
|
|
PERSONAL TRANSPORT: GROUND, WATER, AIR
Planing car. Personal transport
Directory / Personal transport: land, water, air Curious looks accompany this crew everywhere. And no wonder - it looks too unusual in the flood of cars ... a boat on wheels. We are talking about a vehicle that so far exists in a single copy - a gliding amphibian "Triton". It was built by a man who, it would seem, is very far from technology. D.T. Kudryachnov is not a designer, but a professional musician who worked for a long time at the Moscow Academic Musical Theater named after K.S. Stanislavsky and V.I. Nemirovich-Danchenno. Nevertheless, Dmitry Trofimovich showed the talent of an engineer and inventor, unusual for his profession, to solve a very difficult task: to make a full-size car not only float, but also plan (and, if desired, completely transform it into a "clean" boat). Tan appeared original wheel suspensions with quick-release hinges, an unusual steering gear and paradoxical "dry" hydraulic brake system connectors, which had not been seen before in transport technology.
Sea trials confirmed the operability and reliability of all systems and units of the amphibian. The positive expert opinion of the NAMI specialist served as the basis for the registration of "Triton" in the traffic police. In turn, the State Inspectorate for Small Vessels (GIMS) allowed it to sail on all inland waterways of the "L" and "R" category. Since then, the amphibian has faithfully served its owner for the past year. There were reports about Triton in the electronic and printed press. However, the current publication is the most complete. It reveals the logic of the search for original technical solutions that made it possible to create a vehicle that is equivalent in terms of its operational properties to a can on land and on water. Along with a detailed description, extensive graphic material is also presented, which will give interested readers and, possibly, followers not only an idea of the essence of D.T. Kudryachnov, but also, perhaps, an impetus to solving their own technical problems.
Specifications:
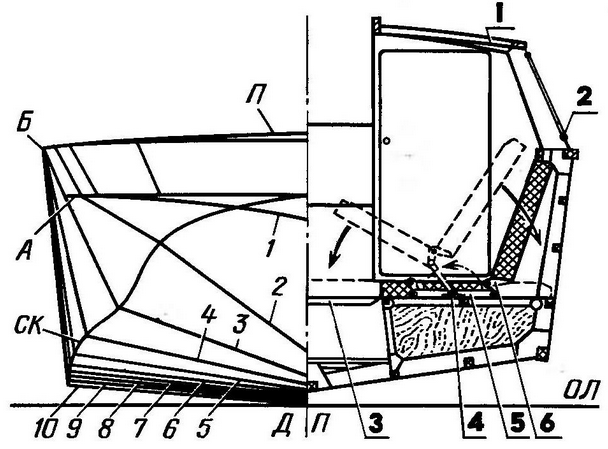
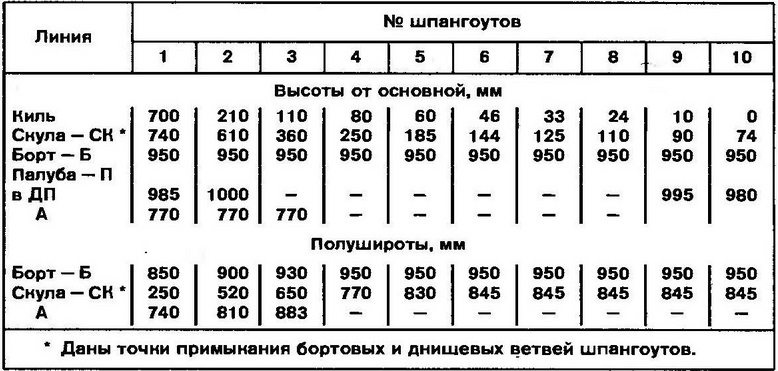
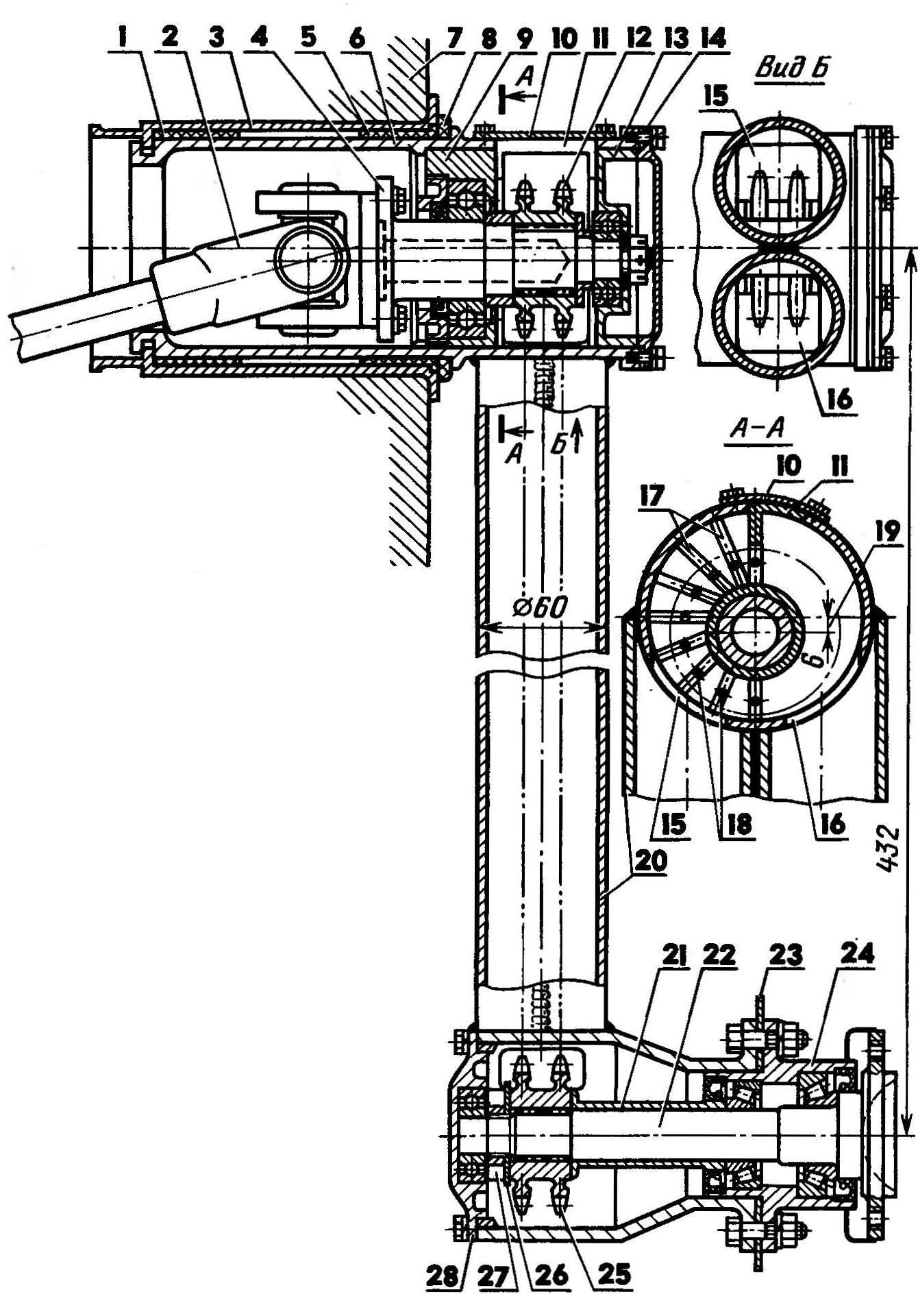
Surprise, as you know, is the beginning of all philosophy. For me, too, it all started with the removal, or rather, with the question: is the amphibian car will forever remain an inferior vehicle? For almost a hundred years, it has been accompanied by two "birthmarks": low speed on the water and non-compliance with navigation safety requirements (low freeboard, poor maneuverability, zero seaworthiness). As a result, the water inspectorate banned its operation on a par with single-purpose vessels. What's the matter? What prevents a wheeled amphibian from being a speedboat on the water? It turned out a lot. First of all - the usual automotive design. Nago must be abandoned. Unlike a floating car, which has a speed of 7-9 km / h on water even with a factory body, the hull of a real amphibian must comply with the conditions of the new "habitat", that is, uncompromisingly repeat the contours of the bottom of a speedboat. The architecture of the surface part can be almost any, but again - taking into account the peculiarities of operation on the water. So, for example, a low-slope deck, common in boat building, is desirable, since it is a workplace when locking, mooring to a pier or approaching an unequipped shore. Further. Nothing should interfere with the hull planing. The entire automobile chassis - wheels, steering gear elements and transmission must be completely removed from the water. Compromises are excluded here. Any fairings, screens or partial preload of the wheels will add speed of no more than 2-3 km / h, and the amphibian will still remain a floating, but - a car. And the last. If for a car even a significant excess of the recommended carrying capacity has little effect on its driving performance, then for an amphibian, the implementation of the planing mode requires strict coordination of its total weight with engine power. There is a threshold, which is unacceptable to cross: if the value of the specific load on the engine is more than critical, the amphibian ceases to be gliding. In our case, this threshold is 22 kg / hp, and due to the particularly difficult operating conditions of the engine on water, only 80% of its rated power is taken into account. Preliminary estimates showed that, according to hydrodynamic requirements and habitability conditions, the overall dimensions of the Triton hull could not be less than the “minimal boat with an automobile engine” type that has developed in boat building, about 5 m long and 2 m wide. car stuffing by 300 kg will exceed the weight of a cabin boat of comparable size (1000 kg). Thus, with a full displacement of 1 kg, it was possible to use the GAZ-300 engine with a limitation of up to 21% of the rated power. The resulting specific load is 80 kg/hp. did not exceed the limits limiting the possibility of gliding. This is how the design features and layout of the Triton are explained. Chassis Sharp-chinned hull contours with a slight flare of the sides have moderate deadrise (5% at the transom). The sides in the places of wheel suspensions are vertical. The bow branches of the frames were given a very large collapse, which made it possible to obtain a spacious, almost rectangular deck in plan. I note that in the theoretical chart (and in the table of space ordinates), the zygomatic splash guards, the vertical sections of the sides in the area of the suspensions and the drop of the bow frames are not shown for simplicity. Structurally, the amphibian body is load-bearing. More precisely, its variety is used - the bearing bottom, the lower part of which is a solid box-shaped platform, consisting of compartments-spaces. The power set of the hull is made according to the longitudinal-transverse scheme using oak and pine. The frames are assembled on knees on both sides. Toptimbers have a variable section with broadening towards the cheekbone. Longitudinal beams and sheathing sheets (aircraft plywood of various thicknesses) are joined "on the mustache". The body is covered with fiberglass on the outside. All connections are made with epoxy adhesive with press screws or clamps. Hardware used only galvanized or cadmium. The internal surfaces of the body are coated with epoxy varnish. Its unsinkability is ensured by sealing the forepeak and sections of the bearing bottom. The inclination of the transom is coordinated with the installation angle of the water jet and is equal to 6 degrees to the vertical. A rigid gangway is mounted on the transom: it is convenient on the water and on land and at the same time serves as a fence for radiators, a silencer and a reverse-steering complex of a water cannon. The hull is made completely closed - without a cockpit and side floods (narrow deck sections along the side). Instead of them - a through central passage along the axis of the amphibian. With the roof open, it connects the fore and aft sections of the deck. To do this, the middle windshield sash folds down, and the tailgate and roof panels fold into a compact package and are attached to the right side. Since a mass of units and assemblies "unnecessary" to the usual rubbing had to be hung on the hull, the problem of weight reduction arose especially acute. At all stages of work, both the choice of materials used, and the dimensions and sections of parts were carefully substantiated.
Plasic ordinates table
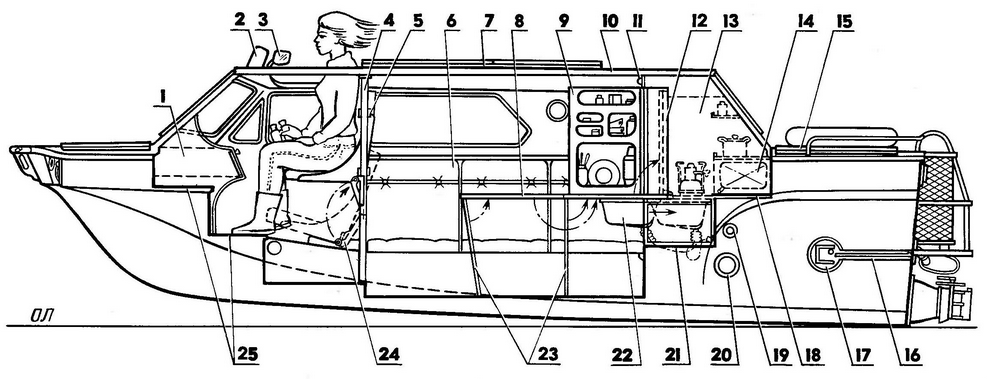
An important reserve for weight reduction was the multi-purpose use of structural elements, subject to their rational relative position. For example, the vertical spars of the bearing bottom also serve as the walls of the lockers; they, being reinforced in the stern, form the basis of the sub-engine Foundation. Different sizes of spacings (400, 550, 600 mm) are not only strictly linked to the layout of the internal space, but also eliminate the duplication of the transverse set, since it is consistent with the mounting dimensions of the chassis units. The wheel suspension support units are supported by two pairs of reinforced frames, and two pillars on the sides of the central aisle partially unload the power set of the roof and at the same time serve as a support for the mast of additional sailing equipment. Cabin The rejection of the onboard potopchins made it possible to expand the cabin from side to side, which significantly increased its usable volume. The interior space is conditionally divided into two parts: a running tube, the boundary of which is the backs of the front seats and pillers, and a saloon with a galley located aft of it and a wardrobe. The front seats - the driver's and navigator's seats - have a non-separable duralumin frame and can be installed in two levels with a height difference of 400 mm. The lower position is normal - "car"; the top is used only on the water to improve visibility in difficult sailing conditions. For this, hatches were made above the seats. Their covers lean back, and sun visors, turned up, protect the driver's face from the oncoming air flow, which is very significant at a speed of 40-50 km / h. Six seats in the cabin are located along the sides on the lockers; four of them are articulated and easily transform into a full size double seat across the hull. To reduce weight, all seats are made of PVC-1 foam boards 50 mm thick, covered with foam rubber and sheathed with leatherette. Equipment and food supplies are stored in twelve lockers and an extensive trunk in the forepeak (above the gas tank). In addition, there are side pockets and a navigator's bag for route maps, binoculars, film and photo equipment and small items. Interior ventilation is natural - through hatches, doors and roof panels ajar or completely open in any combination above the central aisle. A few words about the galley. In fact, it is as if it is not in the cabin, because when the table is pushed into the niche, it is closed and looks like a wardrobe located opposite. However, there is enough space for two "Bumblebees", a pull-out sink with a tap from the drinking water tank and all kitchen utensils. Thermos, small dishes, spices, tea, coffee, sugar are stored in the niches of the volumetric door. Power point The GAZ-21 engine, a gearbox with a differential from Zaporozhets and a self-made gearbox are a single power unit. It is mounted on five rubber pads close to the transom, above the jet. With this arrangement, the length of the engine compartment is extremely reduced. Access to the crank ratchet is through a hole in the transom, covered by a spring-loaded cover with a seal. The engine cooling system is double-circuit. Its aft location required a number of additions: a guide casing was installed for more intensive airflow of the water radiator; the standard four-blade fan impeller was replaced by a light six-blade one turned in the opposite direction; an oil cooler from GAZ-51 was additionally installed. Air enters them through a separate deck duct and partly through a wide gap between the transom and the fan casing.
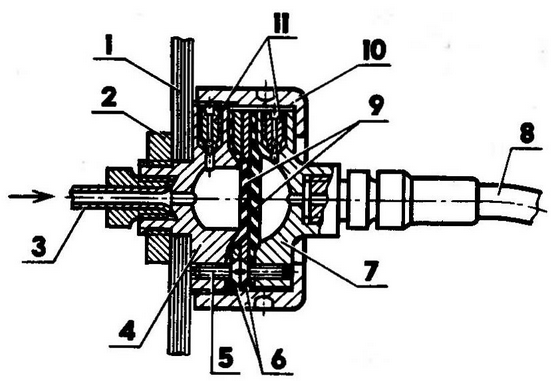
When the water jet is afloat, the second one is automatically connected - an external cooling circuit, consisting of a water heat exchanger embedded in the line between the radiator and the water pump. Outboard water also enters the oil cooling coil in the engine crankcase and into the gearbox jacket. The exhaust gas manifold, enclosed in a lightweight casing, is cooled on land and on water by a two-speed centrifugal electric fan, the control of which is interlocked with the "gas" pedal. When the engine warms up, the fan is off. At medium speeds, it turns on at low speed and at high speeds (over 2500 rpm) - at high speed. Exhaust gases are discharged outside through a pipe that has a compensation spacer in front of the transom - a bellows that absorbs engine vibration. Behind the transom is a muffler rigidly fixed under the bottom step of the ladder. Air enters the engine compartment through air intakes located on both sides of the cabin. It is sent through ship pipes to the engine and gearbox and then discharged through special gratings in the transom. A gear reducer is used to transfer power to the water jet and gearbox. Its gear ratio is 19:18. Spur gears with a module of 3 mm and heat treatment up to 48-52 H1ChS. The noise from such gears, compared with helical gears, is more (by 8-10 dB), however, their use made it possible to reduce the dimensions and weight of the gearbox. (Later, the gears were still replaced with helical gears, although it was not easy to squeeze them into the old case.) The gearbox housing is welded. All holes and seats were processed on a boring machine. A water cooling jacket is welded onto the side walls and bottom of the gearbox. The gearbox control is brought to the "jet - neutral - wheels" sector, located to the right of the driver, next to the gear lever. Here is the handle for reversing the water cannon. A "pantograph" was introduced into the gearbox control line - a kind of intermediate link, which is necessary because the control shaft passing under the plates and the gearbox slider rod are at different heights. Water cannon The Triton jet propulsion unit is made of stainless steel. Based on the design described in the magazine "Boats and Yachts" No. 11 and 25. Of course, with significant "changes: expanded conduit inlet; inspection hatch installed; directing vane fairing lengthened; in the removable (on the thread) part of the fairing there are bearings and seals of the rear shaft support; cross-sections of rotor blades and straightening vanes are halved; the gap between the shell and rotor blades is 0,4 mm; the reverse-steering complex is significantly lightened. The conduit is welded from two symmetrical halves, the knockout of which was significantly lightened due to preliminary longitudinal cuts on the future cylindrical part of the blank. The halves, fitted back-to-back and tied together with wire bandages, are welded in one pass. This technology, in my opinion, gives the least distortion of the geometry of the conduit and reduces the length of the welds to the maximum. Chassis Since both wheel suspension arrangements were not suitable for the Triton, I had to independently manufacture independent single-lever suspensions of a welded structure with the installation angles of the kingpin, camber of the front wheels and the angle of convergence of the rear wheels embedded in them even during manufacture. The angle of convergence of the front wheels is regulated by a transverse link inside the housing. The axes of the levers of all suspensions are hollow, with a large. They are made in such a way that the side steering rods move freely in the front ones, and universal joints, sprockets and bearings with eccentric housings that regulate the tension of the chains are placed in the rear ones. When installed on an amphibian, the suspension arms are inserted into the support sockets with nylon bushings pressed into them and rotated into the working position. These assemblies are quick-release swivel joints resembling a bayonet. But if, with a conventional bayonet connection, the parts are motionless fixed relative to each other, then the axes of the Triton suspension arms have radial freedom in the one-piece sector up to 170 degrees, which is more than enough for the oscillatory cycle of their operation, and for lifting the wheels out of the water to a height higher waterline. Springs and hydraulic shock absorbers are the same for both pairs of suspensions - from the ZAZ-968 car. The upper supports of the springs and shock absorbers are special traps, into which the spring shoes slide along the guides and snap into place with pins. On the water, suspensions with wheels are lifted along the sides by a cable winch. Thus, "Triton", unlike other amphibians, can stay afloat for an unlimited time, since all the units of the undercarriage do not corrode or grow algae and are ready for use on land at any time. Steering Made on the basis of the corresponding mechanism "Zaporozhets". True, with significant additions due to the use of a fundamentally different steering drive scheme, the essence of which is to combine the longitudinal axis of the side rods with the swing axis of the suspension arms and to transfer forces to the knuckles through the bells, supported on the suspension