
|
|
OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH
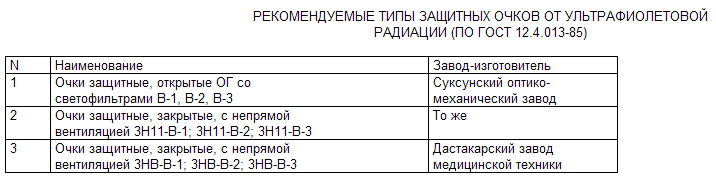
Instructions on labor protection for livestock breeders, pig breeding. Full document
Occupational Safety and Health / Standard instructions for labor protection Introduction The standard industry instruction, hereinafter referred to as the Instruction, on labor protection in pig breeding is a normative act that establishes safety requirements, as well as regulates the safe performance of work at pig breeding enterprises of all forms of ownership, including farms. The instruction was developed in accordance with the requirements of the Fundamentals of the legislation of the Russian Federation on labor protection, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the Guidelines for the development of rules and instructions for labor protection, approved by the Decree of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated July 1, 1993 No. 129. This Instruction is the basis for the development of labor protection instructions for workers by profession and for certain types of work. Instructions for employees are developed by the employer in accordance with the list of professions, which is compiled by the labor protection service with the participation of heads of departments, services of chief specialists (animal engineer, veterinarian, mechanic, power engineer), labor organization services. The list of professions is compiled on the basis of the staffing table approved by the enterprise. The names of professions must comply with the All-Russian classifier of professions for workers, positions of employees and wage categories. Instructions for employees are developed on the basis of orders and orders of the head of the enterprise (employer) and approved by the head of the enterprise after preliminary consultations or approvals with the relevant elected trade union body and the labor protection service, and, if necessary, with other interested services and officials at the discretion of the security service labor. Approved labor protection instructions for employees must be registered by the enterprise labor protection service or a responsible person in the instructions register. The head of the enterprise is obliged to organize the study of instructions on labor protection by employees. Instructions are issued to workers, heads of departments by a labor protection specialist against signature with registration in the journal for issuing instructions. Forms of registers for registration and issuance of instructions, the form of the first page of the instruction on labor protection for workers are given in Appendixes 1, 2. 1. General safety requirements 1.1. Persons who do not have medical contraindications, who have undergone industrial training, introductory and primary safety briefings at the workplace, are allowed to work. With a break in work for more than one year, an employee is allowed after completing an internship under the guidance of a farm manager, a complex, a foreman or an experienced worker who has worked in this profession for at least one year, for 4 shifts when caring for animals and 12 shifts when servicing machines and mechanisms. 1.2. It is prohibited to use the labor of persons under 18 years of age and women in heavy work and in work with harmful working conditions. At pig enterprises, such works are:
1.3. Employees are required to comply with the internal labor regulations. 1.4. Eating and smoking is only allowed in designated areas. It is forbidden to work in a painful, alcoholic, narcotic state. 1.5. When performing work at a pig-breeding enterprise, workers may be exposed to the following dangerous and harmful factors:
1.6. Overalls, footwear, gloves must be issued according to established standards. They must meet the requirements of state standards, technical specifications. 1.7. Driveways, entrances and approaches to fire equipment, equipment and water sources must be free. 1.8. It is necessary to comply with the requirements of the fire safety instructions, know the location and be able to use the means of signaling, fire extinguishing; be able to provide first aid to the victim. 1.9. In the event of a malfunction of equipment, tools, fixtures, as well as in case of violation of safety standards, fire, injury to workers, it is necessary to immediately inform the work manager about this. 1.10. An employee who has committed violations of the requirements of the Instruction on labor protection may be subject to disciplinary liability in accordance with the internal regulations of the enterprise. If these violations are associated with causing material damage to the enterprise, then the employee is liable in accordance with the law. 2. Safety requirements before starting work 2.1. Get a task from the work manager. Learn safe ways to complete the task. Inspect personal protective equipment and, if in good condition, put on:
2.2. Accept the shift from the previous employee, ask him about the occurrence of hazards and hazards during the past shift. 2.3. Turn on lights and ventilation. Check the availability and serviceability of the tool. 2.4. Look around the workplace. Check the presence and strength of the installation of transitional bridges through the manure removal channels. 2.5. Make sure that the feeding aisles are not cluttered with feed, equipment, vehicles. 2.6. Inspect the machine equipment, tighten the bolted connections if necessary, check the reliability of the locks. 2.7. Adjust the force of opening doors and the reliability of fixing doors, feeders, partitions using bolted connections. 2.8. When working with machines and mechanisms, make sure they are in good condition by a test run without load. Eliminate the identified malfunctions yourself or call a service technician. Report a malfunction of the machine or mechanism to the work supervisor. 2.9. Do not start work in the absence of reliable grounding of all non-current-carrying metal parts, which, due to insulation failure, may become energized. Check the grounding resistance at least once a year, it should be no more than 4 ohms. 2.10. Check the condition of the wiring insulation. The insulation resistance must be at least 0,5 MΩ. 2.11. Check the connection of the rail track to the neutral wire and ground loop. The resistance between the grounding bolt and each metal non-current-carrying part of the distributor accessible to touch should not exceed 0,1 Ohm. 2.12. Inspect the connection of the sections of the track - they must be interconnected, and the entire track - with a neutral wire and a ground loop. 2.13. Check the reliability of the fastening of the stops - the limiters of the movement of the distributors on the end sections of the rail track. 2.14. Inspect the fastening of the feeder cable chute. 2.15. Check the serviceability of the machines, the presence and strength of fastening of enclosing and protective devices. 2.16. Check the presence and condition of the animals. Transfer sick animals to an isolation room, call a veterinarian. In cases of death or theft, it is necessary to report to the administration of the enterprise. 2.17. When working on a night shift, it is necessary to take measures against deliberate theft of animals and for self-defense (two guards on duty, use of guard dogs and other means permitted by law). 3. Safety requirements during work When working with boars-producers 3.1. When caring for boars-producers, the established regimen and daily routine should be observed, which contributes to the development of a calm disposition in them. 3.2. When approaching breeding boars, be sure to call them in a calm commanding voice. Rough handling of them causes an aggressive reaction. 3.3. Hang warning signs on the outside of pens and other places where restless animals are kept: "Caution! Bite!". 3.4. When caring for boars-producers, be careful, treat them calmly, confidently, without sharp shouts and beatings, while taking into account the individual characteristics of each animal. 3.5. The service worker should not enter the pens where the sires are kept, stand in the gates and passages during the run, let in and release the sires into the premises or pens during the operation of the manure conveyors. 3.6. To evacuate a boar from a group pen, use a transverse mobile shield. Before entering the group machine, a protective cylinder made of iron sheet, plywood or strong cardboard should be put on. Such a cylinder is attached to the worker's belt, not reaching 6 cm to the floor. 3.7. Grazing or walking boars-producers spend in non-hot time in small groups (with group keeping) or one at a time (with individual keeping). Let restless and vicious boars go for a walk each separately. 3.8. To stop the fights of boars and self-defense against them, you should use water from water hoses or from buckets, as well as shields measuring 1 x 1,5 m. The fangs of boars should be shortened in a timely manner as they grow. 3.9. Machines should be cleaned when there are no animals in them. 3.10. Transfer of boars-producers to the point of artificial insemination should be carried out along the cattle route in the absence of unauthorized persons in it. When working with sows 3.11. Exercise extra care and caution when servicing sows, who become excitable and aggressive before farrowing and while nursing piglets. 3.12. When receiving piglets at farrowing, act boldly, decisively, but not rudely, when weaning piglets from sows, be careful, position yourself in a safe area. 3.13. Service animals only in a well-lit area. 3.14. When cleaning the pens, fix the sow in the pens with a movable partition. 3.15. Open gratings over manure removal channels, covers, manholes of manholes using special hooks. When working with piglets in machines such as SD-F 3.16. When keeping piglets in pens during operation, check the straightness of the location of the feeders along the feeding front. 3.17. Adjust the opening force and the reliability of fixing doors, feeders, partitions using bolted connections. 3.18. Before dispensing feed, check that the chains are securely attached to the feeders. 3.19. Perform electric welding work in machines in the absence of piglets. When working with pigs in pens 3.20. Check out the machinery. It must be correct. Check and tighten all bolted connections and the reliability of fixing the gates, rotation of the sections of the feeders, doors. 3.21. When opening the locks of the door, you should stand on the side of it, not be in the way of the exit of the pigs from the pen. 3.22. Check the water supply to the drinkers, if there is a leak, eliminate it by replacing worn seals. 3.23. Threaded connections must be securely tightened, closures must easily and reliably fix sections and doors. 3.24. Watch the anti-corrosion coating of the machine equipment, restore the damaged surface by applying paint to this surface, especially pay attention to the places where the racks enter the floor. Pig fixation 3.25. When fixing animals for veterinary measures (vaccination, castration, slaughter, blood sampling), safe practices should be followed. 3.26. For fixing pigs weighing up to 100 kg, use the convenient method associated with the use of an ordinary wooden barrel. 3.26.1. Place a 40 cm layer of straw on the bottom of the barrel, lay the barrel horizontally, drive the pig into it or slide the barrel onto the pig. 3.26.2. After the animal is halfway in the barrel, lift the barrel by the free edge and secure it in an inclined position at an angle of 30 - 45°. 3.27. To fix the pigs in the supine position, it is necessary to put the pig on the ground or Nikiforov's operating table. These techniques must be performed by two workers - one holds the hind limbs, the other ears. Then turn the pig onto its side. 3.27.1. With a rope, tie the front and hind legs diagonally in pairs or three legs together. 3.27.2. Or put the animal on its back in a large trough and tie the front and hind legs separately in pairs, while passing one end of the rope from the front legs between the hind legs under the knot, pass the other end from the hind legs between the front legs also under the knot. 3.27.3. Then twist both ends of the rope together, throw it over any crossbar and pull it up as far as possible. 3.28. To fix pigs of different ages, use the Lukyanovsky method. 3.29. On one of the hind limbs above the hock, put a movable loop of a strong rope, throw its free end over a strong pole or crossbar located at a height of 1,5 m, and pull it up so that the animal leans on the front limbs. 3.30. Secure large animals by the upper jaw with a rope loop. 3.30.1. From a strong rope, make a movable loop and throw it over the upper jaw behind the fangs. 3.30.2. Then tie the free end of the rope several times around a tree, a pole, a crossbar. At the same time, one worker keeps the animal. 3.31. For castration of boars and medical procedures on suckling piglets and gilts up to 3-4 months of age, use the following fixation methods. 3.31.1. Lay the piglet on its back in a trough or in a sitting position on your knees, holding the piglet's limbs. 3.31.2. While standing, hold the gilt by the hind limbs in a semi-suspended state and hold it with your legs. Collection of semen from boars and insemination of sows 3.32. Handling of boars during mating or semen collection should be calm and confident. Timid and uncertain handling develops a persecution reflex in boars. 3.33. The transfer of boars to the arena for natural mating or semen collection should be carried out along cattle passes, using self-defense means that exclude contact with the animal (crackers, electric prods). 3.34. Sperm from boars-producers must be taken in an arena equipped with a stuffed animal. 3.35. To train a boar to mount a dummy, first let him cover a few sows in the arena, and then put the dummy in the arena. 3.36. Insert the artificial vagina with the sperm receptacle into the stuffed animal so that its inlet and the hole in the back of the stuffed animal coincide. Check that there are no gaps or sharp edges that can hurt the boar and cause aggressiveness. 3.37. During the collection of sperm, be quiet and do not allow the presence of unauthorized persons. 3.38. When approaching a sow in heat, call her in a calm voice. When inseminating sows, the following safe practices should be followed: 3.38.1. Sows must be in cages (individual). Sows should be inseminated at the moment when they have the "immobility reflex". 3.38.2. Remove the plain stopper from the graduated semen bottle (or vial) and replace it with a tubing stopper. Attach a catheter to a free tube or screw a catheter onto a polyethylene bottle. Check the strength of the connection, if there are burrs and chips, then eliminate them. 3.38.3. Take the bottle in your left hand and, without lifting it above the level of the sow's back, insert the catheter into the sow's vagina with your right hand to a depth of 35-40 cm, and hold the bottle with your other hand. 3.38.4. As soon as the end of the catheter enters the cervix, lift the vial above the level of the sow's back and turn it upside down. 3.39. During the insemination of the sow, follow the technological requirements of artificial insemination, do not cause pain, injury, exclude the aggressiveness of the animal. 3.40. Skillful, non-rough handling of sows during insemination will allow one worker to work more safely. 3.41. Do not work with liquid nitrogen alone. 3.42. Filling the Dewar vessel with liquid nitrogen from transport containers should be done using a flexible metal hose so that its lower end is lowered to the bottom of the vessel. 3.43. Filling the Dewar vessel with liquid nitrogen from another vessel should be done through a wide metal funnel, avoiding liquid overflow from the funnel. In case of accidental spillage of liquid nitrogen, it is necessary to open the door, turn on the ventilation and free the room from workers until the nitrogen vapor is completely removed. 3.44. It is forbidden to look into the neck of the Dewar vessel during its filling with liquid nitrogen. Refueling is completed when the first splashes of liquid nitrogen appear on the neck of the vessel. 3.45. It is necessary to close the Dewar vessels with the lids intended for them. 3.46. Sperm canisters, tweezers, and other items should be introduced slowly into liquid nitrogen to avoid splattering. 3.47. When extracting ampoules, straws or granules with sperm from liquid nitrogen, it is necessary to hold the instrument in the upper part of the neck of the vessel for 1-2 seconds so that the nitrogen droplets evaporate. 3.48. When transferring and transporting Dewar vessels, do not allow them to fall, hit, or sharp shocks. 3.49. To prevent the ignition of combustible materials and the explosion of the Dewar vessel, it is prohibited: 3.49.1. Install Dewar vessels near heating devices. 3.49.2. Remove liquid nitrogen from the Dewar by heating. 3.49.3. Use liquid nitrogen without a manufacturer's certificate or without impurity analysis after 12 refills of the Dewar. 3.49.4. Use vessels as containers for other liquids. 3.49.5. Wipe the internal cavity of the vessels with rags and other cleaning materials of organic origin (ruffs made of synthetic materials are allowed). 3.49.6. After the 12th refueling, it is necessary to perform a cold rinsing of the Dewar vessel (the contents of the vessel are completely poured out and refilled with liquid nitrogen). Irradiation and heating 3.50. When working with a heating and irradiation system, each facility equipped with an IKUF must have posted rules on labor protection, fire safety and first aid instructions for electric shock. 3.51. Employees servicing the heating and irradiation system must be familiar with the instruction manual and comply with its requirements. 3.52. It is necessary to look at sources of ultraviolet and infrared radiation from a close distance with protective glasses (Appendix 3). Prolonged exposure to unprotected parts of the body can cause burns. 3.53. Infrared irradiators must be hung at a height of at least 60 cm from the floor and must not come into contact with combustible materials. 3.54. All metal parts of the installation must be grounded. Before switching on, it is necessary to check the reliability of the grounding. 3.55. During operation, handle ultraviolet lamps with care, as they contain a dosed amount of mercury, which, if the lamps are damaged, can get into the feed and cause poisoning of pigs. 3.56. In the event of a breakdown of ultraviolet lamps, collect mercury with a rubber bulb. Wash the place where the lamps have broken with a XNUMX% solution of potassium permanganate. 3.57. The heating and irradiation system can operate in two modes - manual and automatic. 3.58. During manual operation, the following safety precautions must be observed. 3.58.1. Set the control box switch to the "Manual" position. 3.58.2. Turn on the breaker and set the control box circuit breakers to the "On" position. 3.58.3. Press the "Start" button for infrared sources in the control unit, and the corresponding signal lamp will light up. 3.58.4. Then press the "Start" button on the control unit for ultraviolet lamps - the corresponding signal lamp will light up. 3.58.5. Turn off infrared sources and ultraviolet lamps with appropriate automatic switches to turn off individual groups or with the "Stop" buttons for both groups. 3.59. For automatic operation, set the type of operation switch to the "Automatic" position. 3.59.1. Turn on the breaker and circuit breakers. Automatic operation of the system is carried out by a software time relay in accordance with the program of the daily cycle of turning on and off infrared sources and ultraviolet lamps. 3.59.2. For reliable operation of the system in the "Automatic" operating mode, switch the operating mode at the time of pauses (when the irradiators are turned off). Transportation of pigs 3.60. When transporting pigs, workers should be aware of the peculiarities of their behavior. Exercise special care in relation to animals, above the machines of which warning labels are hung. 3.61. Enter the section to the animals should be two, having the means of self-defense (whip, electric prod, long stick). Animals must be handled with confidence and calmness. 3.62. When transferring animals from sections, precautions must be observed. 3.62.1. Do not stand in the passages and openings in the way of the movement of animals. 3.62.2. Do not go into the middle of a moving herd. 3.63. To expel animals for loading, start from the sections and machines closest to the exit. 3.64. The ways of movement of animals to the place of loading on the territory of the enterprise must be fenced. 3.65. When loading and unloading animals from a vehicle, stationary or mobile ladders with a protective zone fenced off with posts for the worker should be used. The movement of animals should be controlled while in the protective zone of the ladder. 3.66. Pigs should be transported in specially equipped vehicles (livestock trucks) without a leash in such an amount that the animals can lie down. It is not allowed to transport boars and queens in one vehicle. 3.67. When opening the sides of the car, you must make sure that the animals are safely located. 3.68. On the way, a sharp change in speed and direction of movement is not allowed. 3.69. Employees are prohibited from being in the back of a car when transporting pigs. Feed preparation Transportation of root crops 3.70. Carry out the work of the root crops conveyor with the help of starters. 3.71. When the conveyor is working, you must first turn on the inclined conveyor, and then the feeder. 3.72. Adjust the chain tension of the inclined conveyor by moving the drive shaft in the guides. The tension is considered normal if in the middle of the span the chain deviates by 30 - 40 mm when a force of 10 - 12 kg is applied. 3.73. Adjust the feeder drive chain by turning the tension sprocket lever. The tension is considered normal if in the middle of the span the chain deviates by 20 - 30 mm when a force of 10 kg is applied. 3.74. Tension the V-belts by moving the motors using tension screws. The belts are tensioned so that the deflection of each in the middle part when pressed with a force of 7 - 8 kg is 10 - 15 mm. 3.75. All rotating parts, transmission mechanisms must be securely guarded. 