
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING High performance VHF antennas. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
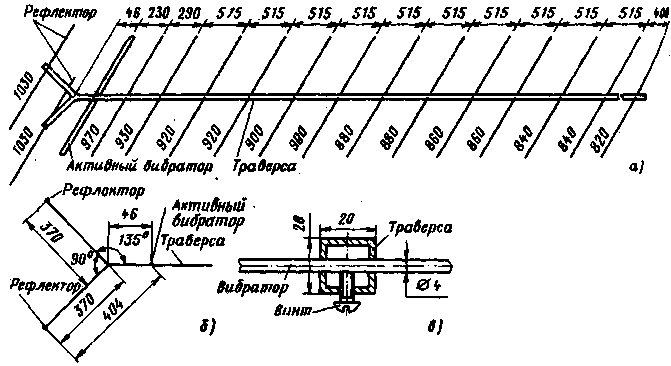
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / VHF antennas The intensive development of VHF bands by radio amateurs over the past two decades has led to the emergence of many antennas of various designs. In recent years, antennas with an elongated traverse have received special distribution. The length of the traverse of such an antenna is several wavelengths, and the number of passive elements reaches two dozen or even more. It is they that are often used by ultrashortwaves when conducting long-range and ultra-long-range communications on VHF through the "aurora", meteor showers, IC3 and the lunar surface. Interest in antennas with an elongated traverse can be explained by the fact that, firstly, with almost the same material costs as for the construction of a conventional "wave channel", their gain is noticeably greater; secondly, the design of such antennas is simple, since all elements are mounted on one carrier beam; thirdly, the relative simplicity of matching the antenna with the feeder captivates, because the RF energy is supplied to only one active element. But these antennas also have some disadvantages: low suppression of back radiation and a significant narrowing of the operating band with an increase in the number of elements. A number of interesting designs of VHF antennas with an extended traverse were developed by the famous French ultrashortwave F. Tonna (F9FT). Antennas F9FT have a sufficiently high efficiency, relatively small size and weight, they do not have matching elements. But perhaps they main advantage - easy repeatability, obtaining identical parameters of each individual antenna (with strict observance of all dimensions of the elements). The latter allows, by arranging several antennas of the same type, to create a complex antenna system with a high gain. The main parameters of the F9FT antenna are shown in the table. The antenna gains given are relative to a half-wave dipole. On fig. 1, a drawing of a 16-element antenna for a 2-meter range is shown. Its traverse is made of rolled square profiles with a side of 20 mm, wall thickness - 1,5 ... 2 mm, or pipes with a diameter of 20 mm. The part of the traverse, where the reflectors and the active vibrator are strengthened, has the form of a "dovetail" (Fig. 1, b). Passive elements are made of aluminum wire with a diameter of 4 mm. The use of other materials (copper, brass, aluminum alloys, bimetal) does not cause a noticeable deterioration in the parameters of the antenna, with the exception of its mass. One of the possible mounting options for reflectors and directors is shown in fig. 1.c. An active vibrator with a wave resistance of 75 ohms (Fig. 2, a) is made of aluminum wire with a diameter of 5 mm, and with a wave resistance of 50 ohms (Fig. 2, b) - from two aluminum tubes with a diameter of 12 mm, connected by an aluminum matching bow made of wire with a diameter of 5 mm. Main parameters of antennas