arms. In this form, each suspension with spring, shock absorber and steering elements is a single mounting block that does not require any adjustment when installed on the body. The ninematina of this scheme, unlike all other schemes of an automobile steering drive, allows you to freely and without violating the mounting angles of the wheels to raise them to an unusual height - 700 mm. The steering mechanism shaft has a device with a cam clutch, which includes either a drum of a cable drive of the water cannon doors, or a wheel control mechanism. All communications for remote control of the engine, gearbox, gearbox, jet reverser, as well as the parking brake and speedometer cables pass under the passenger compartment. Трансмиссия Half shafts with cardans connected to the axles of the chain drive sprockets go to the sides in the region of the rear suspension supports from the gearbox, bush-roller chains (there are two of them for each cat) work inside the sealed tubular levers of the rear suspension in an oil bath. Their tension is adjusted by turning the eccentric bearing housings. Favorable weight distribution of the "Triton" on the wheels is achieved due to the inclination of the front and rear suspensions back. This also gives a smooth ride, since the suspensions experience less dynamic loads on bumps in the road. Brake system Here, too, the Zaporozhets brake system was used in full: a separate hydraulic foot drive for the front and rear wheels, and a manual cable (parking) drive only for the rear. To simplify the installation or dismantling of suspensions in the hydraulic system, I used another quick connection - a "dry" hydraulic connector, which allows you to connect or disconnect the brake hoses without loss of brake fluid and without subsequent laborious running of the entire system. There are four such connectors on the Triton. Each of them consists of two hemispheres covered with elastic membranes: onboard (it ends with the pipeline of the internal highway) and the return (consumable), fixed at the end of the pipeline of the wheel. To the onboard counters are pressed with union nuts. When you press the brake pedal, both membranes are deformed, squeezing fluid from the consumable hemisphere into the working hydraulic cylinder of the wheel - braking occurs. The volume of the consumable hemisphere is 3,5 times the volume used in the working hydraulic cylinders, therefore, any operational losses will be compensated. In the absence of brake fluid in any hemisphere (or even in all four), the brake system does not fail: when you press the pedal, under the action of pressure in the line, the membranes break through, and the brake fluid, freely flowing from the inner to the outer line, does its job as in a normal vehicle hydraulic system. Electric equipment It is completely automobile, although the light signaling is made according to two schemes with a "ground" - "water" switch. The headlights are also left in the "water" scheme in order to use them when approaching the shore in the dark. The front direction indicators also work as go-ahead lights. Both circuits are equipped with ground switches. Headlights, sidelights and distinctive lights are "recessed" in niches along the edges of the deck extensions and are well protected by overhanging sections of the bow deck. The regular indicators of the engine operation mode are supplemented with an electronic tachometer and a "water speedometer", which is used as a pressure gauge with a scale recalibrated in kilometers. It is also possible to control the temperature of the oil in the engine. To do this, the TM-101 sensor, installed in the oil pan, is connected from time to time with a deuhposition toggle switch on the instrument panel to the water temperature indicator device. The buttons for manual control of the "gas" and the air damper of the carburetor are also displayed on the shield. Thanks to the listed "complications" that the amphibian is equipped with (quickly detachable connections, etc.), it is extremely easy to turn it into a "clean" boat. By removing the suspensions, for example, you can tow water skiers or take on board two more passengers or an additional supply of fuel, product, equipment, since without suspensions the carrying capacity (displacement) of an amphibian increases by 170 kg. To do this, it is enough to unscrew the four union nuts of the "dry" connectors, disconnect the side rods from the pendulum levers and unpin the outer ends of the handbrake cables. We carry out such a simple operation almost every time when we go to the Moscow Sea for a month and a half in the summer. Author: D.Kudryachkov
▪ Modernization of tractor servomechanism
Energy from space for Starship
08.05.2024 New method for creating powerful batteries
08.05.2024 Alcohol content of warm beer
07.05.2024
▪ Notebook Toshiba Libretto W100 ▪ Acnodes PCM8019 Rugged Embedded Computer ▪ Gardening is one of the best antidepressants ▪ New type of basalt discovered
▪ section of the site Car. Article selection ▪ video game article. History of invention and production ▪ article What explains the cases of killing of rhinos by African elephants? Detailed answer ▪ article Oral care. Health care
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese







 See other articles Section
See other articles Section 