
|
|
OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH
Instructions on labor protection for livestock breeders, cattle. Full document
Occupational Safety and Health / Standard instructions for labor protection Introduction "Standard branch instruction on labor protection in livestock breeding. Cattle" (hereinafter referred to as the Instruction) establishes labor protection requirements and regulations for the performance of work when servicing cattle (hereinafter referred to as cattle) at enterprises of all forms of ownership, including farms farms. The instruction was developed in accordance with the requirements of the Fundamentals of the legislation of the Russian Federation on labor protection, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, state standards of the labor safety system, the Rules for labor protection in animal husbandry, instructions for the operation of machines and mechanisms and based on the results of an analysis of the causes of accidents in cattle breeding . This Instruction is the basis for the development of labor protection instructions for employees by profession and for certain types of work at enterprises. Instructions for employees are developed by the employer in accordance with the list of professions, which is compiled by the labor protection service with the participation of heads of departments, services of chief specialists (animal engineer, veterinarian, mechanic, power engineer), labor organization services. The list of professions is compiled on the basis of the staffing table approved by the enterprise. The names of professions must comply with the All-Russian classifier of professions for workers, positions of employees and wage categories. Instructions are developed on the basis of orders and orders of the head of the enterprise (employer) and approved by the head of the enterprise (employer) after preliminary consultations with the labor protection service (if necessary, with other interested services and officials at the discretion of the labor protection service) and agreement with the elected trade union body. Approved labor protection instructions for workers or by profession must be registered by the labor protection service of the enterprise or the responsible person in the instructions registration log. The head of the enterprise (employer) is obliged to organize the study of instructions. Employees of rental collectives, farm enterprises must be trained and tested on labor protection in the manner prescribed for state-owned enterprises. The issuance of instructions to employees is carried out against signature with registration in the journal for issuing instructions. Samples of the first and last pages of the instruction on labor protection for workers and the form of the register for issuing instructions are given in Annexes 1, 2 and 3. 1. General requirements 1.1. Persons at least 18 years of age who have undergone a medical examination to determine their suitability for the performance of the assigned work are allowed to service cattle, operate machinery and equipment. 1.2. Persons under the age of 18 may be allowed to work with the permission of the medical commission and with the consent of the elected trade union body of the enterprise. 1.3. Persons under the age of 16 are not allowed to work. In exceptional cases, with the permission of the medical commission and the elected trade union body of the enterprise, persons who have reached the age of 15 may be accepted. 1.4. It is not allowed to use the labor of persons under 18 years of age and women in heavy work and in work with harmful working conditions. At workover enterprises such works are:
1.5. Persons at least 18 years of age, trained and certified, who have passed introductory and primary safety briefings at the workplace, are allowed to service bulls. 1.6. Work on mobile feeders is allowed for workers who have a driver's license of the corresponding vehicle. 1.7. Workers with the first qualification group in electrical safety are allowed to work on maintenance of milking machines, equipment for the primary processing of milk, equipment of feed shops. 1.8. Employees who are in direct contact with dairy products, upon admission to work, and subsequently periodically undergo medical examinations and examinations for tuberculosis, brucellosis, intestinal infections and helminths in the prescribed manner. 1.9. Employees should not shy away from undergoing medical examinations, following recommendations based on the results of examinations. In case of violation of these requirements, the employee is not allowed to perform his duties. 1.10. All newly hired employees, as well as employees transferred from another job, undergo introductory and primary workplace safety briefings and training in safe methods and techniques for performing work, fire safety measures, and methods of providing first aid to victims. 1.11. Employees servicing electrified equipment undergo additional training and instruction in electrical safety with the assignment of the first group of admission. 1.12. Employees who have a break in work for more than two years, prior to the start of independent work, are trained in labor protection, as when entering a job. 1.13. Employees of farm enterprises, cooperatives, rental collectives must comply with the rules for admission to independent work in the manner established for state enterprises. 1.14. Newly hired workers perform work under the supervision of a manager (employer, foreman or other official) for at least two weeks, after which an admission to independent work is issued. 1.15. Employees must comply with the requirements of the internal labor regulations, which establish the start and end times of work, breaks for rest and meals. 1.16. Due to the special nature of the work, the working day of machine milking operators and workers who milk cows by hand may be divided into parts with a total duration of work not exceeding the established duration of the working week. 1.17. Employees are obliged to comply with labor and technological discipline, requirements for labor protection and industrial sanitation, and take care of the property of the enterprise. 1.18. The employee must perform only the work for which he has been trained and instructed, not delegate his work to other persons. 1.19. Employees should not violate the rules of conduct in production premises, work under the influence of alcohol and drugs, in a sick or tired state, drink alcohol and smoke at the workplace. 1.20. In the process of caring for animals, operating machinery and equipment, workers may be exposed to the following hazardous and harmful production factors, in relation to which precautionary measures must be observed:
1.21. Employees are required to comply with the established requirements for handling mechanisms, machines and equipment: know the principle of operation, be able to start and stop them, know the installation locations and purpose of instrumentation and industrial alarms and the rules for using them. 1.22. Employees should not use faulty technical means and inventory in their work; be in the way of vehicles and animals; cross over conveyors in places not equipped with walkways; jump on the steps of a moving vehicle and jump off it on the go; touch electrical wires, open the doors of electrical cabinets; influence electrical wires with water, metal and other objects; approach closer than 8 - 10 m to an electric wire lying on the ground in case of a break or damage to the power line; turn on or stop (except in emergency cases) machines and mechanisms, the operation of which is not included in their duties. 1.23. It is unacceptable: to sit down, stand up, put clothes and other objects on the casings and fences of dangerous parts of machines and equipment, go beyond the fences of electrical installations; remove warning posters, guards and protective covers from electrical equipment. 1.24. Employees must use personal protective equipment at work: special clothing (cotton overalls or overalls, a vest with a warm lining), special footwear (rubber boots) issued in accordance with the current "Model Industry Standards for the Free Issue of Special Clothing, Special Footwear and Employees to Workers and Employees" other personal protective equipment", and sanitary clothing (cotton gown, scarf), and when servicing infectious animals - a rubberized apron and rubber gloves. All work related to milking cows, primary processing and dispatch of milk, as well as caring for sick animals, should be performed in sanitary clothing, other work - in special. 1.25. Special and sanitary clothing and footwear must be used in accordance with the purpose, be in good condition and clean and stored in specially designated places. 1.26. In order to prevent the ingress of foreign objects into milk, it is not allowed to stab working clothes with pins and needles, store hairpins, mirrors and other items of a personal toilet in pockets. 1.27. Employees are required to follow the rules of personal hygiene:
1.28. If you feel unwell, have a fever, develop pustular or other skin diseases, burns, cuts, you should inform the work manager and consult a doctor. 1.29. Employees must know and be able to apply the methods of providing first (pre-medical) assistance to the victim (Appendices 4, 5). 1.30. Employees who violated the requirements of the Labor Protection Instructions when performing a particular job are liable in the manner established by the internal labor regulations of the enterprise and the current legislation of the Russian Federation and the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. 2. Safety requirements before starting work 2.1. Inspect special and sanitary clothing and footwear. If there are shortcomings in the condition of clothes and shoes, eliminate them. Dress your clothes and headgear so that there are no hanging ends. Put your hair under a headdress, fasten your clothes with all buttons. 2.2. Inspect the workplace, floors, walkways, steps, foot grates. If you notice malfunctions, foreign objects, spilled water - everything that can interfere with work, remove or inform the work manager about the need to make repairs. 2.3. Visually check the serviceability of the grounding of electrified equipment, the insulation of wires of electrical appliances and equipment. 2.4. Check the serviceability of the leashes, inspect the animals. In the presence of diseased animals, notify the supervisor or veterinary specialist. Pay attention to the warning signs above the stalls of vigorous or obstinate animals. 2.5. Check gates and doors. They should open easily to full width and close tightly. Bolts, hooks and other locking devices of doors should be easily unlocked. It is not allowed to tie gates and doors with a rope, twist with wire, hammer with nails. 2.6. Check the serviceability and operability of the alarm; availability of fire extinguishers, sand and other fire extinguishing agents. 2.7. Check the availability of water, soap, towels in the washroom. 2.8. Arrange equipment, tools so that it is convenient and safe to work with them. 3. Safety requirements during work Care of cows and young animals 3.1. When performing production operations for feeding, watering, milking, manure removal, observe the established regime for keeping animals and the daily routine, which contributes to the development of a calm and obedient disposition in them. 3.2. Take special care when caring for animals with a yellow sign posted above the stalls or sections that says: "Caution! Cheerful cow" or "Caution! Kicking." 3.3. When approaching animals, be sure to call them in a calm voice. Animals must not be rudely called out, teased, beaten, abruptly pulled back and turned. Rough handling of animals can cause defensive jerks and injury. 3.4. Feed and water the animals only from the side of the feed passage, without entering the pen. This is especially true for sires, cows, and young animals for fattening. 3.5. If it is necessary to enter the machine at a time when animals are there (examination or removal of a sick animal, repair of equipment, fences, etc.), enter only two people, and the belaying worker must have means to scare away animals (electrostack, stick). Machines should be cleaned in the absence of animals or separated by a portable shield. 3.6. When caring for heifers and first-calf heifers, when accustoming them to milking, be careful, as when dealing with obviously obstinate animals. 3.7. When rearing calves using group suction, use cows with a calm disposition as wet nurses. 