
|
|
OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH
Electrical safety in educational institutions. Occupational Safety and Health
Occupational Safety and Health / Legislative basis for labor protection Electrical injury In modern educational institutions, in particular, in specialized classrooms, electrical appliances and installations are widely used. Unlike other sources of danger, electric current cannot be detected remotely without instruments, so its impact on humans is always unexpected. The danger of electric shock arises when a person comes into direct contact with exposed live parts of electrical installations, when touching metal housings of electrical receivers that accidentally become energized, as well as as a result of the action of the so-called step voltage that appears near places where live parts are shorted to ground. Electrical injury Compared to other types of occupational injuries, it is a small percentage (2-3%), but in terms of the number of injuries with severe and, especially, fatal outcomes, it occupies one of the first places. Electrical injuries occur for the following reasons:
Types of injuries associated with the impact of electrical energy on a person can vary in severity and depend on a number of factors, including the structure of the body, voltage, type and frequency of the current, the duration of the current and the path of its flow, the scheme of connecting the human body to the electrical circuit, environmental conditions. Passing through the human body, electric current has thermal, electrolytic, biological, mechanical and light effects. Thermal effect of current causes heat and burns to parts of the body. Electrolytic action of current consists of the electrolytic decomposition of fluids in the human body, including blood. Biological effect of current manifests itself in irritation and excitation of living tissues and is accompanied by involuntary convulsive contraction of the muscles of the lungs and heart. These are responses of the body that are caused by a violation of the bioelectric processes occurring in the human body. mechanical action leads to rupture of body tissues, light - damage to the eyes. The irritating effect of current on body tissue can be direct or indirect. direct action is caused by the passage of current directly through the tissues experiencing irritation. Indirect or reflex action manifests itself in the excitation of tissues through which current does not flow. Electrical current causes two types of injury: electrical injury and electrical shock. electrical injury - These are local lesions of tissues and organs. These include: electrical burns, electrical marks and electrometallization of the skin, mechanical damage as a result of involuntary convulsive contractions of muscles during the flow of current (ruptures of the skin, blood vessels and nerves, dislocations of joints, bone fractures), as well as electroophthalmia - inflammation of the eyes as a result of exposure to ultraviolet electric arc rays. Different types of electrical injuries can accompany each other. The most dangerous is considered to be an electric shock, which leads to the stop of the heart and lungs. The degree of influence of electric current on a living organism, as already mentioned, depends on the magnitude and duration of the current flow, the electrical resistance of a person, the type, frequency and path of the current. The main damaging factor is the strength of the current flowing through the human body, causing various reactions of the body: from a feeling of mild itching (0,6-1,5 mA alternating current frequency 50 Hz and 5-7 mA direct current) to involuntary convulsive contraction of muscle tissue ( 25 mA AC and 80 mA DC), as well as cardiac fibrillation and cardiac arrest (100 mA and above). When selecting and calculating technical devices and other means of protection, three main parameters are taken into account: the strength of the current I flowing through the human body, the touch voltage U and the duration of the current flow t. Touch voltage - this is the potential difference between two points in an electrical circuit that are simultaneously touched by a person. If a person simultaneously touches two conductors of an electrical circuit, then the touch voltage will be equal to the source voltage. If a person touches a damaged installation that is grounded, the touch voltage will be significantly lower than the source voltage, since any grounding device reduces the potential of the electrical installation body that is energized to an acceptable value (subject to the requirements for the design and resistance value of the grounding device in accordance with the Rules electrical installation devices - PUE). Step voltage - this is the difference in electrical potentials between two points on the surface of the earth on which a person stands at the same time (with both legs). Methods and means of protection against electric shock in electrical installations electrical installations is a set of machines, apparatus, lines and auxiliary equipment (together with the structures and premises in which they are installed) intended for the production, transformation, transmission, distribution of electrical energy and its conversion into other types of energy. The design of electrical installations must meet the requirements of the PUE in accordance with their purpose. To ensure the safety of personnel servicing electrical installations, both individual protective equipment and methods, and their combinations, i.e. protection systems, are used. Protection against touching live parts of electrical installations is wire insulation, fencing, blocking and protective equipment. Wire insulation characterized by its electrical resistance. The high insulation resistance of wires relative to the ground and electrical installation housings creates safe conditions for operating personnel. During operation of electrical installations, the condition of electrical insulation deteriorates due to heating, mechanical damage, the influence of climatic conditions and the surrounding production environment (chemically active substances and acids, temperature, pressure, high humidity or excessive dryness). Fences solid and mesh are used. They must be fire resistant. In installations with voltages above 1000 V, the minimum permissible distances from live parts to fences, standardized in the PUE, must be observed. Locking used in electrical installations with fenced live parts. It automatically provides voltage relief from live parts of electrical installations in the event of unauthorized entry into the fence. Protection against voltage that appears on the housings of electrical installations as a result of insulation failure is protective grounding, grounding and protective shutdown. Protective earth installed in electrical networks with insulated and grounded neutrals. It is a deliberate connection to the ground of non-current-carrying metal casings of electrical installations. Protective grounding is necessary to reduce the voltage relative to the ground to a safe value on the metal casings of electrical installations that are not normally energized and become energized as a result of insulation damage. Depending on the voltage, power and mode of the neutral of the electrical installation, the PUE provides permissible values of the resistance of the grounding device. Protective grounding installed in networks with a solidly grounded neutral with voltages up to 1000 V, since protective grounding alone does not provide sufficiently reliable and complete protection. Grounding is the intentional connection of electrical installation housings with a neutral wire coming from the grounded neutral of the current source. The operating principle of grounding is the transformation of a short circuit to the housing into a single-phase short circuit, in which the protection (fuses, circuit breakers) is activated and the electrical installation is turned off. Almost all machine tools, electric motors, workshop metal lamps, etc. are subject to zeroing. Safety shutdown - this is a fast-acting protection that ensures automatic shutdown of an electrical installation when there is a danger of electric shock to a person (in the event of a short circuit to the housing, a decrease in the insulation resistance of the network, as well as in the event of a person touching a live part directly). Protective disconnection is recommended to be used as a primary or additional protective measure if safety cannot be ensured by grounding or grounding, or if the use of these methods is difficult or economically impractical. Electrical protective equipment (Fig. 4) are designed to protect people working in electrical installations from electric shock and exposure to an electric arc and electromagnetic field. These include:
When working in electrical installations, if necessary, also apply personal protective equipment (goggles, helmets, gas masks, mounting belts, safety ropes, etc.). Providing first aid to victims of electric current The main condition for success when providing first aid to victims of electric current is the rapid release of the victim from the action of the current and the correct sequence of further actions. To provide first aid for electric shock, you must:
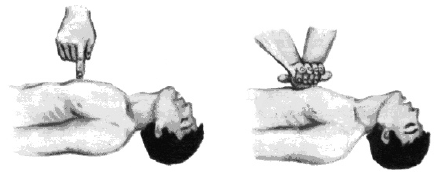
If the victim faints, you need to bring him to consciousness by giving him ammonia to sniff. If the victim breathes poorly (rarely, convulsively) or there are no signs of life (breathing, heartbeat, pulse), it is necessary to do artificial respiration and chest compressions. If the victim has a clearly visible pulse, only artificial respiration should be performed. Artificial respiration should be performed using the “mouth to mouth” method, in which the person providing assistance exhales air from his lungs into the victim’s lungs directly through the mouth at intervals of 5 seconds (12 respiratory cycles per minute).
To maintain blood circulation in the victim in the event of cardiac arrest, it is necessary to perform indirect (closed) heart massage simultaneously with artificial respiration. If resuscitation (revival) is carried out by one person, then every two breaths 15 compressions are made on the sternum. With the help of two people, the ratio of “breathing to massage” is 1:5. In some cases, when the heart has stopped in a healthy person, it is enough to apply a few pressures on the chest to restore the natural functioning of the heart. Providing pre-medical care can be lengthy, since ultimately only a doctor can make a conclusion about death. The cause of a prolonged absence of a pulse in a victim when other signs of recovery appear (restoration of spontaneous breathing, constriction of the pupils, etc.) may be fibrillation hearts. However, even in this case, it is necessary to continue revival until the doctor arrives. Authors: Volkhin S.N., Petrova S.P., Petrov V.P.
▪ Help with fractures, dislocations, bruises and sprains ▪ Documentation on labor protection in the workplace
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Angry Birds brought in $67,6 million in revenue ▪ Burger King Restaurants of Tomorrow
▪ section of the site Radio - for beginners. Article selection ▪ article Civil procedural law. Lecture notes ▪ Article How much liquid does a person need? Detailed answer ▪ article Bodiak garden. Legends, cultivation, methods of application ▪ article Stop electric meter. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering ▪ article Digital VHF radio tuning scale. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 See other articles Section
See other articles Section 