
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Radiation indicator. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
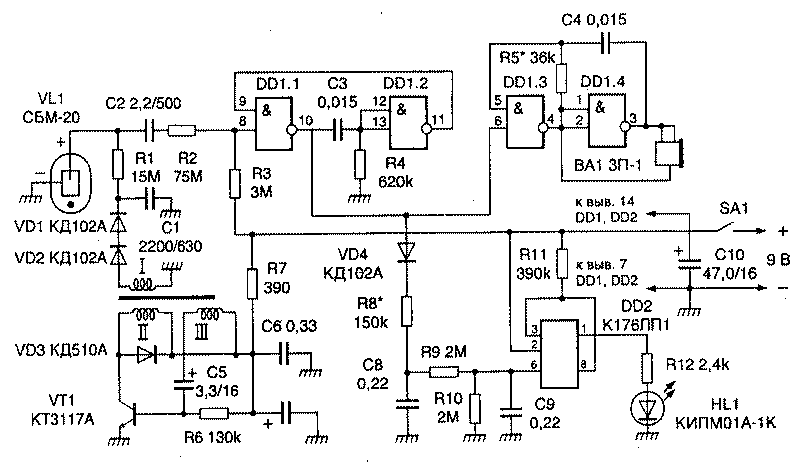
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Dosimeters The device is designed for continuous monitoring of the general radiation situation and detection of sources of ionizing radiation. The schematic diagram of the device is shown in Fig.1. The function of the VL1 ionizing radiation sensor is performed by the SBM-20 Geiger counter. The high voltage at its anode forms a blocking generator assembled on the T1 transformer. Voltage pulses from the step-up winding I through the diodes VD1, VD2 charge the filter capacitor C1. The counter load is the resistor R1 and other parts associated with the input 8 of the element DD1.1. Elements DD1.1, DD1.2, capacitor C3 and resistor R4 form a single vibrator. It converts the current pulse that occurs in the Geiger counter at the moment of its excitation by an ionizing particle into a voltage pulse with a duration of 5 ... 7 ms. Elements DD1.3, DD1,4, capacitor C4 and resistor R5 are a controlled (by input 6 element DD1.3) audio frequency oscillation generator, to the paraphase output of which (pins 3 and 4 of elements DD1.4, DD1.3) is connected piezo emitter BA1. In it, an acoustic impulse-click is excited by a pack of electrical impulses. An integrator is assembled on the VD4 diode, resistors R8-R10 and capacitors C8, C9, which controls the operation of the threshold amplifier DD2. The voltage on the capacitor C9 depends on the average excitation frequency of the Geiger counter - when it reaches its value corresponding to the opening voltage of the field effect transistor included in the DD2 chip, the HL1 LED turns on. The frequency and duration of LED flashes increase with increasing radiation levels. The details of the device are mounted on a printed circuit board made of double-sided fiberglass 1,5 mm thick. The foil on the part installation side is used only as a common grounded conductor. Capacitor C1 type K73-9, C2 - KD-26, C5 - K53-30 or K53-19. In the case of replacing them with capacitors of other types, it should be borne in mind that leaks here can dramatically increase the power consumption of the device, which, of course, is undesirable. For the same reason, the choice of diodes VD1 and VD2 is also limited: the reverse current of these diodes is a load for a high-voltage converter and should not exceed 0,1 μA. Capacitors C7 and C10 - type K50-40 or K50-35, the rest - K10-17-26 or KMe. Resistor R1 - KIM or C3-14, R2-R12 -MLT, C2-33 or C2-23. Chip DD1 can be type K561LA7. The KD510A diode can be replaced by any other silicon one with a pulse current of at least 0,5 A. Almost any LED is suitable, the criterion here is sufficient brightness. The two-crystal piezo-emitter ZP-1 can be replaced by a single-crystal one with an acoustic resonator ZP-12, ZP-22 or ZP-3. Without noticeable changes in consumer properties and any alterations in the device, you can use the STS-5, SBM32 or SBM32K counter and other Geiger counters. The pulse transformer T1 of the high-voltage voltage converter is wound on a MZOOONM ferrite ring of size K16x10x4,5, pre-coated with a thin tape of lavsan or fluoroplast. Winding I is wound first - 420 turns of wire PEV-2 0,07 mm. The wire is laid coil to coil in one direction, leaving a gap of 1-2 mm between the beginning and end of the winding. Further, having covered winding I with a layer of insulation, winding II is wound - 8 turns of wire with a diameter of 0,15-0,2 mm in any insulation, and on top of it winding III - 3 turns of the same wire. The wire of these windings should also be as evenly distributed as possible along the magnetic conductor. The finished transformer, covered with a layer of waterproofing, for example, wrapped with a narrow strip of PHL tape, is fixed on the board with an MXNUMX screw between two elastic washers. The device does not require adjustment - correctly assembled, it starts working immediately. But there are two resistors in it, the values \u5b\u8bof which may need to be clarified. This is resistor RXNUMX, by selecting which the frequency of the sound generator is adjusted so that it matches the frequency of the mechanical resonance of the piezoelectric emitter, and resistor RXNUMX, the value of which determines the alarm threshold. Correction of the alarm threshold may be required when reconfiguring the device for operation in conditions of increased background radiation. The device is easy to use and does not require any special training from the owner. A rare click of acoustic pulses following one after another without visible order, the absence of an alarm signal (LED flashes) indicate that the device is in a natural radiation background. This background clicking is almost independent of the time of day, season, and location of the device, slowing down somewhat only deep underground and speeding up in the highlands. An increase in the count rate when the device is moved, and even more so, an alarm triggering, gives sufficient reason to believe that the device is located in the area of a radiation source of artificial origin. The position of this source, its dimensions, connection with one or another visible object can be determined either by turning the device (it has maximum sensitivity on the part of the Geiger counter), or by moving it - the direction to the source is determined by increasing the count rate. When searching for a source of radiation, the dimensions of which are much smaller than the Geiger counter itself, it is recommended to scan suspicious places - move the device, changing its direction of movement and orientation. Thus, the position of the source of radioactivity invisible to the naked eye can be determined with an accuracy of 2...3 mm. The alarm threshold in the device is set slightly above the natural radiation background with all its possible deviations from the average value. Only a very few reasons, not related to the appearance of sources of radiation of artificial origin, can put it into an alarm mode (from the public ones - flights at high altitude). Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
The world's tallest astronomical observatory opened
04.05.2024 Controlling objects using air currents
04.05.2024 Purebred dogs get sick no more often than purebred dogs
03.05.2024
▪ By 2030, one in five cars in Japan will be self-driving
▪ section of the site Standard instructions for labor protection (TOI). Selection of articles ▪ article Where did kefir come from? Detailed answer ▪ article Educator. Job description ▪ article Post to copper-colored tin solder. Simple recipes and tips ▪ article Obedient handkerchief. Focus Secret
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: