoxia - decrease), a change in consciousness from euphoria to coma. Capnography allows timely detection of ventilation disorders: hypoventilation (increased CO2 in the final exhaled air - FetCO2 > 6,4%), hyperventilation (FetCO2 < 4,9%), uneven ventilation (angle of inclination of the alveolar capnogram plateau - 5°). During mechanical ventilation, if there is no capnograph, the volume of ventilation is controlled by the minute volume of respiration (Vist.), measured using a volumetric spirometer, which is installed in the expiratory path. In addition, the minute inspiratory volume (Vappar.) is monitored, which is necessary to calculate the oxygen concentration in the inhaled gas mixture and determine the tightness of this system - "ventilator-patient". The tightness control is also achieved by the pressure in the "device-sick" system, measured by means of a monovacuometer. Pulse oximetry allows timely detection of impaired oxygenation in the lungs, hypoxemia (SaO2 < 94%. In addition, based on the nature of the plethysmogram, one can judge the state of microcirculation and cardiac output. An additional study of blood gases helps to assess the degree of impaired gas exchange in the lungs (by the magnitude of the alveolo-arterial gradient of oxygen tension. Some monitors can provide an assessment of the biomechanics of breathing during mechanical ventilation based on the compliance of the lungs and chest (C, normally 60-100 ml) and resistance (resistance) of the respiratory tract (R, normally 2-3 cm). Monitoring of neurological functions Monitoring of neurological functions is carried out by assessing consciousness on the Glasgow scale (based on the eye opening reaction, motor and verbal responses to an increasing stimulus: 15 points - normal, 3 points - brain death). In addition, intracranial pressure and cerebral blood flow are determined (for example, using a transcranial Doppler monitor). Renal function is most commonly monitored by measuring hourly urine output, which is normally > 0,5 ml/kg/h. Author: Kolesnikova M.A. << Back: local anesthesia (Superficial anesthesia. Regional anesthesia. Cervical plexus anesthesia (CPS). Brachial plexus anesthesia (BPA). Anesthesia of peripheral nerves in the wrist. Anesthesia of the lower extremities. Epidural anesthesia. Lumbar anesthesia. Cervical vagosympathetic blockade according to A. V. Vishnevsky) >> Forward: Artificial lung ventilation
▪ Constitutional law of the Russian Federation. Crib ▪ General foundations of pedagogy. Lecture notes ▪ History of political and legal doctrines. Crib
The existence of an entropy rule for quantum entanglement has been proven
09.05.2024 Mini air conditioner Sony Reon Pocket 5
09.05.2024 Energy from space for Starship
08.05.2024
▪ Electronic collars for dog training ▪ Viltrox AF 35/1.8 Z full frame lens
▪ section of the site Application of microcircuits. Article selection ▪ article by Miguel de Cervantes Saavedra. Famous aphorisms ▪ article Why fruits can ripen on their own? Detailed answer ▪ article Use of technical teaching aids. Standard instruction on labor protection ▪ article A simple VHF FM receiver. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 See other articles Section
See other articles Section 