3.76. Remove jammed products only when the conveyor is stopped. Washing, chopping root crops 3.77. Before starting the grinder, fill the tub with water. Adjust the water flow by opening the valve depending on the contamination of the incoming product. Do not allow water to overflow from the bath. 3.78. First, turn on the chopper engine, and then the auger engine, this will ensure a uniform supply of root crops to the rotating disk and prevent it from being pressed with feed. 3.79. Load the grinder when there is water in the bath and the auger is running. The supply of root crops must be continuous. 3.80. Set the size of the product to be ground using the handle located in the control cabinet. 3.81. When washing potatoes without chopping, remove the deck and the top disk of the chopper, and in its place install the stopper of the lower disk. 3.82. During the operation of the root crop grinder, do not allow the presence near its workers who are not familiar with the documentation for the operation of this machine. 3.83. Perform inspection, cleaning, lubrication, adjustment of mechanisms and removal of guards after the mechanisms have completely stopped. 3.84. Perform all repair and maintenance work only with the disconnected switch on the line supplying voltage to the grinder. 3.85. Maintenance and repair of electric devices located inside the control cabinet should only be allowed by workers with an electrician qualification group of at least the third. 3.86. Do not repair electrical equipment or damaged wiring by yourself. If you find a malfunction in the electrical equipment or wiring of the machine, immediately stop the grinder, turn off the breaker and call an electrician. 3.87. When repairing the grinder, use only serviceable tools that ensure safe work. 3.88. If extraneous noises and knocks appear in the machine, immediately stop the grinder and identify the cause that caused them. Grain crushing 3.89. When operating the crusher, follow the following safety procedures. 3.89.1. Before putting the crusher into operation, run it in the adjustment mode, to do this, set the switch on the control cabinet to the "Adjustment" position. 3.89.2. Switch each motor on and off in sequence and make sure that the direction of rotation is correct. 3.89.3. Then run the crusher in the operating mode at idle speed with the automatic regulator turned off. To break in, set the switch to the "Run" position and the regulator toggle switch to the "Off" position. 3.89.4. Switch on the electric motors in the following sequence: unloading auger, crusher and loading auger. Stop - in reverse order. 3.89.5. Run the crusher in the operating mode at idle with the automatic regulator on. Set the regulator toggle switch to the "On" position and loosen the damper locking knob. Turn on the electric motors of the unloading auger and crusher. 3.89.6. Verify that the hopper flap lever lifts smoothly. In the uppermost position, the lever should press the limit switch and turn on the sound siren. 3.89.7. Shut down the crusher and make sure that when it is turned off, the shutter immediately closes the grain tank outlet window. Run the crusher under load for 30 minutes. 3.90. Before starting the crusher in the operating mode, install the loading auger with the intake part on a heap or pit with grain. 3.91. Release the stopper of the damper lever, hopper. 3.92. Set the mode switch to the "Operation" position, and the regulator toggle switch to the "Off" position, then the mains switch on the control cabinet to the "On" position. 3.93. Set the damper levers to a position that ensures the quality of the grind. 3.94. At sub-zero ambient temperature, turn on the lighting lamp in the control cabinet. 3.95. After warming up the control cabinet for 30 min. successively pressing the "Start" buttons turn on the unloading auger, crusher and loading auger. 3.96. If necessary, the crusher can be operated in manual mode. At the same time, constantly monitor the reading of the ammeter, the arrow of which should be at around 60 A. 3.97. Do not remove or open covers and hatches until the rotating parts of the crusher have come to a complete stop. 3.98. If there are extraneous knocks and noises in the crusher, immediately stop the crusher, identify and eliminate the cause. 3.99. Do not work if there is no or defective aspiration in the room where the crusher is installed. 3.100. Perform all maintenance and troubleshooting operations only with the switch on the line that supplies voltage to the crusher turned off. Attach a warning sign to the switch and control cabinet: "Do not turn it on! People are working!". 3.101. During operation, stop the crusher only when the product is completely used up. Feed supply 3.102. The end feed feeder must be switched on and off from the central control panel. In this case, the sequence of turning on the feeder must be observed: first - the inclined conveyor, and then - the horizontal conveyor. Stopping is done in reverse order. 3.103. During the operation of the end feed feeder, every shift, make sure that end feed is constantly in the bunker. 3.104. The bunker must always be closed with a lid; work related to repairs in the bunker should be carried out in the absence of compound feed and the power supply turned off. Feed steaming 3.105. Before starting the steamer-mixer, supply power to the control cabinet by setting the package switch to the "On" position, and the signal lamp will light up. 3.106. Press the mixer motor start button. Turn on the electric motor of the loading conveyor. 3.107. Load the feed mixture components with the agitator running. When the preset level is reached, the loading conveyor motor should automatically switch off. 3.108. To prepare steamed feed mixtures, supply steam to the mixer. To do this, open the steam valve. 3.109. Steam supply to the mixing steamer should be carried out with the filling neck and inspection hatch tightly closed. Control the temperature with a thermometer. Produce the steaming of feed mixtures at a temperature of 90 - 95 °C. 3.110. Do not supply steam to the mixer at a pressure higher than 70 kPa. 3.111. To stop the steam supply, turn off the valve so that water flows into the steam line, and then completely close the valve. 3.112. Humidify the feed through the sprinkler. 3.113. After the end of the process of steaming and mixing, unload the finished feed. 3.114. By pressing the button in the control cabinet, start the electric motor of the unloading gate. When the gate reaches the extreme right position, the electric motor will turn off and the electric motor of the unloading auger will automatically turn on. 3.115. After unloading the feed, turn off the gate drive, which will close the unloading mouth and automatically turn off. 3.116. After completing the work related to the steaming of the feed, turn off the power supply to the steamer-mixer. 3.117. Do not leave food in the mixer for a long time (more than one shift). From long-term storage, the food sticks and clogs the working organs. 3.118. During operation, do not allow the presence of unauthorized persons near the steamer-mixer. 3.119. Perform inspection, cleaning, lubrication, adjustment of mechanisms with the steamer-mixer disconnected from the power supply. 3.120. If extraneous noises appear in the machine, immediately stop the steamer-mixer, identify and eliminate the cause of the noise. 3.121. Perform all maintenance work only with the power off. Hang warning posters above the switch and on the control cabinet: "Do not turn it on! People are working!". 3.122. Maintenance and repair of electrical equipment must be carried out by employees with an electrician qualification of at least the third group. 3.123. Start the mixer-steamer after installation, repair or a long stop with the permission of the chief engineer (mechanic) after checking the technical condition. Cooking 3.124. Open the boiler lid and hang it on the bracket so that it does not fall back. 3.125. Fill the brew vessel of the boiler with feed components, pour the required amount of water. 3.126. Close the boiler lid. Set the temperature limit with the switch knob, and the green lamp will light up, indicating that the boiler is in operation. 3.127. Close the funnel valve when a continuous jet of steam comes out of the funnel. 3.128. If there is air in the steam jacket, purge the valve. Having reached the set pressure in the jacket, the boiler will switch to low heating if mode 1 is set, and turn off if mode 2 is set. 3.129. Turn off the boiler after the end of the work by turning the switch knob to the "Off" position. 3.130. Unload the boiler by smoothly rotating the flywheel of the worm gear, while tilting the boiler. 3.131. Dismantle, clean, troubleshoot the boiler when there is no steam in the jacket, and also when the boiler is disconnected from the mains. 3.132. When using digesters, do not allow:
Conveyors and conveyors for supplying feed and prepared feed mixtures 3.133. Check that the drive is securely fastened to the drive section and tighten if necessary. 3.134. Adjust the chain tension by moving the drive shaft in the brackets with tension screws. 3.135. Adjust the drive chain by changing the position of the plate on which the drive is installed, by screwing or unscrewing the nuts. 3.136. Check the condition of the electrical equipment. Do not work without grounding or if it is defective. 3.137. Perform all repair and maintenance work with the electrical voltage switched off. Mixing and distribution 3.138. When distributing food to animals, it is necessary to observe the established regimen and daily routine, which will contribute to the development of a calm disposition in them. 3.139. Control the operation of the mechanisms of the dispenser-mixer from the seat using buttons, handles, levers. 3.140. To load the dispenser-mixer with feed, install it in the feed shop or under the conveyor supplying feed from the feed shop. 3.141. Then turn on the mixer, feed the feed components into the hopper of the distributor-mixer. Change the direction of rotation of the agitator 2 - 3 times during feeding. 3.142. Load the feed components into the mixer dispenser through the grate, which must always be on the loading neck. 3.143. When loading and mixing the components of the feed mixture, the speed lever must be in the neutral position. 3.144. After filling the hopper with feed mixture, turn on the drive lever, sound the horn and make sure that there are no bystanders or animals near the dispenser. 3.145. Having approached the dispenser-mixer to the feeders, turn on the distributing augers and open the gates. 3.146. After dispensing all the feed, close the gates, turn off the dispensing augers and agitator, turn on the reverse and return the dispenser for reloading if the animals still need feed. 3.147. Adjust the amount of feed dispensed by changing the gate opening. 3.148. Adjust the closing density of the gates by tightening the bolts. 3.149. During the operation of the dispenser-mixer, keep an eye on the power cable, do not allow it to be pulled and run over. 3.150. The safety clutch must be adjusted to the maximum torque that occurs on the shaft during operation. 3.151. Adjust the clutch by tightening the spring with the adjusting nut. The safety clutch spring must be compressed to a length of 126 mm. 3.152. Eliminate the noticed malfunctions in the distributor only when the electric motor is stopped and the main switch is turned off, while posting a poster on the switch: "Do not turn it on! Repair!". 3.153. When distributing feed using handcarts, do not allow them to be overloaded above the edge of the boards. It is necessary to push the cart away from you in the direction of travel. 3.154. Keep an eye on the floors in the stern aisle, the floors should be flat and non-slip. 3.155. When distributing feed using overhead tracks, pay attention to the condition of the attachment of the overhead track, as well as the divergence of the rails at the junctions. 3.156. Move the trolley along the rail track by pushing it away from you, while people and animals should not be in the way of movement. 3.157. When unloading a trolley with a tipping body, the worker must be at the end of the body. 3.158. During operation, keep an eye on the grounding of the trolley monorail and on the stops at the ends of the monorail track. 3.159. Use the trolley during operation only for its intended purpose. Drinking 3.160. Installation and repair of automatic drinkers should be carried out in the absence of animals in the machine. 3.161. Elements of the design of automatic drinking bowls must be free of sharp corners, edges and burrs. 3.162. Having found a leak from the autodrinkers, try to fix it. If you cannot fix the problem on your own, call a mechanic. 3.163. When watering pigs from drinking troughs, do not allow them to overflow or leak. Troughs and drinkers should be periodically cleaned of foreign objects. Manure removal 3.164. In the cold season, before starting the manure conveyor, make sure that the scrapers and the chain of the inclined conveyor are not frozen to the bottom. 3.165. Before starting the conveyor, turn on the circuit breaker using the "On" button. At the same time, the green lamp with the inscription "Automatic on" will light up. 3.166. Press the start button "Inclined Conveyor", then - "Horizontal Conveyor". 3.167. To turn off the incline and horizontal conveyors, just press the "Stop" or "Inclined conveyor" button. 3.168. After turning off the horizontal conveyor, let it run for 2 - 5 minutes. inclined conveyor. 3.169. After finishing work, turn off the circuit breaker using the "Network" switch. The green light should turn off. 3.170. During the operation of the scraper, make sure that the slider does not reach the rotary device. 3.171. Extend the scraper periodically as it wears out. When one side of the scraper is completely worn out, turn it 180° and continue to use it until it is completely worn out. 3.172. Watch the chain tension. The chain is considered to be normally tensioned if it rotates smoothly, without jerks, and does not come off the drive sprocket. 3.173. After each stop of the scraper, turn off the "Power" switch located on the control box. 3.174. During inspection, repair and other maintenance work, the control panel must be completely disconnected from the electrical voltage. Work in wells, closed containers 3.175. Before performing work in wells, slurry collectors, manure collectors, receive targeted instruction and a work permit approved by the employer. The order should indicate the content of the work, safety measures during their implementation, the start and end time of work, the composition of the team and data on the briefing on labor protection with the obligatory signature of the workers. 3.176. A team working in a well, a closed tank, should consist of three workers: one - to work in the well, two - on the surface, one is engaged in insurance of the descending worker, the second transfers the necessary tools and materials. 3.177. Before descending into a well, a closed container, it is necessary to make sure that there are no harmful gases in them, for which a GSB-3M "Jin-gas" safety gas detector or other device is used. 3.178. Gas found in a well or other container must be removed. To remove gas from wells, use:
3.179. The complete absence of gas in the well or closed container must be checked by a secondary check with the GSB-3M "Jin-gas" gas detector, and only after that is it allowed to descend into the well or closed container. 3.180. If it is not possible to check for the presence of asphyxiating gases in a well or a closed container, it is allowed to descend into them only in a hose gas mask (types PSh-1 and PSh-2) with a hose extending 2 m away from the manhole. 3.181. When descending into a well or a closed container to a depth of up to 3 m, safety belts with shoulder straps (type C and D) should be used. With a greater depth of the well, safety belts with shoulder and hip straps (type D) should be used. 3.182. The rope for lowering and raising the worker must be strong, securely and firmly tied to the safety belt. 3.183. In the event of several people descending into the well, each of them must be insured by a worker located on the surface. 3.184. Portable ladders used for descending into wells must be made of non-sparking materials and securely fastened. 3.185. If the descent is made along the brackets, they should first be checked for strength with a rod. 3.186. To work in a gas mask, workers who have passed a medical examination, have been instructed and are skilled in handling a gas mask should be allowed. 3.187. It is allowed to work in a well or a closed container in a hose gas mask continuously for no more than 15 minutes, after which rest on the surface with the gas mask removed for at least 20 minutes must follow. 4. Safety requirements in emergency situations 4.1. Do not touch lying, protruding from the floor or hanging electrical wires and cables. 4.2. If you find a break or unreliable fastening of the grounding conductor, bare wires, damaged electrical installations, inform the electrician on duty or the work manager and do not put the electrical installation into operation until the malfunction is eliminated. 4.3. It is forbidden to independently eliminate malfunctions of electrical equipment, electrical wiring. Their repair and maintenance is allowed only to electrical personnel with a qualification group of at least the third. 4.4. In the event of a power outage, extraneous noise, vibration, burning smell, turn off the equipment and inform the work manager about this. 4.5. If the scrapers of the root crop conveyor jam, turn off the conveyor, drain the water from the tub and eliminate the cause. 4.6. Push the feed stuck in the unloading opening of the steamer-mixer with a wooden shovel or other safe devices (pusher, hook), having previously turned off the electric motor of the unloading gate. 4.7. If an increased electrical voltage appears on the equipment, immediately turn off the electrical equipment and inform the work manager or the electrician on duty about this. 4.8. In the event of a fire, stop the machine (equipment), turn off the main switch and start extinguishing the fire with the available means: fire extinguishers, sand, earth, or cover the flame with a tarpaulin. If the fire cannot be extinguished on your own, immediately inform the fire department and the work manager, give a fire alarm. 4.9. When clothing ignites, it must be torn off and extinguished; when most of a person’s clothing is engulfed in flame, it must be rolled up in a cloth or blanket (leaving the head open) and the fire must be extinguished. 4.10. In the event of an accident or a fire, to remove animals from the machines, sections of the room, use a jet of water, shields, electric prods. Do not stand in doors, aisles, or in the way of animals. 4.11. Extinguish flammable liquids (gasoline, kerosene, alcohol) with a fire extinguisher, directing the jet under the base of the flame, or throw sand, earth, or cover the burning surface with a wet tarpaulin. 4.12. Explosive substances (fodder dust) are plentifully sprayed with a spray of water from a hydrant. 4.13. Extinguishing electrical equipment, having previously de-energized it, is allowed only with carbon dioxide fire extinguishers, dry sand, felt felt or other non-conductive means. In case of extinguishing with sprayed water, the distance from the nozzle of the fire nozzle to burning electrical installations must be at least 4 m. The fire nozzle must be grounded, it is necessary to work in dielectric boots and gloves. 4.14. If you detect a gas leak or its presence in wells, closed containers, immediately inform the emergency service and the work manager, take measures to prevent fire and explosion. 4.15. In case of poisoning with poisonous gases in a well or container, pull the victim into fresh air or transfer to a dry, warm room, give him first aid and, if necessary, take him to a medical facility. 4.16. In case of leakage of liquid nitrogen from the Dewar vessels and its increased concentration in the room, causing headache, dizziness, loss of consciousness, suffocation, immediately turn on the ventilation, take the victim to fresh air. 4.17. When dealing with a liquid nitrogen leak, use only insulating or hose-type gas masks. When working in a gas mask, you must take a break for 5 minutes. every 30 min. work. 4.18. Warm up frozen water pipes with hot water or sand, steam, but not with an open flame (torch, blowtorch). 4.19. If an employee is injured, stop work, eliminate or neutralize the source of danger and provide first aid (Appendix 4) to the victim, inform the medical institution, the work manager or the person replacing him. 4.20. Every worker should be able to use a first aid kit. The composition of the first aid kit is given in Appendix 5. 5. Safety requirements at the end of work 5.1. Tidy up your workspace and inventory. 5.2. Together with the changer, inspect the animals, sections, machines, make sure that there are animals, and that there are means of restraint. 5.3. When handing over a shift, inform the shifter about the emerging dangers, hazards, and faulty equipment. 5.4. Report to the head of work on the shortcomings, malfunctions and measures taken during the work and during the inspection. Pay the attention of the changer to the behavior of the boars-producers and, in the prescribed manner, hand over the duty, making the appropriate entries in the log. 5.5. After finishing work on electrical equipment, turn off the power supply. 5.6. Clean the equipment of feed residues. 5.7. Check and, if necessary, tighten the screw connections. 5.8. Check the tension of belts, chain drives and the condition of the guards. 5.9. Lubricate the equipment in accordance with the table and lubrication scheme indicated in the operation manual. 5.10. Collect cleaning material, production waste and take them to the designated collection point. 5.11. Remove protective clothing, clean it, hand it over for cleaning or storage. Follow the hygiene requirements, take a shower. Appendix 1 to the Standard industry instruction on labor protection in animal husbandry. Pig breeding Appendix 2 to the Standard industry instruction on labor protection in animal husbandry. Pig breeding
Appendix 3 to the Standard industry instruction on labor protection in animal husbandry. Pig breeding
Appendix 4 to the Standard industry instruction on labor protection in animal husbandry. Pig breeding Providing first aid 1. Electric shock. After releasing the victim from the action of electric current, lay him on a bed and cover it warmly, quickly (within 15 - 20 s) determine the nature of the required first aid, organize a doctor's call and take the following measures: 2. If the victim is breathing and conscious, put him in a comfortable position, unfasten his clothes. Before the doctor arrives, provide the victim with complete rest and access to fresh air, while monitoring his pulse and breathing. Do not allow the victim to get up and move before the arrival of the doctor, and even more so continue to work. 3. If the victim is unconscious, but his breathing and pulse remain stable, which must be constantly monitored, let him smell ammonia and spray his face with water, ensuring complete rest until the doctor arrives. 4. In the absence of breathing, as well as infrequent and convulsive breathing, or cardiac arrest (lack of pulse), immediately perform artificial respiration or chest compressions. Begin artificial respiration and heart massage no later than 4-6 minutes. from the moment of cessation of cardiac activity and respiration, since after this period clinical death occurs. Never bury the victim in the ground. 5. Perform artificial respiration "from mouth to mouth" or "from mouth to nose" as follows. Lay the victim on his back, unfasten clothing that restricts breathing, place a roller of clothing under the shoulder blades. Ensure that the airway is clear, which may be obstructed by a sunken tongue or foreign material. To do this, tilt the head of the victim as much as possible, placing one hand under the neck and pressing the other on the forehead. In this position, the mouth usually opens, and the root of the tongue moves to the back of the larynx, providing airway patency. If there is foreign matter in the mouth, turn the victim's shoulders and head to the side and clean the mouth and throat with a bandage, handkerchief or shirt edge wrapped around the index finger. If the mouth does not open, then carefully insert a metal plate, a plaque between the back teeth, open the mouth and, if necessary, clean the mouth and throat. After that, kneel down on either side of the victim’s head and, holding the head tilted back, take a deep breath and, pressing your mouth tightly (through a handkerchief or gauze) to the victim’s open mouth, blow air into him strongly. At the same time, cover the nose of the victim with the cheek or fingers of the hand on the forehead. Make sure that the air enters the lungs and not the stomach, this is revealed by the distention of the abdomen and the lack of expansion of the chest. If air has entered the stomach, remove it from there by quickly pressing for a short time the area of \uXNUMXb\uXNUMXbthe stomach between the sternum and the navel. Take measures to free the airways and repeat the blowing of air into the lungs of the victim. After blowing in, release the mouth and nose of the victim for free exit of air from the lungs. For a deeper exhalation, lightly press on the chest. Perform each air injection after 5 seconds, which corresponds to the rhythm of your own breathing. If the victim's jaws are so tightly compressed that it is not possible to open the mouth, perform artificial respiration using the mouth-to-nose method, blow air into the victim's nose. When the first spontaneous breaths appear, time the artificial breath to coincide with the beginning of the spontaneous breath. Perform artificial respiration until deep and rhythmic breathing of the victim is restored. 6. Perform external heart massage in case of cardiac arrest, which is determined by the absence of a pulse, dilated pupils and cyanosis of the skin and mucous membranes. When performing an external heart massage, lay the victim on his back on a hard surface or place a board under him, free his chest from clothing and raise his legs by about 0,5 m. Position yourself to the side of the victim and determine the place of pressure. To do this, feel for the lower soft end of the sternum, and 3-4 cm above this place along it, a pressure point is determined. Place the part of the palm adjacent to the wrist joint on the place of pressure, while the fingers should not touch the chest, place the palm of the second hand at a right angle on the back of the palm of the first hand. Make a quick (push) and strong pressure on the sternum and fix it in this position for about 0,5 s, then quickly release it, relaxing your hands, but do not take them away from the sternum. Apply pressure approximately 60 - 80 times per minute. Massage the heart until your own (not supported by massage) regular pulse appears. 7. If it is necessary to simultaneously perform artificial respiration and heart massage, the procedure for conducting them and the ratio of the number of injections to the number of pressures on the sternum is determined by the number of persons providing assistance: 7.1. If one person is helping, then perform artificial respiration and heart massage in the following order: after two deep breaths, do 15 chest compressions, then again two deep breaths and 15 chest compressions, etc. 7.2. If you provide assistance together, then one makes one blow, and the second after 2 s produces 5-6 pressures on the sternum, etc. 8. Perform artificial respiration and heart massage until the body's vital functions are fully restored or until a doctor arrives. 9. Injuries. Lubricate abrasions, injections, bites, minor wounds with iodine or brilliant green and apply a sterile bandage or seal with a strip of adhesive plaster. For a large wound, apply a tourniquet, lubricate the skin around the wound with iodine and bandage it with a clean gauze bandage or a sterile bandage from an individual package. If there is no bandage or bag, take a clean handkerchief or cloth and, on the place that will lie on the wound, drip iodine to make a spot larger than the wound, and apply the spot on the wound. Apply the bandage so that the blood vessels are not squeezed, and the bandage is kept on the wound. In case of injury, give a tetanus toxoid injection in a medical institution. 10. Stop bleeding. When bleeding stops, lift the injured limb up or position the injured part of the body (head, torso, etc.) so that they are elevated, and apply a tight pressure bandage. If during arterial bleeding (scarlet blood flows in a pulsating stream) the blood does not stop, apply a tourniquet or twist. Tighten the tourniquet (twist) only until the bleeding stops. Mark the time of applying the tourniquet on a tag, a piece of paper and fix it on the tourniquet. The tourniquet is allowed to be kept tightened for no more than 1,5 - 2 hours. In case of arterial bleeding, take the victim to a doctor as soon as possible. Transport it in a comfortable and, if possible, fast vehicle, always with an accompanying person. 11. bruises. For bruises, apply a tight bandage and apply cold soaks. In case of significant bruises of the torso and lower extremities, take the victim to a medical facility. Bruises in the abdomen lead to ruptures of internal organs. Immediately take the victim to a medical facility at the slightest suspicion of this. Do not let such patients drink and eat. 12. Fractures of bones. For a closed fracture, place the limb in a comfortable position, while handling it carefully, avoid sudden movements, and apply splints. Put splints on both sides, while putting cotton under the splints so that the splints do not touch the skin of the limbs, and be sure to capture the joints above and below the fracture sites. Tires can be worn over clothing. In the case of an open fracture, stop the bleeding, smear the edges of the wound with iodine, bandage the wound and apply splints. Do not touch with your hands and do not set the fragments of bones protruding from it into the wound. In the absence of tires, use plywood, boards, fork holders. As a last resort, bandage the broken leg to the good leg and the arm to the chest. In case of a fracture of the collarbone and scapula, put a tight cotton roll into the axillary region of the injured side, and hang your hand on a scarf. If your ribs are broken, wrap your chest tightly or with a towel as you exhale. If the spine is fractured, carefully place the victim on an ambulance stretcher, boards or plywood, make sure that the torso does not bend (to avoid damage to the spinal cord). In case of broken bones, take urgent measures to deliver the victim to the nearest medical facility. 13. Dislocations. In case of dislocation, ensure the immobility of the injured limb, apply splints without changing the angle that formed in the joint during dislocation. Dislocations should be set only by doctors. When transporting the victim to a medical facility, place the victim on a stretcher or in the back of a car, and cover the limb with rollers from clothes or pillows. 14. Burns. In case of a thermal burn, remove clothing from the burned area, cover it with sterile material, put a layer of cotton wool on top and bandage it. Do not touch burns, puncture blisters, or tear off pieces of clothing stuck to burns while treating. Do not lubricate the burnt surface with ointments and do not cover with powders. In case of severe burns, take the victim to the hospital immediately. 14.1. In case of an acid burn, remove clothing and thoroughly for 15 minutes. rinse the burned area with a stream of water, then rinse with a 5% solution of potassium permanganate or a 10% solution of baking soda (a teaspoon in a glass of water). After that, cover the affected areas of the body with gauze soaked in a mixture of vegetable oil and lime water, and bandage. 14.2. In case of alkali burns, the affected areas within 10-15 minutes. rinse with a stream of water, and then with a 3 - 6% solution of acetic acid or a solution of boric acid (a teaspoon of acid in a glass of water). After that, cover the affected areas with gauze soaked in 5% acetic acid solution and bandage. 15. Frostbite. In case of frostbite of the XNUMXst degree (skin is edematous, pale, cyanotic, loses sensitivity), bring the victim into a cool room and rub the skin with a dry, clean cloth until redness or a feeling of warmth, lubricate with fat (oil, lard, boric ointment) and apply an insulated bandage. Then drink hot tea to the victim and transfer to a warm room. With frostbite II - IV degree (bubbles with bloody fluid appear on the skin and it becomes purple-bluish in color - II degree; layers of the skin and underlying tissues become dead, the skin becomes black - III degree; complete necrosis of the skin and tissues - IV degree) on the affected apply a dry bandage to the skin, let the victim drink hot tea or coffee and immediately send to the nearest medical facility. 16. Heat and sunstroke. At the first signs of illness (headache, tinnitus, nausea, rapid breathing, intense thirst, sometimes vomiting), place the victim in the shade or bring into a cool room, free the neck and chest from tight clothing, if the victim is conscious, give cold water to drink , head, chest and neck periodically moisten with cold water, let's sniff ammonia. If the victim is not breathing, perform artificial respiration according to paragraph 4 of this Appendix. 17. Poisoning with poisonous gases. If signs of poisoning appear (headache, tinnitus, dizziness, dilated pupils, nausea and vomiting, loss of consciousness), remove the victim immediately to fresh air and organize the supply of oxygen for breathing using a rubber cushion or an oxygen cylinder. In the absence of oxygen, lay down the victim, raise his legs, let him drink cold water and let's sniff cotton wool moistened with ammonia. If breathing is weak or stops, perform artificial respiration until a doctor arrives or breathing is restored. If possible and the victim is conscious, give him plenty of milk to drink. 18. Damage to the eyes. In case of clogging of the eyes, rinse them with a 1% solution of boric acid, a stream of clean water or a damp cotton (gauze) swab. To do this, lay the head of the victim so that you can direct the jet from the outer corner of the eye (from the temple) to the inner. Don't rub your clogged eye. If splashes of acid and alkali get into the eye, rinse it for 5 minutes. clean water. After washing the eye, apply a bandage and send the victim to a doctor. Appendix 5 to the Standard industry instruction on labor protection in animal husbandry. Pig breeding Composition of the first aid kit 1. Tablets of validol and nitroglycerin - used for severe pain in the region of the heart. 2. Tablets of analgin, amidopyrine - used as an analgesic for headaches, bruises, dislocations, fractures, 1 - 2 tablets. 3. Tincture of valerian, corvalol - with slight pain in the heart, with nervous excitement. 4. Tablets of besalol or its analogues - for pain in the abdomen. 5. Sodium bicarbonate (soda) - for heartburn (inside), externally to wash the skin if acid gets on it. 6. Citric acid - for washing the skin when alkali gets on it. 7. Potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate) - for washing wounds, gargling. 8. Hydrogen peroxide - for the treatment of wounds. 9. Hygroscopic surgical cotton wool. 10. Sterile bandage, 10 m x 5 cm. 11. First aid dressing package. 12. Bactericidal adhesive plaster - for the treatment of microtraumas. 13. A solution of iodine, brilliant green - for the treatment of wounds. 14. Ammonia solution (ammonia) - for inhalation from a cotton swab in case of fainting, loss of consciousness. 15. Thermometer. 16. Tourniquet. 17. Fingertips. 18. Scarf for a garter. 19. Tires. 20. Scissors.
▪ Livestock breeder, cattle. Standard instruction on labor protection ▪ Motorist of the bagerny pump house. Standard instruction on labor protection
Artificial leather for touch emulation
15.04.2024 Petgugu Global cat litter
15.04.2024 The attractiveness of caring men
14.04.2024
▪ Data transfer speed will double ▪ Large animals and deadly diseases ▪ Road traffic can exacerbate allergies ▪ NexFET with double-sided cooling
▪ section of the site Sites of amateur radio equipment. Article selection ▪ Montague and Capulet article. Popular expression ▪ article How did an American swimmer make the entire Soviet team wear a mustache? Detailed answer ▪ article Chamenery angustifolia. Legends, cultivation, methods of application ▪ article Starch stains under the action of iodine. Chemical Experience
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 See other articles Section
See other articles Section 