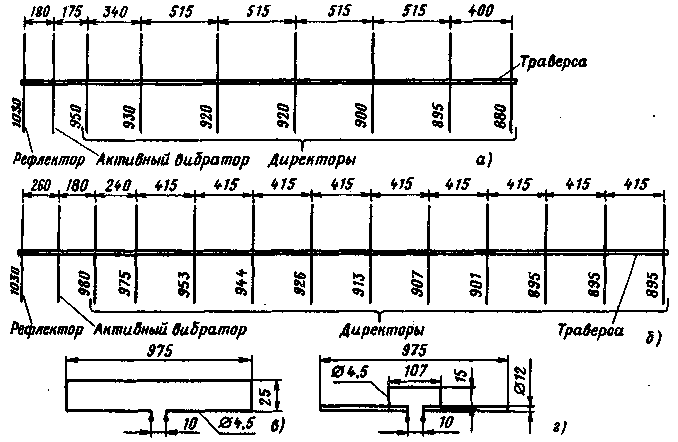
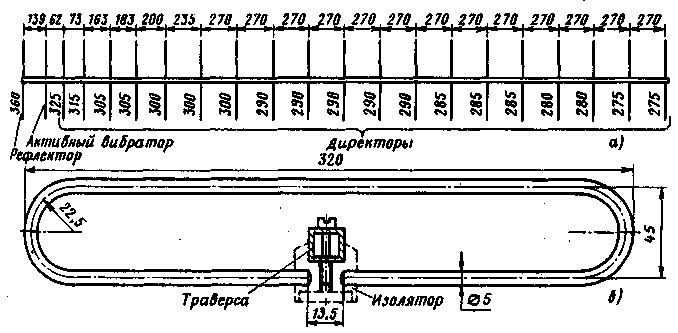
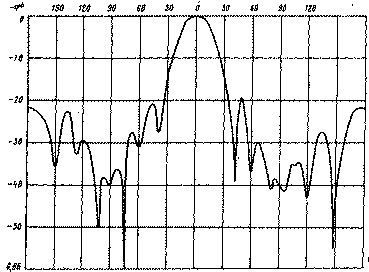
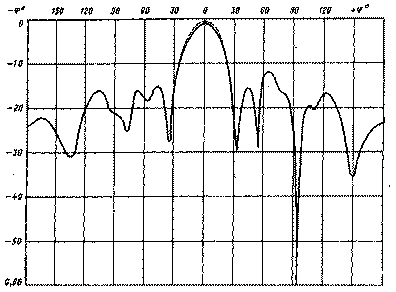
The active vibrator must be securely isolated from the traverse. Fiberglass, Teflon, organic glass, etc. can be used as an insulating material. On fig. 3a and 3b schematically show 9- and 13-element antennas for the 2-meter band. The design of active vibrators with different wave impedance for these antennas is shown in fig. 3, in (75 ohms) and 3, d (50 ohms). Some difference in the size of these active vibrators from those used in the 16-element antenna is due to the desire to better match these antennas to the feeder. The cross section of the carrier traverse for these antennas is the same as for the 16-element (20x20 mm). Structurally, a 9- and 13-element antenna is performed in the same way as a 16-element one. Figure 4a shows a schematic drawing of a 21-element antenna for a range of 70 cm. The distances between the elements indicated in the figure refer to the case of using a feeder with a characteristic impedance of 75 ohms. When feeding the antenna with a 50-ohm cable, the distances should be as follows: reflector - active vibrator - 139 mm, active vibrator - director 1 - 48 mm, director 1 - director 2-68 mm, director 2 - director 3 - 182 mm. The remaining directors are located at the distance indicated in the figure. For the traverse, a square profile with a side of 16,5 mm is used (a tube with a diameter of 16 ... 17 mm can be used). All passive elements are made of aluminum wire with a diameter of 4 mm and are fixed directly on the traverse (see Fig. 1, c). An active vibrator (Fig. 4b) is made of aluminum wire with a diameter of 5 mm. At the point of attachment to the traverse, it must be isolated from it. At first glance, it may seem that the direct supply of a balanced vibrator with an unbalanced coaxial cable cannot give good results, since in this case the voltage ratio at its ends is approximately 2:3. And this will inevitably lead to the formation of radiation with vertical polarization, thereby deteriorating the antenna gain and its radiation pattern. However, experiments show that it is possible to feed the antenna in this way, but the input impedance of the active vibrator must be consistent with the wave impedance of the supply feeder, and the active element is reliably isolated from the traverse. In this case, almost all the supplied RF energy is radiated by the active vibrator into the surrounding space, and a large number of passive elements quite well forms the main lobe of the antenna radiation diagram strictly along its axis. On fig. 5 and 6 show the horizontal and vertical radiation patterns of a 16-element F9FT antenna for the 2-meter band.