3.8. Cows and heifers in heat should be handled with care as they are known to be aggressive animals. When approaching an animal, call it in a calm voice. 3.9. When transferring the animal to the arena for artificial insemination or manual mating, walk from the side, holding the animal on a short rein. 3.10. If using frozen semen, inspect the Dewar before inseminating to make sure it is in good condition. A sign of a violation of the tightness of the Dewar vessel is the formation of frost on its surface. 3.10.1. Introduce semen canisters, tweezers, and other instruments into liquid nitrogen slowly to avoid splattering when in contact with relatively warm objects. 3.10.2. When extracting semen doses from liquid nitrogen for 1 - 2 seconds, hold the instrument in the upper part of the neck of the vessel to evaporate the remaining nitrogen. 3.11. During childbirth, strictly follow the instructions and commands of the veterinarian. 3.11.1. Before the start of the birth process, cover the floor of the stall and the manure removal channel with clean bedding, remove slippery places in a timely manner. Do not stay in close proximity to the head and limbs of the cow. 3.11.2. When assisting with pathological childbirth, do not wrap the ends of the rope around your hand. 3.11.3. When correcting misplaced fetal head or limbs, watch the behavior of the cow so that she does not rise abruptly and cause injury. 3.12. When animals enter and exit, doors in rooms, sections, pens should be opened to their full width and secured, while being on the side of the door in a safe place so that animals cannot cause injury. 3.13. During operation of the manure conveyor placed in an open channel, it is forbidden to let animals out of the room and let them in. Caring for sires. Collection and storage of semen 3.14. When serving a sire, firmly remember that he can be dangerous and, if safety requirements are violated, can cause injury, including death. The injury can be inflicted on the head, horns, limbs, tail, torso of the animal. 3.15. Inspect and check the condition and serviceability of the bull’s stall fencing, the reliability of the two-way leash-collar, each chain, carabiners, the condition of the nose ring and its fastening to the horns, the serviceability of the stick-carrier and other equipment and devices used when servicing the bull. The length of the stick-carrier must be at least 2 m. Inspection is carried out from the side of the aft or evacuation passages, without entering the machine. 3.16. Inspect the paths leading the bull to the arena or run area, making sure they are clean, dry, and free of debris. 3.17. There must be safety islands and protective fences on the way of the bulls-producers for taking semen or for a walk. Check their serviceability and reliability. Safety islands must be made of steel pipes with a diameter of 75 - 100 mm, at least 2 m long, installed vertically at a distance of 0,4 m from each other. The lower ends of the pipes must be embedded in concrete to a depth of at least 0,5 m. 3.18. Pay attention to the behavior of the bull. If the bull is in an excited state, shows anxiety - identify the cause and eliminate it. 3.19. The sire bull should be treated kindly, but firmly and confidently. Shy and uncertain handling develops a bull's reflex of chasing a person. Rough handling, violation of the daily routine, mode of use and irregular exercise cause the animal to display a violent temper, the development of a defensive reflex. It is forbidden to shout at the bull, to tease and beat him, to hurt him by sharply turning the nose ring or pulling it, to use odorous substances in the presence of the bull. 3.20. Necessary painful medical procedures should be carried out in sanitary clothing, and then change it to a special one. The bull must be securely fixed. Workers directly caring for a bull should not take part in painful procedures. 3.21. Do not allow the appearance of bulls in the room, and even more so near the stall and in the arena of strangers and animals. 3.22. The accustoming of the bull to new workers should not be done on the days of taking the semen. A new worker or operator (cattleman) after a long break (10 - 12 days or more) should start caring for a bull by feeding him delicious food (concentrates, root crops). 3.23. Before entering the stall of the bull for cleaning, cleaning and washing the animal, transfer it to a short leash, fix its head with an additional chain with a carabiner from the side of the feed passage. In close contact, do not turn your back on the bull. 3.24. Serve a bull with a restless, angry disposition (which should be reminded of by a yellow stencil with a warning inscription posted on the outside of the stall) by putting on eyecups and firmly fixing a wooden plate at the ends of the horns. 3.25. Before taking the bull out of the premises, close the gates of the walking and barnyards, remove all obstacles in the way of the bull and do not allow it to deviate from the established route. Do not allow the counter or crossing movement of the bulls. Do not breed cows at the same time as the bulls. 3.26. Lead the bull out of the stall by the reins with the carabiner hooked to the collar ring, lightly holding the bull by the nose ring with the carrier stick. The bull is removed from the double leash only after the stick-carrier is hooked on the nose ring. 3.27. It is not allowed: to lead a bull without insurance with a stick-carrier; for the occasion attached to the nose ring; be in front of the bull or near his head; take off from the double leash without first engaging the nose ring with the stick-carrier. 3.28. Stud bulls should be walked on special grounds that provide them with active exercise, or, as directed by the work manager, on individual yards on a leash. The bull must be tied with a chain, fastened with a carabiner at one end to the collar ring, and at the other to the bracket or post at the entrance. The length of the chain must be no more than 2,5 m in order to ensure free engagement of the carrier stick on the nose ring without entering the platform. Do not enter the area where there is an unfixed bull. Group walks on the walking area are allowed only for bulls with a calm disposition. 3.29. At the end of the walk, bring the bull into the stall, fix it from the side of the aisle with a double leash, and only after that unhook the rein from the collar and disengage the stick-carrier from engagement with the nose ring. Attach the nose ring to the horns with a strap. 3.30. When a bull becomes aggressive towards a service worker, it is necessary to change the color of the special clothing, or transfer the bull to another place, or change the service worker. 3.31. Before transferring the bull to a new place, you should keep it for several days on a reduced diet, immediately give tasty food in the new place, so that the new environment is associated with the bull getting treats. 3.32. It is necessary to obtain semen from sires in specially equipped premises. When semen is taken on a live stand (the second bull), a technician and two cattlemen serving the bulls must be in the arena, and when semen is taken on a stuffed animal, a technician and one cattleman. Cattlemen must ensure the safe behavior of the bulls. 3.33. The semen-collecting technician should serve only the group of bulls permanently assigned to him. This is necessary to study the characteristics of each bull and an individual approach to them. 3.34. Before taking the seed, inspect the machine, make sure it is in good working order, check the strength and safety of the locking device of the machine. The technician should inspect the artificial vagina for burrs, sharp edges that can hurt the bull and cause aggressiveness. When taking the seed, be quiet and do not allow the presence of unauthorized persons. 3.35. Do not bring more than two bulls into the arena at the same time. 3.36. In preparation for taking the seed (cleaning, washing, wiping, tying an apron), do not lean close to the bull. 3.37. Take the bull out of the arena only after he calms down. 3.38. It is not allowed to conduct a free mating, in which the bull is released into a herd of cows. It is necessary to use only manual mating. At the same time, the bull is taken by the reins and with the help of a carrier stick hooked to the nose ring into the arena equipped with a fixation machine, in which the cow is placed. In the absence of a fixing pen, the cow should be tied to a post. During the cage, the carrier stick is unhooked from the nose ring, holding the bull by the reins. At the end of the mating, the stick-carrier is again hooked on the nose ring and the bull is taken out of the arena, first, and then the cow. 3.39. When freezing semen, use only serviceable Dewars. Free the damaged Dewar vessel from the semen and liquid nitrogen stored in it, and then put it on warming for at least three days in an isolated room with good ventilation. Do not stay in the room where the Dewar vessels are heated. 3.40. Use face shields or goggles when handling liquid nitrogen. Mittens or gloves should come off easily; the legs of trousers or overalls must be worn over boots or tops of boots. 3.41. Do not work with liquid nitrogen alone. 3.42. Fill the Dewar vessel with liquid nitrogen from the transport tank using a flexible metal hose so that its lower end is lowered to the bottom of the vessel. This prevents the jet of liquid nitrogen and the metal hose from being ejected from the neck of the vessel. 3.43. Fill the Dewar vessel with liquid nitrogen from another vessel through a wide metal funnel, avoiding spilling it. 3.44. Pouring liquid nitrogen into Dewar flasks having an internal temperature equal to the ambient air temperature should be done slowly, in small portions with pauses of 5–6 s. Rapid filling of Dewars can result in fluid escaping and cause suffocation or burns. 3.45. In case of accidental spillage of liquid nitrogen, immediately open the door, free the room from people and turn on the ventilation. 3.46. Do not look into the neck of the Dewar while it is being filled. Finish filling the vessel when the first splashes of nitrogen appear on the neck of the vessel. 3.47. Close Dewars only with lids designed for them. 3.48. When carrying and transporting Dewar vessels, do not allow them to fall, hit, or sharp shock, so as not to cause damage to the vessels and the release of liquid nitrogen. 3.49. To prevent the explosion of the Dewar vessel, it is prohibited:
grazing 3.50. Before the start of the grazing period, examine and prepare the grazing areas for animals: clear the pasture from foreign objects (wire, stones, thorny bushes, etc.), fill in or fence pits, old wells. 3.51. Inspect and prepare watering places for animals. The approach to the water should be wide enough, even, gentle, with a slope not exceeding 6%. The shore of the reservoir should not be swampy, swampy and should be protected from collapse. 3.52. When grazing cattle, herds should be formed from animals of the same age and sex. Herds of meat-producing animals may consist of cows-nurses and calves of the dairy period. 3.53. Keeping a sire in a common herd on pastures (except for distant pastures for fattening meat cattle) is prohibited. 3.53.1. In the summer, when cattle are grazing, a sire should be in a bull house or on a leash in a separate machine in a barn. 3.53.2. In the summer camp for the bull-producer, a section or pen must be fenced off, equipped with a feeder and a drinking trough, where the bull can be kept loose or on a leash. To protect from sunlight and precipitation, a canopy should be provided. 3.54. To drive cattle when grazing, use a belt whip. It is not allowed to drive animals with piercing, cutting and other sharp objects, use short sticks, rubber hoses and other improvised means. 3.55. Grazing a herd of cattle should be no less than two. When grazing, use only trained, unobstinate horses. 3.56. When grazing on a horse, before mounting the horse, bridle the horse, check the correctness of the saddle and the strength of the girth. After tightening the girths, adjust the length of the stirrup. For normal driving, the length of the putlish is determined by the length of the outstretched arm. Riding in the saddle is allowed only in shoes that freely fit into the stirrup. 3.57. Take the saddled horse out of the stable on a lead. Do not mount a horse in a stable or any other building, do not enter or enter it on horseback. 3.58. While in the saddle, do not loosen the reins and do not lose control of the horse. It is not allowed to wind the reins around the hand. 3.59. When grazing livestock using an electric fence, observe the following requirements: 3.59.1. Connect the electric fence to a power source with a voltage of no more than 6 V. 3.59.2. Do not touch live electric fence wires, especially in wet or rainy weather. 3.59.3. Under the wire of the electric fence, periodically mow the grass, after turning off the power. 3.59.4. The wire of the electric fence should not come into contact with metal objects that are not part of the fence. 3.59.5. Do not arrange resting places near the electric fence, do not perform any work not related to the maintenance of the installation. 3.59.6. Do not lay near the electric fence of pedestrian and carriageways. They must be at least 1 m away from the fence. 3.59.7. Perform technical inspection and troubleshooting of the electric fence only after turning off the power. 3.60. To avoid a fire in the pasture, do not leave unextinguished fires, do not make a fire in strong winds, near grain crops, hayfields, wooden and other easily combustible objects. Loading and transporting feed 3.61. During the operation of the forager it is prohibited:
3.62. When loading the silage mass with a clamshell loader, install the loader so that it has sufficient stability, provides a wide range of work, maximum filling of the load gripping body, and ease of loading into vehicles. 3.63. Sound a warning signal before starting work. Having approached the loaded forage, set the loader to the working position, put the tractor and the feeder on the brakes, unlock the bulldozer shovel. The jacks and bulldozer shovel must be lowered to the stop on the supporting surface by turning the control knobs to the appropriate position. 3.64. Set the control knobs for lifting and turning the boom and extension, turning the handle for opening and closing the grapple to the appropriate position and bring the grapple to the material to be loaded, grab the load and load it into the vehicle. 3.65. It is forbidden to be within the turning radius of the loader boom, load the loader in excess of its carrying capacity. 3.66. If the silage has not been hauled out of the trench for several days, it should be resumed only after the foreman or other work manager has inspected the trench. Overhanging forage peaks must be brought down with the working body of a loader installed at a safe distance, or with a long sling and similar improvised means, being at the bottom of the trench. 3.67. Unloading of silage (silage) from the tower is allowed to begin only after the end of the fermentation period. 3.68. Remove the sealing film only in an insulating gas mask and under the supervision of another operator. 3.69. Carry out the unloading of feed in the following order: 3.69.1. Make sure there are no people in the tower before unloading the feed. Check the zeroing of the equipment, put up a sign on the starter of the unloader: "Do not turn it on! People are working." 3.69.2. Open the unloading hatches above the mass level and the door on the dome, turn on the pneumatic conveyor fan and ventilate the tower for 1 hour. If there are devices for monitoring the gas composition of the air, follow their readings. 3.69.3. Entering and staying in the tower while lowering the unloader and during its operation is prohibited. 3.69.4. With the pneumatic method of unloading, stay at a safe distance from the falling mass. 3.70. Start loading the feeder from the rear (far) side. If necessary, you can increase the loading area using the lever for turning the handle of the working body. 3.71. When you have finished loading within the range of the boom, raise the dozer shovel and jacks, place the boom in the transport position, and only then move to a new loading location. 3.72. Work performed with a bulldozer shovel should only be carried out with the feeder unhooked. Before starting work, raise the jacks, place the boom and the extension on the support and stand, unlock the bulldozer shovel. 3.73. At night, work is allowed only with sufficient lighting, if it is not enough, you should use a portable lamp. 3.74. At the end of the work, put the loader in the transport position. 3.75. Work related to maintenance, troubleshooting, cleaning from dirt, perform only when the engine is stopped. 3.76. The dismantling of the loader can only be carried out if the boom is turned into a zone close to the longitudinal axis of the machine, with the working body lowered. 3.77. Before loading, inspect the body of the feeder so that there are no people or foreign objects in it by chance. 3.78. When loading the feeder, observe the following safety requirements:
3.79. When freeing a bale of hay or straw from twine or wire, place it in a stable, comfortable position for work. Cut the twine by moving the knife away from you. 3.80. When cutting wire on a bale with needle-nosed pliers, hold the wire on both sides of the cutting point, as loose ends can spring back and cause injury. 3.81. Do not test the sharpness of a knife blade or needle nose pliers with your finger. 3.82. Store the knife and needle-nose pliers for cutting twine and wire in serviceable, durable cases or sheaths in a cabinet or drawer. 3.83. Collect the freed wire or twine and fold it in a certain place. Do not allow pieces of wire to get into the feed, this can lead to injury to hands when removing leftover feed from the feeders, as well as to injury and death of animals. 3.84. Before transporting feed to the place of distribution with a mobile feeder, check the completeness and serviceability of the tractor and the feeder. Check for brake shoes. 3.85. Check the completeness and serviceability of the hitch of the tractor and the feeder. The drawbar of the feeder must have a working adjustable support and a spring to hold the drawbar in a predetermined position. 3.86. The pins for connecting the tractor with the feeder must match the thickness of the holes in the trailer hinges and the tractor fork. 3.87. Make sure that the hoses and tubes of the hydraulic system, the protective cover on the telescopic cardan gear, the safety chain (cable), the guards on the chain drives and on the drive of the longitudinal conveyor are present and in good condition. 3.88. Check the serviceability and operation of the chassis, steering, brake system, electrical equipment and signaling of the unit. 3.89. Install viewing mirrors on the tractor cab brackets so that it is possible to observe the operation of the transverse conveyor from the tractor driver's workplace. 3.90. Aggregate the feeder with the tractor in the following sequence:
3.91. Check the serviceability and reliability of fastening of the protective casing of the telescopic cardan transmission; the main brake cylinder in a special socket on the drawbar of the feeder, and the plug in the socket on the rear wall of the tractor cab. 3.92. Attach only one feeder to the tractor. 3.93. Constantly monitor the serviceability of the hydraulic system and hitching devices of the tractor and the feeder. 3.94. Before driving the machine, give a warning signal and make sure that there are no bystanders in the vicinity. 3.95. Check the operation of the feeder at idle in the following sequence:
3.96. Check the operation of the brake system of the feeder. When braking, both front wheels must be simultaneously blocked. 3.97. Connect the PTO shaft of the feeder to the PTO shaft of the tractor just before dispensing the feed. In all other cases, the cardan shaft must be installed in the transport position. 3.98. When transporting feed by horse-drawn vehicles, harness horses only to serviceable carts, sledges. When driving a horse, follow these steps correctly:
3.99. The place for the rider on the vehicle must have a solid foothold. 3.100. When entering the premises, you must dismount and lead the horse on a leash. Preparation of feed and feed mixtures 3.101. It is not allowed to process grain without cleaning it from metal and other solid impurities (stones, sand, glass, etc.). 3.102. Make sure that the hammers, cutting and other working parts of the machine are securely fastened and properly balanced, that there is lubrication in the friction units (gearboxes, bearings, etc.), and that there are no foreign objects on the feed conveyors, hoppers and feeders. 3.103. Make sure safety guards are in place, people are clear of the rotor plane and discharge throat, sound a warning, and run the crusher at idle to identify hidden deficiencies and correct them. 3.104. In case of increased vibration that occurs due to uneven wear of the hammers or their partial breakage (rotor imbalance), stop the machine immediately and replace the worn parts in compliance with the balancing requirements. 3.105. Push the products hanging in the bunker and getting stuck in the receiving mouth using a pusher with a length of at least 1 m, made of wood or plastic, easily destroyed in case of capture. 3.106. When clogging the cyclone with feed, stop the crusher, check the condition of the sluice gate, clean the gate and cyclone. 3.107. Clean buckets of elevators, magnetic separators and other clogging working parts of transporting devices with the equipment turned off using scrapers to prevent hands, feet, clothes from getting into the working parts' area of operation. 3.108. All adjustments, maintenance and cleaning from clogging of the working parts of the machine should be carried out only with the engine turned off and completely stopped, using measures that protect against accidental start-up of the machine. Hang a sign on the starting device: "Do not turn it on! People are working." 3.109. After the engine reaches nominal speed (determined by ear, by tachometer, ammeter, depending on the design of the machine), turn on the unloading auger of the crusher and slowly open the valve on the feeding hopper or turn on the feeding conveyor. Ensure uniform grain supply with a metering device or by setting the feeder lever to the required position. 3.110. In the process of operation, monitor the serviceability and mode of operation of the machine, aspiration installations, electrical equipment, avoid overheating of the bearings and the machine body, and the appearance of extraneous noise. Do not leave running equipment unattended. 3.111. When stopping the machine, first stop the product supply (turn off the feeder or close the damper), and then, after making sure that the crushed product has stopped flowing, turn off the engine. 3.112. Remember: the machines have an inertial motion and until they are completely stopped, it is impossible to open the hatches of the sluice gates, the cover of the crushing chamber, tighten the threaded connections and perform any kind of maintenance. 3.113. In the process of mechanical release of grain and other bulk materials from bunkers, silos and warehouses, it is forbidden for anyone to enter the storage facilities. Bunkers, silos, hatches must be permanently closed with lids, and bunker storage tanks - with protective gratings. Inspection hatches must be equipped with protective gratings. Conveyor pits must be fenced. 3.114. The descent into bunkers, silos and storages with a depth of more than 2 m should be carried out only with a work permit with the participation of the work manager and the insured person using a descent winch, a safety belt and, if necessary (high dust content, the presence of a rotting product, etc.) a hose gas mask . Loading the container with the product during the descent and the presence of a person there should be excluded. 3.115. Do not smoke or use open fire in the room where the grinder, raw materials and processed products are located. 3.116. In case of high noise level and prolonged work (more than 0,5 h), use hearing protection - earplugs, antiphons, and in case of increased dusting - goggles and respirators. 3.117. At each stop of the equipment, remove flour dust from the machine, equipment. Periodically perform wet cleaning and ventilation of the room, humidify the air with water from a spray bottle or spray to avoid creating an explosive concentration of dust in the air. 3.118. When chopping stalked feed, set the chopper's product pipeline and the visor to the desired position, excluding feed spreading and the possibility of injury to workers. 3.119. Turn the grinder into operation by pressing the "Start" button. At the same time, the pre-start alarm should turn on, and then the chopper electric motor will start. 3.120. Adjust the feed of the crushed product to the feed conveyor with the hopper gate according to the rated load of the electric motor in accordance with the operating instructions for the machine. 3.121. Feed the feed evenly for chopping. Make sure that stones, sticks and other foreign objects do not get into the chopper along with the feed. 3.122. While the grinder is in operation, do not stand in front of the ejection of the mass, as a solid object may fall into it and cause injury. 3.123. In the process of work, monitor the implementation of the technological process, do not allow the deflectors to clog. 3.124. When clogging, push the processed feed into the opening of the receiving hopper of a running machine only with a pusher with a handle at least 1 m long. 3.125. At the end of the work, wait for the complete cleaning of the grinding chamber from the product and turn off the grinder. Feed mixing 3.126. Before turning on the mixer, make sure that there are no foreign objects in the mixer hopper and on the unloading and loading conveyors. Keep a close eye on this as you work. 3.127. Do not operate mixer with V-belt guard removed and chaincase doors open. 3.128. Before loading feed into the mixer, make sure that the gate of the unloading conveyor is closed. 3.129. Load pre-cut feed into the mixer with a cutting length of up to 3 cm. The feed should be fed evenly, there should be no foreign inclusions in them - stones, wire, etc. 3.130. The degree of loading should be such that during the mixing process at both ends of the mixer hopper there is an empty space for mixing the mass. Overfilling the hopper can cause damage and create an emergency. 3.131. After loading the mixer tank with feed, close the loading door tightly. 3.132. The mixer is started by a switch located on the end wall. 3.133. To unload the feed mixture from the mixer hopper, use the handle to open the unloading gate. At the same time, the unloading conveyor automatically turns on and the feed mixture is fed to the inclined conveyor and unloaded into the vehicle. 3.134. Adjust the unloading capacity with a damper. Correct stuck food only with a wooden scraper. It is forbidden to use for this purpose a pitchfork, a shovel, other improvised metal objects. 3.135. Close the damper after unloading the feed mixture. The mixer is stopped by a switch located on the end wall and by turning off the power supply to the mixer in the control cabinet. 3.136. Do not cycle the mixer motor on and off repeatedly during mixing and unloading. This overloads the power supply and may cause an accident. 3.137. When cutting the safety pin, the mixer hopper must be unloaded manually. 3.138. When working in winter conditions, manually rotate the unloading conveyor before starting the mixer. If the conveyor belt does not turn, tear off the frozen scrapers and chain from the chute. 3.139. At the end of the shift, run the mixer and conveyors idly, freeing them from feed residues. Leave the unloading window open in winter to avoid freezing. 3.140. Perform maintenance, adjustment and troubleshooting only with the engine disconnected from the mains. A sign should be hung on the switching device with the inscription: "Do not turn it on! People are working." Preparation of milk replacer (WMS) 3.141. When preparing the milk replacer at the plant type AZM-0,8, fill the tank of the plant with cold water. Determine the amount of water filled by the level indicator. 3.142. By pressing the power button, start the mixer and pour mixed feed into the mixer tank, for which open the damper and turn on the electric motor of the loading auger. 3.143. After loading is complete, turn off the auger and close the damper. The stirrer remains switched on. 3.144. Steam supply is carried out with tightly closed neck and hatch covers. Before supplying steam, make sure that the seals between the lid and the body of the unit are present and in good condition and that the device for easy opening is working. 3.145. To supply steam to the mixer, open the steam supply valve and use the thermometer to control the heating temperature of the mixture. The temperature should not exceed 85 - 90 °C. 3.146. When the set temperature is reached, close the steam valve and leave the mixture to malt. During malting every 10 - 15 minutes. turn on the agitator to mix the mixture. 3.147. To cool the mass, cold water is sent to the mixer jacket. Premixes are added to the cooled mass and mixed with a stirrer. 3.148. Before opening the cover of the unit, close the steam inlet valve, clean the hole in the condensate drain, open the valve and make sure that the condensate comes out without pressure. 3.149. When draining condensate, make sure that there are no people in front of the drain hole. 3.150. Open the lid carefully, while standing on the side in which it opens. 3.151. When using hot water for the preparation of milk replacer, beware of splashing it, for which constantly monitor the tightness of the connection of pipes and hoses, and the serviceability of the taps. 3.152. When loading and servicing the top of the milk replacer brewer, use a ladder with railings or a stable stand. 3.153. When filling drinkers or containers with a filling nozzle, be careful not to splash milk replacer, which can lead to slippery areas on the floor. Therefore, sprinkle the spilled mixture with sand or sawdust and clean it up immediately. 3.154. After the finished product is dispensed, wash the unit first with cold water, then with a cleaning solution and rinse with warm water. Carry out the washing operations of the unit mechanically, turning on the agitator for a short time. Feed distribution 3.155. When entering and leaving the livestock building, make sure that the gate is fully open and fixed, there are no people, animals, foreign objects in the way of movement. 3.156. When dispensing feed with a stationary feeder, before switching on the feed line or any part of it from the control panel, give a warning sound or light signal. 3.157. Do not overload stationary feed-distributing installations, as well as foreign objects (stones, fragments of boards, metal objects, etc.), tools, inventory that can lead to breakdowns and a traumatic situation. 3.158. When servicing open stern conveyors, cross over them using walkways. 3.159. When clogging cable-washer, auger, scraper feed-distributing installations with feed, perform cleaning with the electric drive turned off using scrapers with a wooden or plastic handle. Post a sign on the starting device: "Do not turn it on! People are working." 3.160. In order to eliminate the dustiness of the air environment of the working area during the distribution of bulk feed, constantly monitor the tightness of the equipment and the efficiency of ventilation. 3.161. When transporting feed by horse-drawn transport, distribute feed when the transport has completely stopped, being on the floor. 3.162. When transporting feed using a handcart, observe the following sequence of operations and safety requirements:
Watering livestock 3.163. Drinkers should provide free watering for livestock at any time. If there is a shortage of water or drinking bowls, in order to avoid crowding of animals, organize a watering place one by one. 3.164. Keep drinkers in good condition, do not allow water to leak. 3.165. When cleaning drinking bowls from contaminants that have got into them, use scrapers. 3.166. When watering livestock from automatic drinking bowls or watering troughs on walking or feeding grounds in winter, regularly break off the ice. 3.167. Fill drinking troughs with water in the absence of animals. If it is necessary to fill the troughs with water in the presence of animals, do not stand in the way of their movement. 3.168. The mobile drinker at the watering place must be slowed down. 3.169. Wells with any method of raising water must be fenced and covered with covers. Break off the ice around them regularly, sprinkle the approaches to the well with sand. 3.170. The place of water intake from surface water sources should be wide enough for the entrance and turn of the vehicle, aggregated with the water dispenser; the entrance to the water should be smooth, gentle, with a slope of no more than 12 °; the shore of the reservoir must be protected from collapse. 3.171. When feeding milk or milk substitutes to calves on a watering machine or from feeders equipped with bucket holders, avoid splashing the product to avoid slippery spots. milking cows 3.172. Before starting milking, check the serviceability and correct assembly of the milking machines. 3.173. When milking on milking machines, check the serviceability of the mechanism for opening the doors of milking machines, protective fences, and signaling devices. 3.174. Inspect the milk pipeline: glass pipes should not have chips, cracks. 3.175. Milking should take place in a calm environment. Treat animals calmly and confidently. Rough handling, unaccustomed noise disturb cows and can cause injury. 3.176. Wash your hands with warm water and soap up to the elbow and dry them with a clean individual towel, put on sanitary clothing (robe and scarf). 3.177. Prepare the cluster for safe milking:
3.178. Check and, if necessary, adjust the amount of vacuum in the vacuum line. 3.179. Connect the milking cluster to the vacuum line (the milk hose clamp must be closed) and check that the lid is firmly attached to the bucket. 3.180. Check the operation of the pulsator. The pulsator must work clearly, with a frequency of pulsations according to the technical characteristics of the milking machine. 3.181. Open the milk hose clamp, check that there are no air leaks through the milk glasses. Check for ripples in the liner. 3.182. Prepare the udder for milking: inspect it, wash the udder and teats with warm water (40 - 45 °C) from a sprayer or bucket, dry with a towel and massage. The preparation of the udder for milking should not cause pain in the animal. If there are cracked nipples, lubricate with petroleum jelly or antiseptic ointment. If mastitis is present, milk with extreme caution or use a catheter into a separate bucket. 3.183. Milk the first stream of milk from each nipple by hand into a special mug with a black plate at the bottom and check for milk clots and blood impurities. Such milk should be drained into a separate bowl. 3.184. In the cold season at low temperatures, warm the teat cups in warm water. 3.185. When starting milking, put the milking bucket on the side, closer to the front legs of the cow. Connect the machine to the vacuum line and open the vacuum cock. 3.186. When attaching teat cups, beware of hitting with hind limbs and tail. Be especially careful when milking animals that are known to be restless and have warning signs attached to their stalls. 3.187. At the end of milking, remove the cups, for which, supporting the collector with one hand, close the milk hose clamp with the other and remove the milking machine. 3.188. For safe transportation of the milking bucket with the machine, hang the collector on the hook of the milking bucket, and roll the hose into a coil and place it under the handle of the milking bucket. 3.189. Use a special trolley to transport flasks of milk. When carrying by hand, carry the flask with two people, without violating the rules for carrying weights manually (Appendix 6). 3.190. During milking of cows, it is not allowed to distribute feed, turn on the manure conveyor. 3.191. When machine milking cows, use safe equipment troubleshooting techniques: 3.191.1. The vacuum value in the vacuum line is lower than the setting value: eliminate air leakage, for which make sure that the milking machines are correctly connected to the vacuum line and the udder of the cows, see if there are open milk taps in the barn and dairy. If the measures taken are not sufficient, report the problem to a locksmith. 3.191.2. Pulsator does not work or works intermittently:
3.191.3. Noise of sucked air in one of the milking machines:
3.191.4. The milking cluster milks slowly:
3.191.5. The viewing cone falls out during operation - cut the liner to the size in accordance with the mark on the mounting rod. 3.191.6. There is no air leakage into the milking machine collector. The milk hose and manifold are completely filled with stagnant milk - check the condition and cleanliness of the surfaces of the membrane, valve and valve hole. Replace or clean them if necessary. 3.191.7. Washer pulsator does not work or works intermittently:
3.191.8. The pulse booster does not work:
3.191.9. Feeder conveyor chain jamming:
3.192. At the end of machine milking, empty the milk line and the primary treatment system from milk residues, for which follow these steps:
3.193. Depending on the type of milking machine, flush the milking machines, milk pipeline, milk equipment using safe methods and techniques in accordance with the requirements set out in the operating instructions. 3.194. When manually milking cows, be careful, taking into account the possibility of injury to the limbs, tail, horns, pressing against partitions, fences. 3.195. When milking by hand, use stools suitable for height, leg and tail restraints. 3.196. When carrying sanitary udder wash, do not spill it. To avoid water getting into the tops of the boots, do not tuck special clothing (trousers, overalls) into the tops, but let it over. 3.197. After milking each cow, wash your hands with soap or rinse with a disinfectant solution. 3.198. When carrying out control milkings and other animal and veterinary measures, view the numbers of cows only from the side of the feed aisle. Do not lean close to the cow's head when viewing ear numbers, collar numbers. Primary milk processing and milk storage 3.199. Primary milk processing includes:
3.200. At the site of primary milk processing, beware of electric shock, burns from steam, hot water, chemicals (acids, alkalis), injury from moving machines and moving parts of mechanisms and equipment. 3.201. When operating milk centrifugal pumps, use safe maintenance and troubleshooting techniques: 3.201.1. Make sure that there are no foreign objects on the surface of the pump and motor. 3.201.2. Make sure that the milk lines on the suction and discharge sides are assembled correctly, and that the taps are correctly positioned and turned off. 3.201.3. Let the pump idle for a short time and, if there are no deviations in its operation and the electric motor, start pumping milk. 3.201.4. During operation of the pump, periodically check the heating of the electric motor. In case of overheating of the electric motor, noise, knocking, stop the pump until the cause of the malfunction is eliminated. 3.201.5. Troubleshooting, removing the coupling guard, opening the cover, tightening the stuffing box should be done when the pump is completely stopped. 3.201.6. After stopping the milk supply, turn off the electric motor, disassemble the pump and rinse the pump and milk lines thoroughly. 3.202. The procedure for the safe operation of plate milk coolers should be as follows: 3.202.1. Check the condition of the sealing rubber gaskets, the connection of the milk and brine pipelines. 3.202.2. Before start-up, run water through the entire installation system and make sure it is tight. 3.202.3. During operation, monitor the cooling temperature. The brine section must not be frozen. 3.202.4. If the milk supply stops, immediately stop the brine supply. 3.202.5. Turn off the milk cooler in the following sequence: shut off the brine supply, stop the milk and water pumps, disconnect the brine pipeline, flush and clean the installation. 3.203. When operating pasteurization-cooling units, the sequence of work should be as follows: 3.203.1. Check the presence and condition of the rubber seals of the lids, the presence of a seal on the pressure gauge and a red line on the dial indicating the maximum allowable steam pressure. 3.203.2. Close the lid tightly, connect the milk, water and steam lines. 3.203.3. Before starting the unit, turn on the milk purifier and, when its rotation speed reaches the required number of revolutions, pass water through the system, while turning on the milk pump. 3.203.4. By the time the milk is put into the unit, the separator-milk cleaner must operate at full speed in order to prevent milk from overflowing from the drum into the bowl of the bed. 3.203.5. After rinsing with water, turn on the hot water and steam supply and circulate the milk in manual mode until the required pasteurization temperature is reached, then switch the pasteurized milk flow from circulation to direct direction - to a container or to automatic mode. 3.203.6. Open steam valves gradually, as if the glands are loosely stuffed, steam can break through and burn your hands. Do not operate a pasteurizer that emits milk and steam. 3.203.7. During work:
3.203.8. During operation of the pasteurizer it is not allowed:
3.203.9. Observe the following procedure for stopping the installation:
3.204. When servicing milk tanks: 3.204.1. Check before filling:
3.204.2. To illuminate the inner surface of the container, use portable lamps with a voltage not higher than 12 V. 3.204.3. When inspecting the upper parts of the tank, do not stand on the pipelines, use steps or stepladders. 3.204.4. Upon completion of work, make sure that the tank is completely empty of the product, and proceed to wash it. The washing procedure should be as follows:
3.204.5. To prevent the supply of steam, cleaning solutions, water to the container by other persons, turn off the taps and valves of the pipelines, turn off the pumps and electric motors and post a sign: "Do not turn on! People are working." 3.204.6. The containers should be washed by hand with the valves of the pipelines closed and the electric motor turned off. Signs should be posted on the cranes and the starting device of the electric motor: "Do not turn on! People are working." 3.205. Use safe work practices when operating the centrifuge: 3.205.1. Load the laboratory centrifuge disk with butyrometers symmetrically in the following quantity: 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12, 14, 15, 16, 18, 20, 21, 22, 24. To load a number of butyrometers that cannot be arranged symmetrically, an additional butyrometer of the same mass should be placed. 3.205.2. Close the butyrometer caps carefully. When screwing the cork, shaking and counting the fat on the butyrometer scale, be sure to wrap the butyrometer with a towel, keep it from yourself and others at arm's length and always above the dishes (basin) with water. Hold the butyrometer by the widest part, as the junction of the body with the graduated tube may break and cause injury to the hands. 3.205.3. Do not make any repairs, lubrication, cleaning or inspection while the centrifuge bowl is rotating. 3.205.4. Do not allow the number of revolutions of the centrifuge drum to be higher than the passport ones. 3.205.5. If the centrifuge is running with increased vibration or with a change in even sound, stop the operation and check the correct installation of the butyrometers, and then the serviceability of the bearings, screw pair, spring. 3.205.6. Do not touch the disc until the centrifuge has come to a complete stop. 3.205.7. Do not brake the drum with foreign objects or in other ways, except for those provided for in the instructions. If it is necessary to speed up the stop of the centrifuge disk after the time relay is turned off, press the "brake" button and keep it pressed until the disk stops completely. 3.205.8. It is possible to open the centrifuge lid only after making sure that the electric motor has automatically switched off, the signal lamp on the control panel has gone out and the centrifuge has stopped. 3.206. When steaming flasks, the procedure should be as follows: 3.206.1. Check:
3.206.2. Turn on the exhaust fan to suck out the steam. Hold the flask to be steamed on the surface of the flask steamer bowl with a wooden block. 3.206.3. Do not press the pedals that open the steam or water valves unless there is a flask on the surface of the flask steamer bowl, pressed with a wooden block. 3.206.4. Remove the steamed flask wearing gloves and only after the steam valve pedal is released. 3.206.5. Stop the flask steamer in the following order:
3.207. When storing milk in refrigeration units, do not allow freon leakage. With a content of 30% freon in the air, death can occur in a person, contact with liquid freon in the eyes leads to blindness, and on the skin - to frostbite. 3.207.1. Having started work, make a visual inspection of the refrigeration equipment, check its tightness. The operation of refrigeration equipment with faulty automatic safety devices is not allowed. 3.207.2. Determine the places of ammonia leakage using special chemical paper indicators, freon - electronic halide leak detectors. 3.207.3. Do not mechanically remove frost from cooling radiators - only sweeping frost is allowed. 3.207.4. In the room where the refrigeration units are located, smoking, the use of open fire is not allowed. 3.208. Before starting the compressor, check for oil in the crankcase. 3.208.1. Turn on the water that enters the jackets of block cylinders. 3.208.2. To enable the compressor to start, open the bypass valve between the suction and discharge manifolds and turn on the motor. 3.208.3. When normal speed is reached, fully open the discharge valve, then carefully open the suction valve to prevent fluid from entering the cylinder. During normal operation of the compressor, the suction manifold and valve are covered with frost. 3.208.4. Clean the oil pump filter at least once per shift by turning the handle. If there is a shortage of oil, replenish it using a pump or through a rubber hose, connected at one end to an oil valve, and lowered into a vessel with clean oil at the other. At the same time, first reduce the pressure in the crankcase to a pressure below atmospheric pressure, stop the supply of liquid ammonia to the evaporator system and close the suction shut-off valve of the compressor. 3.208.5. After replenishing the crankcase with oil, close the oil valve, carefully open the compressor suction shut-off valve and restore liquid ammonia to the evaporative system. 3.209. When stopping the compressor, first close the appropriate control valve, then the compressor suction shut-off valve and stop the motor. 3.210. After the flywheel has stopped turning, close the compressor discharge valve, stop the cooling water supply to the condenser (if no other compressors are running) and to the compressor jackets. 3.211. When servicing heat exchangers, monitor the refrigerant and water (condenser) or refrigerant (evaporator) inlet and outlet temperatures, the refrigerant or refrigerant level, and the temperature of the product to be cooled. Preparation and use of cleaning and disinfecting solutions 3.212. Preparation of washing and disinfecting solutions should be carried out in designated rooms or places equipped with general and local ventilation. 3.213. When working with solutions of acids and alkalis of medium concentration (sulfuric acid - up to 50%, nitric and hydrochloric acids - up to 20%, alkali - up to 10%), use rubber technical gloves. 3.214. Dilution of concentrated acids and alkalis is carried out in a filtering gas mask with box "B". 3.215. Preparation of bleach solutions should be carried out in a gas mask with a COX box. 3.216. When preparing cleaning and disinfecting solutions, use hermetic goggles with anti-fogging NP films and rubber gloves. 3.217. Dissolve caustic alkalis by adding small pieces to the water with continuous stirring. Take pieces of alkali only with tongs. 3.218. Break large pieces of caustic alkalis into small ones in a specially designated place, having previously covered them with a dense cloth and put on goggles, rubber gloves and an apron. 3.219. Add concentrated detergent solutions to the container only after filling it with water. 3.220. Transfer detergent and disinfectant solutions in containers with a lid, filling their volume to no more than 90%. 3.221. Store and transport glass containers with aggressive liquids in sturdy double-handled chip baskets. 3.222. Carry out washing and disinfection of technological equipment, inventory, containers and vehicles in accordance with the Sanitary and Veterinary Rules for dairy farms of collective farms, state farms and subsidiary farms (approved by the Main Directorate of Veterinary Medicine of the USSR Ministry of Agriculture on 26.06.85). Manure removal Manure cleaning with scraper and scraper electrified installations 3.223. Inspect the manure channel to make sure there are no foreign objects in it. 3.224. Check the presence and serviceability of the transitional bridges through the manure channels, as well as the presence and serviceability of the fences of the pits of the manure channels and the rotary devices of the installation, drive stations. 3.225. Check the grounding of all non-current-carrying metal parts, the presence of protective fences and devices. Make sure they are secure. If necessary, correct the malfunctions or report them to the work manager. 3.226. Check the operation of the scrapers, chain or rope of the machine. 3.227. If the channels are blocked by gratings, check the reliability of the overlap, make sure that they are strong and that there are no sharp or protruding parts on them. 3.228. Make sure there is a vehicle under the tilt chute boom. 3.229. Check the good condition of the inventory (shovels, scrapers, scrapers). They should be tightly planted on the handle. The handles must be smooth, without burrs, cracks and knots. 3.230. Before switching on the conveyor, remove the walkways over the horizontal conveyor, make sure that the animals are tethered and standing still and that there is no danger to the workers present. 3.231. Check the operation of the conveyor (scraper unit) at idle. To do this, give a prearranged signal warning about the start of the installation, turn on the conveyor (scraper installation) and make sure that there is no extraneous noise, vibration, or burning smell. 3.232. In cold weather, before starting the conveyor, make sure that the chain and scrapers are not frozen to the channel chute. 3.233. Do not turn on the unit during the movement of animals, milking, veterinary and sanitary activities. 3.234. During the operation of the conveyor, clean the stalls with scrapers with handles of sufficient length, while being out of the zone of action of the working bodies of the installation. Avoid touching or hitting scrapers with animals. 3.235. Observe the following requirements when operating the manure handling equipment:
3.236. During the operation of the scraper, make sure that the slider does not reach the rotary device. 3.237. Check the tension of the conveyor chain. The chain is considered normally tensioned if it calmly, without jerks, comes off the drive sprocket. 3.238. Periodically, as it wears out, pull out the scraper. After complete wear of one side of the scraper, it must be turned 180 °. 3.239. Before finishing work, wash the turning and tensioning devices and the working parts of the conveyor (scraper) with water. 3.240. At the end of work, first turn off the horizontal conveyor, then the inclined conveyor. 3.241. In the cold season, after turning off the horizontal conveyor, the inclined conveyor should run idle for at least 2-3 minutes. until the tray is completely cleaned so that the chain and scrapers do not freeze. 3.242. Perform all maintenance and repair work on the unit with the general switch and knife switch turned off. A sign is posted on the switch: "Do not turn it on! People are working." 3.243. When finished, check:
3.244. Use special tools to disconnect and connect the conveyor chain. Do not disconnect the conveyor chain if the container with the load is not removed from the tensioner, the scraper if the tie screws are not removed. 3.245. Maintenance of the inclined conveyor at a height is carried out using scaffolds with a width of at least 1 m, having a solid flooring and enclosing railings with a height of at least 1 m, or stairs. 3.246. Do not leave a running unit unattended. 3.247. In the cold season, cover the opening of the inclined conveyor with a shield or an apron made of heavy fabric to prevent freezing of the chain and scrapers. 3.248. Use sawdust, crushed peat or straw as bedding. Do not allow long-stalk feed residues or bedding material to enter the manure channel. Transportation of manure to manure storage 3.249. When transporting manure to a manure storage using a piston pump (UTN-10 unit), before turning on the pump, check:
3.250. During operation of the unit, monitor the oil pressure in the hydraulic system according to the pressure gauge. 3.251. If at the moment of switching the hydraulic distributors the pressure gauge shows a sharp fluctuation of the oil pressure in the hydraulic system, it is necessary to adjust the switching of the hydraulic distributors with stops. 3.252. All repairs, lubrication, adjustments, etc. carry out with the unit turned off and de-energized. Post a sign on the starting device: "Do not turn it on! People are working." 3.253. When using a tractor with a bulldozer linkage for cleaning and transporting manure, the speed of the tractor inside the building and on walking areas should not exceed the speed of a pedestrian. 3.254. It is forbidden to operate the tractor indoors with a defective spark arrester. 3.255. Do not leave a working tractor with a bulldozer attachment unattended in the livestock building and near the gate, in the path of the animals. 3.256. When loading manure from the overpass, make sure that the bulldozer attachment blade does not extend beyond the edge of the overpass. 3.257. During loading, the driver of the vehicle must leave the cab and wait for the signal about the end of loading outside the working area. Work in wells, closed containers 3.258. Before performing work in wells, slurry collectors, manure collectors, take a briefing on safety measures at the workplace and obtain a work permit for performing work of increased danger. The work order should indicate the content of the work, safety measures during their implementation, the start and end time of work, the composition of the team and data on the briefing on labor protection with the obligatory signature of the workers. 3.259. A team working in a well, a closed tank, must consist of at least three workers: one - to work in the well (tank), two - on the surface, one of them is engaged in insurance working in the well (tank), the second passes the necessary tools. 3.260. In the case of several people descending into a well (closed container), each of them must be insured by an employee on the surface. The surface worker must not perform other work. 3.261. Fence the well or container and install safety signs at a distance of at least 5 m from the well or container, install tripods at night and attach signal red lights to them. 3.262. Check the availability of foam fire extinguishers, sand and other fire extinguishing agents at the work site. 3.263. Before descending into the well (closed container), make sure that there are no harmful gases in them, for which use the safety gas detector GSB-3M "Jean-gas" or the LBVK lamp. 3.264. The gas found in the well (or closed container) must be removed. To remove the gas, use:
3.265. Check the complete absence of gas again with the GSB-3M "Jin-gas" gas detector or the LBVK lamp and only after that go down into the well or a closed container. 3.266. When descending into a well (closed container) to a depth of up to 3 m, use a safety belt with shoulder straps (type B and D). With a greater depth of the well, a safety belt with shoulder and hip straps (type D) should be used. 3.267. Tie the descent rope securely and firmly to the safety belt. The rope must be tested for breaking and have a safety margin. The length of the rope should be 3 m more than the depth of the well (tank). While working in the well, periodically use a rope to signal a worker on the surface. 3.268. If the gas cannot be completely removed from a well or a closed container, it is allowed to descend into them only in a hose gas mask (types PSh-1 and PSh-2) with a hose extending 2 m away from the manhole. 3.269. It is allowed to work in a well or a closed container in a hose gas mask continuously for no more than 15 minutes, after which rest on the surface with the gas mask removed for at least 20 minutes must follow. 3.270. If the descent is made along the brackets, then first make sure that they are intact and strong. 3.271. To illuminate a well or a closed container, use only rechargeable lamps with a voltage of not more than 12 V or miner's lamps. Lanterns and lamps must be sealed. Open flames are not permitted. 3.272. Portable ladders used for descent must be made of non-sparking materials. Ladders must have shoes or fittings to securely fasten them to the bottom of the well or tank. 3.273. To avoid an explosion, do not perform operations and work that can cause sparks. 3.274. Workers on the surface should not approach the well, containers with burning cigarettes or open flames. Transportation of cattle 3.275. Workers performing work on loading and transporting sires must undergo an extraordinary briefing on labor protection and obtain a work permit. 3.276. Getting started, inspect the passages, walkways through the manure removal channels. They must be free from foreign objects and serviceable. 3.277. Check gates and doors. They should open freely, they should not have protruding nails, wire, fragments of boards and other objects that can cause injury to people and animals. 3.278. Make sure that the decks and guards of the loading ramps and ladders are in good condition. 3.279. Before entering a fattening section equipped with electric stops, turn them off and put a sign on the switch: "Do not turn on! People are working." 3.280. It is forbidden to enter the section to animals one at a time and without self-defense equipment (electrostack, stick, whip). 3.281. Before loading, large animals with an evil disposition should be injected with tranquilizers, put on eyecups that limit the field of vision, and attach wooden plates to the horns. 3.282. Not allowed during loading (unloading):
3.283. When driving livestock, take precautions: do not stand in the way of traffic and in the doorways of sections and premises, do not go into the middle of the herd, beware of vigorous and aggressive animals. 3.284. Start loading cattle from the sections or stalls closest to the exit. Calves, heifers can be sent to the loading area in groups, and bulls, cows and fattening bulls - one at a time. 3.285. When loading (unloading) a sire, use a collar with two reins and a carrier stick hooked on the nose ring. The bull must be led by two cattlemen. Tying and untying the bull in the vehicle should be done remotely, from the side of the cab. 3.286. Loading (unloading) of livestock should be carried out only in the daytime or with sufficient artificial lighting. 3.287. When transporting livestock, it is not allowed:
3.288. When loading and unloading livestock, stay in the safety zone of the ladder. Heating and irradiation of young animals 3.289. When servicing installations intended for local heating with infrared radiation and ultraviolet irradiation of calves, know and follow the requirements of the operating instructions, safety precautions and fire safety, be able to apply first aid techniques in case of electric shock, burns. 3.290. Observe the mode of heating and irradiation of calves established by the operating instructions. Exceeding the dose of heating and radiation can cause burns to unprotected parts of the body in workers servicing animals. 3.291. When using UV lamps for a long time during operation or immediately after irradiation, carefully ventilate or ventilate the room to prevent the accumulation of ozone and nitrogen oxides. 3.292. Infrared lamps should be installed at a height of at least 1,6 - 1,7 m from the floor and at least 0,6 m from any combustible surfaces (wooden fences, bedding). 3.293. When adjusting the height of the suspension, the irradiator must be disconnected from the mains. 3.294. Do not carry out unauthorized maintenance and repair work on the unit. Report all malfunctions to the supervisor or electrician and request immediate troubleshooting. 3.295. Do not clean the premises, machines, sections, distribute feed during the operation of the lamps, especially ultraviolet radiation. 3.296. If it is necessary to be present in the room during the operation of ultraviolet and infrared radiation lamps, use safety glasses with light filters B-1, B-2, B-3. Special clothing must be fastened with all buttons. 3.297. During operation, be especially careful with UV lamps containing mercury, which, if the lamp is damaged, can enter the environment and cause poisoning of workers or animals. 3.298. In the event of a breakdown of ultraviolet radiation lamps, collect spilled mercury with a rubber bulb. Wash the place where the lamp broke with a XNUMX% solution of potassium permanganate. Carrying out veterinary and sanitary measures 3.299. When carrying out veterinary and sanitary measures, servicing sick animals, put on sanitary clothing and shoes - a cotton robe, a scarf or cap and rubber boots, and when caring for infectious animals, an additional rubber apron and rubber gloves. Wearing sanitary clothing outside production facilities or areas where animals are handled is not allowed. 3.300. Eating, drinking water and smoking while working at enterprises that are unfavorable for infectious diseases are prohibited. When serving sick animals, do not touch your face with your hands, wipe your mouth, nose with them. 3.301. In the event of an abortion in a cow, notify the supervisor or veterinarian, remove the fetus with the placenta in a tightly packed, liquid-tight box, and remove the litter and burn. 3.302. The tool in contact with the infected material is subjected to sterilization or treatment with antiseptic solutions. 3.303. Inventory, fixation machines and other equipment after the recovery of the animal or at the end of quarantine, clean, rinse with a hot solution of creosol preparations, and then treat with a 5% solution of carbolic acid, creolin or other disinfectants as directed by a veterinarian. 3.304. When carrying out veterinary measures, the animal must be fixed. When carrying out small, painless operations, fixation is carried out by squeezing the nasal septum with special forceps or fingers. To do this, you need to stand in front of the right shoulder joint of the animal, take the top of the right horn of the animal with your left hand, and grab the nasal septum with the fingers of your right hand and squeeze it. Stud bulls are held by the nose ring. 3.305. Head fixation is carried out by holding the nasal septum or by tying the animal to a pole with a rope. 3.306. To limit the mobility of the animal, the following methods can be used:
3.306.1. The thoracic limb is fixed with a soft rope twist applied to the forearm, or by pulling the metacarpus to the forearm with a sliding figure-of-eight loop. When examining and clearing the hooves, the limb is lifted with a rope (belt) attached to the lower end of the metacarpus and thrown over the withers. 3.306.2. The pelvic limb is fixed with a pole and a soft rope. To do this, above the hock joint, a pole is fixed with a sliding loop and the two lift the limb by its ends and take it back. 3.307. When carrying out painful procedures, it is necessary to use fixation machines. In the absence of fixation machines for fixation in the supine position, it is necessary to use physical or medical knocking down of animals. 3.308. Rectal examination of cows should be carried out only in machines. Conducting research through partitions in machines, as well as unfixed animals is not allowed. 3.309. When disinfecting premises, processing animals, solutions should be prepared in rooms equipped with general or local ventilation. To open barrels, cut bags, use a tool designed for this purpose. 3.310. Prepare baits for rodents with anticoagulants and acute toxic agents should be in a well-ventilated area, fume hood or outdoors in calm weather. Baits should be placed in bait boxes and placed in places inaccessible to animals and remote from the paths of movement of workers. 3.311. When using drugs that irritate the mucous membranes of the eyes and respiratory organs, work in filtering gas masks with a brand A box, when using alkalis and acids - in goggles of brand PO-3. Use rubber gloves to protect your hands. 3.312. Before starting sanitization, turn off the equipment and lighting from the power supply, hang signs on the switches: "Do not turn it on! People are working." 3.313. Spray aerosols indoors from the windward side through a window or a hole in the wall, avoiding dispersion of the drug outside the treated room. 3.314. When disinfecting the territory, premises, do not allow the solution jet to hit the bare wires of overhead power lines. 3.315. When working with equipment and machines that create pressure, constantly monitor the readings of the pressure gauge, do not allow the pressure to rise above that indicated in the passport. 3.316. When operating installations with an internal combustion engine, ensure that exhaust gases are removed from the room. 3.317. Work on the introduction of powdered disinfectants into the soil should be carried out only in calm weather or with low air movement, starting from the leeward end of the treated area. 3.318. Do not enter an area treated with poisonous and potent substances. Work is resumed only with the permission of the veterinary specialist responsible for disinfection. 3.319. Poisonous substances spilled on the floor should be immediately removed by neutralization or sprinkled with sand, sawdust and removed. 4. Safety requirements in an emergency 4.1. When an electrical voltage appears on the metal parts of machines and equipment, fences of stalls, sections, etc. stop work immediately, move out of the area of electrical current and notify an electrician or supervisor. 4.2. In the event of a sudden power outage, notify the electrician or the work manager and take measures to prevent sudden switching on of electrical installations: turn off the "Start" buttons, disconnect the equipment from the mains with a knife switch. 4.3. Do not troubleshoot electrical wiring or electrical equipment yourself. In the event of a malfunction, notify the electrician or the work supervisor. 4.4. If a fire is detected or signs of fire appear (smell of burning, smoke, temperature increase), it is necessary:
4.5. When extinguishing a fire, the combustible substance should be isolated from atmospheric oxygen and cooled to a temperature that prevents combustion. 4.5.1. Flammable liquids (gasoline, kerosene, alcohol) are extinguished with a fire extinguisher, directing a jet under the base of the flame, or they throw sand, earth, or cover the burning surface with a wet tarpaulin. 4.5.2. Explosive substances (fodder dust) are plentifully watered with a spray of water from a hydrant. 4.5.3. Most solid combustible substances (hay, straw, coal, peat, sawdust) are extinguished with water, covered with sand or earth, covered with wet felt or tarpaulin. When burning material of a large volume (stacks, bales, bales, etc.), it is pulled apart and each part is extinguished separately. 4.5.4. Extinguishing electrical equipment, having previously de-energized it, is allowed only with carbon dioxide fire extinguishers, dry sand, felt felt or other non-conductive means. In case of extinguishing with sprayed water, the distance from the nozzle of the fire nozzle to burning electrical installations must be at least 4 m. The fire nozzle must be grounded, it is necessary to work in dielectric boots and gloves. 4.6. If you detect a gas leak or the presence of gas in wells, closed containers, immediately inform the emergency service and the work manager and take measures to prevent fire and explosion. 4.7. In case of poisoning with poisonous gases in a well or container, pull the victim into fresh air or transfer to a dry, warm room, give him first aid (Appendix 4) and, if necessary, take him to a medical facility. 4.8. In case of leakage of liquid nitrogen from the Dewar vessels and its increased concentration in the room, causing headache, dizziness, loss of consciousness, suffocation, immediately turn on the ventilation, take the victim to fresh air. 4.9. When dealing with a liquid nitrogen leak, use only insulating or hose-type gas masks. Do not use filtering gas masks and respirators, as they do not protect against oxygen deficiency. 4.9.1. When working in a gas mask, you must take a break for 5 minutes. every 30 min. work. 4.10. If liquid nitrogen comes into contact with the skin, wash the affected area with clean water. Remove clothing, gloves or mittens, protective shield or goggles contaminated with liquid nitrogen immediately and replace with clean ones. 4.11. Carry out emergency work (heating of water pipes, welding) using fire and high temperatures according to a work permit under the supervision of the work manager with the implementation of appropriate fire and explosion safety measures. 4.11.1. Warm up frozen water pipes with hot water or sand, steam, but not with an open flame (for example, a blowtorch). 4.12. In the absence or malfunction of protective guards on machinery and equipment, stop work, take measures to turn off the equipment and notify the work manager. 4.13. When caring for a sire bull, in the event of a pronounced disobedience of the bull (attack on the worker), it is necessary to stop the attack by vigorously pressing the nose ring with a stick-carrier. After subduing the bull, release the pressure on the nose ring immediately. 4.14. If the stick-driver broke under the pressure of the bull, pacify it with a water jet, foam from a fire extinguisher, or throw a dressing gown, bag, tarpaulin and other improvised means over the bull's head. If the attack continues, immediately take cover in a safe area and wait for help. 4.15. If you happen to meet a sire bull, if you do not have the means for self-defense, try to hide in a place inaccessible to the bull and expect help. 4.16. Bulls with a violent temper are taken out of the stall together on strong stretch marks, insuring themselves with a carrier stick. 4.17. When pulling a failed animal out of a canal, feeder, etc. be careful and attentive, use logs, ropes. 4.18. In the event of a sudden manifestation of aggression on the part of animals, separate them and, first of all, isolate the aggressive animal, pacify it and other excited animals by using a whip, a carrier stick, a water jet or foam from a fire extinguisher, or cover the head of an aggressive animal with improvised means (robe, bag, etc.). .P.). 4.19. In unfavorable weather conditions (thunderstorm) while grazing, drive the cattle to a permanent parking place - to a summer camp, a barn, or an area where there is less chance of being struck by lightning. You can not be placed on a hill, under transmission lines, near lonely trees, towers, etc. When grazing on a horse, you must dismount and keep the horse on the lead. 4.20. In case of an accident (injury as a result of exposure to an animal, electric shock, fall, etc.), provide first aid in relation to the nature of the injury received by the victim in the following sequence:
5. Safety requirements upon completion of work 5.1. Tidy up your workplace in accordance with job responsibilities. 5.2. Report to the head of work on all violations identified in the course of work, as well as on the measures taken to eliminate them. 5.3. In accordance with the established procedure, hand over the shift to the shifter (cattle operator, milkmaid, night duty), report on the behavior or health of animals that may pose a danger in further work with them. 5.4. Put special clothes and shoes in order and place in a closet or other place reserved for this purpose, for drying and storage. 5.5. Perform personal hygiene practices: wash your hands and face with soap and water, treat your hands with a disinfectant solution, take a shower if possible. Annex 1 to the Model Industry Instructions on Labor Protection in Livestock. Cattle
Annex 2 to the Model Industry Instructions on Labor Protection in Livestock. Cattle
Appendix 3 to the Model Industry Instructions on Occupational Safety and Health. Cattle Appendix 4 to the Model Industry Instructions on Occupational Safety and Health. Cattle Provision of pre-medical first aid 1. Electric shock 1.1. After releasing the victim from the action of electric current, lay him on a bed and cover it warmly, quickly - within 15 - 20 seconds - determine the nature of the required first aid, organize a doctor's call and take the following measures: 1.1.1. If the victim is breathing and conscious, put him in a comfortable position, unfasten his clothes. Before the doctor arrives, provide the victim with complete rest and access to fresh air, while monitoring his pulse and breathing. Do not allow the victim to get up and move before the arrival of the doctor, and even more so continue to work. 1.1.2. If the victim is unconscious, but his breathing and pulse are stable, keep an eye on them, let him smell ammonia and spray his face with water, ensuring complete rest until the doctor arrives. Never bury the victim in the ground. 1.1.3. In the absence of breathing, as well as infrequent and convulsive breathing, or cardiac arrest (lack of pulse), immediately perform artificial respiration or chest compressions. Begin artificial respiration and heart massage no later than 4-6 minutes. from the moment of cessation of cardiac activity and respiration, since after this period clinical death occurs. 1.1.4. Perform mouth-to-mouth or mouth-to-nose artificial respiration as follows:
1.1.5. Sit on your knees on either side of the victim's head and, keeping your head tilted back, take a deep breath and, firmly pressing your mouth (through a handkerchief or gauze) to the victim's open mouth, blow air into him strongly. At the same time, cover the nose of the victim with the cheek or fingers of the hand on the forehead. Make sure that the air enters the lungs and not the stomach, this is revealed by the distention of the abdomen and the lack of expansion of the chest. If air has entered the stomach, remove it from there by quickly pressing for a short time the area of \uXNUMXb\uXNUMXbthe stomach between the sternum and the navel. 1.1.6. Take measures to free the airways and repeat the blowing of air into the lungs of the victim. After blowing in, release the mouth and nose of the victim for free exit of air from the lungs. For a deeper exhalation, lightly press on the chest. Perform each air injection after 5 seconds, which corresponds to the rhythm of your own breathing. 1.1.7. If the jaws of the victim are compressed so tightly that it is not possible to open the mouth, then carry out artificial respiration according to the mouth-to-nose method, blow air into the victim's nose. 1.1.8. When the first spontaneous breaths appear, time the artificial breath to coincide with the beginning of the spontaneous breath. 1.1.9. Perform artificial respiration until deep and rhythmic breathing of the victim is restored. 1.2. Perform external heart massage in case of cardiac arrest, which is determined by the absence of a pulse, dilated pupils and cyanosis of the skin and mucous membranes. 1.2.1. To perform an external heart massage, lay the victim on his back on a hard surface or place a board under him, free his chest from clothing and raise his legs by about 0,5 m. 1.2.2. Position yourself on the side of the victim and determine the place of pressure, to do this, feel for the lower soft end of the sternum and 3-4 cm above this place along it, the point of pressure is determined. 1.2.3. Place the part of the palm adjacent to the wrist joint on the place of pressure, while the fingers should not touch the chest, place the palm of the second hand at a right angle on the back of the palm of the first hand. Make a quick (push) and strong pressure on the sternum and fix it in this position for about 0,5 s, then quickly release it, relaxing your hands, but do not take them away from the sternum. Apply pressure approximately 60 - 80 times per minute. 1.2.4. Massage the heart until your own (not supported by massage) regular pulse appears. 1.3. If it is necessary to simultaneously perform artificial respiration and heart massage, the procedure for conducting them and the ratio of the number of injections to the number of pressures on the sternum is determined by the number of persons providing assistance. 1.3.1. If one person is helping, then perform artificial respiration and heart massage in the following order: after two deep breaths, do 15 chest compressions, then again two deep breaths and 15 chest compressions, etc. 1.3.2. If you provide assistance together, then one makes one blow, and the second after 2 s produces 5-6 pressures on the sternum, etc. 1.3.3. Perform artificial respiration and heart massage until the body's vital functions are fully restored or until a doctor arrives. 2. Injuries 2.1. Lubricate abrasions, injections, bites, minor wounds with iodine or brilliant green and apply a sterile bandage or seal with a strip of adhesive tape. For a large wound, apply a tourniquet, lubricate the skin around the wound with iodine and bandage it with a clean gauze bandage or a sterile bandage from an individual package. 2.2. If there is no bandage or bag, take a clean handkerchief or cloth and, on the place that will lie on the wound, drip iodine to make a spot larger than the wound, and apply the spot on the wound. 2.3. Apply the bandage so that the blood vessels are not squeezed, and the bandage is kept on the wound. 2.4. When injured, it is necessary to make an anti-tetanus injection in a medical institution. 3. Stop bleeding 3.1. To stop the bleeding, lift the wounded limb up or position the injured part of the body (head, torso) so that they are elevated, and apply a tight pressure bandage. 3.2. If during arterial bleeding (scarlet blood flows in a pulsating stream) the blood does not stop, apply a tourniquet or twist. 3.3. Tighten the tourniquet (twist) only until the bleeding stops. Mark the time of applying the tourniquet on a tag, a piece of paper and fix it on the tourniquet. The tourniquet is allowed to be kept tightened for no more than 1,5 - 2 hours. 3.4. In case of arterial bleeding, take the victim to a doctor as soon as possible. Transport it in a comfortable and, if possible, fast vehicle, always with an accompanying person. 4. Bruises 4.1. For bruises, apply a tight bandage and apply cold soaks. In case of significant bruises of the torso and lower extremities, take the victim to a medical facility. 4.2. Bruises in the abdomen lead to ruptures of internal organs. Immediately take the victim to a medical facility at the slightest suspicion of this. Do not let such patients drink and eat. 5. Bone fractures 5.1. For a closed fracture, place the limb in a comfortable position, while handling it carefully, avoid sudden movements, and apply splints. Put splints on both sides, while putting cotton under the splints so that the splints do not touch the skin of the limbs, and be sure to capture the joints above and below the fracture sites. Tires can be worn over clothing. 5.2. In the case of an open fracture, stop the bleeding, smear the edges of the wound with iodine, bandage the wound and apply splints. Do not touch with your hands and do not set the fragments of bones protruding from it into the wound. 5.3. In the absence of tires, use plywood, boards, fork holders. As a last resort, bandage the broken leg to the good leg and the arm to the chest. 5.4. In case of a fracture of the collarbone and scapula, put a tight cotton roll into the axillary region of the injured side, and hang your hand on a scarf. If your ribs are broken, wrap your chest tightly or pull it off with a towel as you exhale. 5.5. If the spine is fractured, carefully place the victim on an ambulance stretcher, boards or plywood, make sure that the torso does not bend (to avoid damage to the spinal cord). 5.6. In case of broken bones, take urgent measures to deliver the victim to the nearest medical facility. 6. Dislocations 6.1. In case of dislocation, ensure the immobility of the injured limb, apply splints without changing the angle that formed in the joint during dislocation. Dislocations should be set only by doctors. 6.2. When transporting the victim to a medical facility, place the victim on a stretcher or in the back of a car, and cover the limb with rollers from clothes or pillows. 7. Burns 7.1. In case of a thermal burn, remove clothing from the burned area, cover it with sterile material, put a layer of cotton wool on top and bandage it. Do not touch burns, puncture blisters, or tear off pieces of clothing stuck to burns while treating. Do not lubricate the burnt surface with ointments and do not cover with powders. In case of severe burns, take the victim to the hospital immediately. 7.2. In case of an acid burn, remove clothing and thoroughly for 15 minutes. rinse the burned area with a stream of water, then rinse with a 5% solution of potassium permanganate or a 10% solution of baking soda (a teaspoon in a glass of water). After that, cover the affected areas of the body with gauze soaked in a mixture of vegetable oil and lime water, and bandage. 7.3. In case of alkali burns, the affected areas within 10-15 minutes. rinse with a stream of water, and then with a 3 - 6% solution of acetic acid or a solution of boric acid (a teaspoon of acid in a glass of water). After that, cover the affected areas with gauze soaked in 5% acetic acid solution and bandage. 8. Frostbite 8.1. In case of frostbite of the XNUMXst degree (skin is edematous, pale, cyanotic, loses sensitivity), bring the victim into a cool room and rub the skin with a dry, clean cloth until redness or a feeling of warmth, lubricate with fat (oil, lard, boric ointment) and apply an insulated bandage. Then drink hot tea to the victim and transfer to a warm room. 8.2. With frostbite II - IV degrees (blisters with bloody fluid appear on the skin and it becomes purple-bluish in color - II degree; the layers of the skin and underlying tissues become dead, the skin becomes black - III degree; complete necrosis of the skin and tissues - IV degree) on the affected apply a dry bandage to the skin, give the victim hot tea or coffee to drink and immediately send to the nearest medical facility. 9. Heat and sunstroke 9.1. At the first signs of illness (headache, tinnitus, nausea, rapid breathing, intense thirst, sometimes vomiting), lay the victim in the shade or bring into a cool room, free the neck and chest from tight clothing. If the victim is conscious, let him drink cold water, moisten his head, chest and neck periodically with cold water, let's sniff ammonia. If the victim is not breathing, perform artificial respiration according to paragraphs 1.1.1 - 1.1.9 of this Appendix. 10. Poisoning by poisonous gases 10.1. If signs of poisoning appear (headache, tinnitus, dizziness, dilated pupils, nausea and vomiting, loss of consciousness), remove the victim immediately to fresh air and organize the supply of oxygen for breathing using a rubber cushion or an oxygen cylinder. 10.2. In the absence of oxygen, lay down the victim, raise his legs, let him drink cold water and let's sniff cotton wool moistened with ammonia. 10.3. If breathing is weak or stops, perform artificial respiration until a doctor arrives or breathing is restored. 10.4. If possible and the victim is conscious, give him plenty of milk to drink. 11. Eye damage 11.1. In case of clogging of the eyes, rinse them with a 1% solution of boric acid, a stream of clean water or a damp cotton (gauze) swab. To do this, lay the head of the victim so that you can direct the jet from the outer corner of the eye (from the temple) to the inner. 11.2. Don't rub your clogged eye. 11.3. If acid and alkali get into the eye, rinse it for 5 minutes. clean water. After washing the eye, apply a bandage and send the victim to a doctor. Appendix 5 to the Model Industry Instructions on Occupational Safety and Health. Cattle Composition of a first aid kit 1. Tablets of validol and nitroglycerin - used for severe pain in the region of the heart. 2. Tablets of analgin, amidopyrine - used as an analgesic for headaches, bruises, dislocations, fractures, 1 - 2 tablets. 3. Tincture of valerian, corvalol - with slight pain in the heart, with nervous excitement. 4. Tablets of besalol or its analogues - for pain in the abdomen. 5. Sodium bicarbonate (soda) - for heartburn (inside), for washing the skin if acid gets on it. 6. Citric acid - for washing the skin when alkali gets on it. 7. Potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate) - for washing wounds, gargling. 8. Hydrogen peroxide - for the treatment of wounds. 9. Hygroscopic surgical cotton wool. 10. Sterile bandage 10 m x 5 cm. 11. First aid dressing package. 12. Bactericidal adhesive plaster - for the treatment of microtraumas. 13. A solution of iodine, brilliant green - for the treatment of wounds. 14. Ammonia solution (ammonia) - for inhalation from a cotton swab in case of fainting, loss of consciousness. 15. Thermometer. 16. Tourniquet. 17. Fingertips. 18. Scarf for a garter. 19. Tires. 20. Scissors.
▪ Manual harvesting of root crops. Standard instruction on labor protection ▪ Conducting sports competitions. Standard instruction on labor protection
Artificial leather for touch emulation
15.04.2024 Petgugu Global cat litter
15.04.2024 The attractiveness of caring men
14.04.2024
▪ The antenna reduces phone radiation ▪ The largest indoor swimming pool will be built ▪ New digital production of micro and macro satellites with a space simulator ▪ Oxidizing molecules slow down aging
▪ section of the site Experiments in chemistry. Article selection ▪ article Protection of the population in emergency situations. Basics of safe life ▪ article Why is a crow considered a harmful bird? Detailed answer ▪ article Senior creative manager of the radio station. Job description ▪ article Simple LC oscillator. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Comments on the article: a guest Very carefully selected material, it helped me a lot in my work !!! Irina Thank you for the detailed material, it helped me a lot!
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese



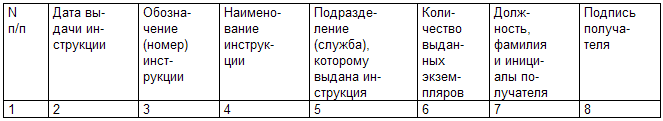
 See other articles Section
See other articles Section 