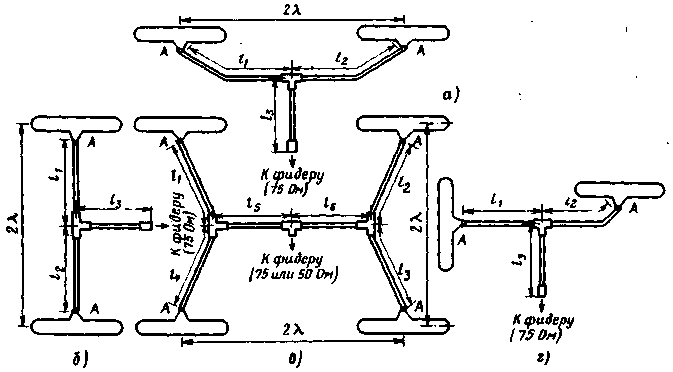
To get more power. antennas of the same type are combined into a system. By doubling the number of antennas of the same type, the system gain can increase by 2.5 dB. The maximum value is achieved only under the condition of the optimal distance between the antennas and the strict phasing of the latter. The optimal distance for 16-element 2-meter antennas and for a 21-element 70 cm antenna is 2l. Figure 7 shows the layout options for antenna systems. If, for example, it is required to coordinate with a feeder having a characteristic impedance of 75 ohms, an antenna system of two antennas with an active element with an impedance of 75 ohms, the following must be done. The vibrators of both antennas are connected through a tee with segments of a coaxial cable (their impedance is 75 Ohms) with a length that is a multiple of l / 2 (l1 \u2d l2 \u1,2,3d cpl / 50, where n \u4d XNUMX, .... s is the cable shortening factor) , with a quarter-wave transformer The latter is made of a coaxial cable with a characteristic impedance of XNUMX ohms with a length of cl / XNUMX. For correct phasing of the antenna system, the central conductors of the coaxial cable segments are connected to point A (see Fig. 7). It is very easy to match four antennas of the same type (see Fig. 7, c). In this case, a segment of cables with the same wave impedance (50 or 75 Ohm) of length l1=l2=l3=l4=spl/2, l5=l6=cl/4 is used. Figure 7d shows a variant of combining two antennas, which results in a radiation pattern with circular polarization. It is expedient to use such systems when working through amateur radio satellites of the Earth, as well as when receiving signals reflected from the lunar surface. Both antennas are mounted mutually perpendicular on the same traverse, vibrators of the same name are fixed as close to each other as possible. For coordination, segments of a coaxial cable with a characteristic impedance of 75 ohms are used (l1=sp1l/4, l2=sp2l/2, where n1=1, 3, 5,...; n2=1,2, 3,...; l2 -l1=l/4) and 50 ohm (l3=cl/4). This circular polarized antenna system has the same gain as a single antenna. Finally, some practical advice. For convenience and quick assembly of antenna systems, it is recommended to supply sections of matching cables with high-frequency connectors of the SR-75 and SR-50 types, and use HF tees to connect them. Such nodes are easy to protect from the influence of precipitation. If the specified connectors are not available, the cable segments can be carefully soldered, and the junctions can be covered with polystyrene or epoxy resin. It is advisable to install all fixing screws on the underside of the traverse and paint over them. The tubes of the elements are closed from the ends with nylon caps or rubber stoppers. It is advisable to place the cable connection points to the vibrators in nylon cups. To prevent long traverses from bending, they can be supported in the usual way with diagonal rods. The latter must be the same length for all antennas arranged in the system. Literature
Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
A New Way to Control and Manipulate Optical Signals
05.05.2024 Primium Seneca keyboard
05.05.2024 The world's tallest astronomical observatory opened
04.05.2024
▪ Apples promote the growth of new neurons ▪ The magnetic moment of the muon is the fifth force of nature ▪ Reconstructed appearance of Nicolaus Copernicus
▪ section of the site Normative documentation on labor protection. Article selection ▪ article Model of a catamaran. Tips for a modeler ▪ article What is Darwin's theory? Detailed answer ▪ database administrator article. Job description ▪ article Magnetic pictures. physical experiment
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: