
|
|
Lecture notes, cheat sheets
State and municipal finances. Federal budget of the Russian Federation - the main financial plan of the country (lecture notes)
Directory / Lecture notes, cheat sheets Table of contents (expand) LECTURE No. 4. The federal budget of the Russian Federation is the main financial plan of the country The budget plays an important economic, social, political role in the reproduction process. The state influences the redistribution of national income between industries. Through the budget, the state can influence weaker, non-monetary sectors (such as agriculture, culture, education, health care, etc.). Federal budget - the form of formation and spending, based on the financial year, of funds intended for the fulfillment of expenditure obligations of the Russian Federation. Like any other economic category, the budget performs certain functions: the formation of a budget fund, its use, control over the use of funds for their intended purpose. The first function is associated with the formation of income, consisting of tax and non-tax revenues. The main source of income is the income of economic entities received as a result of the redistribution of the national product. The structure of budget revenues is not constant and depends on the economic development of the country in a certain period. Another function is related to the targeted use of budgetary funds. Finally, the third function involves the creation of a control associated with both the first and the second function. Targeted use of budgetary funds is subject to control. There is a special reporting form for this. In accordance with the RF Budget Code, the budget has its own structure. The main constituent elements are budget revenues and expenditures. Income and expenses, in turn, are subject to grouping. The budget classification of the Russian Federation is a grouping of revenues, expenditures and sources of financing budget deficits at all levels. The budget classification of the Russian Federation includes: 1) classification of budget revenues of the Russian Federation; 2) functional classification of RF budget expenditures; 3) economic classification of RF budget expenditures; 4) classification of sources of internal financing of budget deficits of the Russian Federation; 5) classification of sources of external financing of the federal budget deficit; 6) classification of types of state internal debts of the Russian Federation, constituent entities of the Russian Federation, municipalities; 7) classification of types of the state external debt of the Russian Federation and state external assets of the Russian Federation; 8) departmental classification of federal budget expenditures. In accordance with Chapter 4 of the RF BC, the classification of RF budget revenues is a grouping of budget revenues at all levels of the RF budget system. The classification of budget revenues of the Russian Federation includes the code of the administrator of budget revenues, groups, subgroups, articles, sub-items, elements, programs (subprograms) and codes of economic income classification. The economic classification of income is a grouping of general government transactions by economic content. There is a distinction between income on own and regulatory. Own fixed on a permanent basis (these are taxes, non-taxes, gratuitous transfers). Regulatory income - payments for which the standards for deductions (Table 1) to lower budgets are established. Table 1 Standards
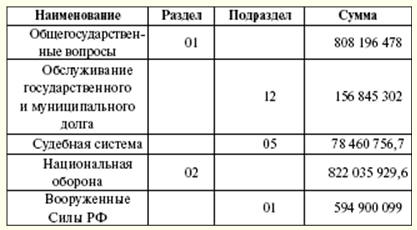
The functional classification of expenditures of the budgets of the Russian Federation is a grouping of expenditures of budgets of all levels. It reflects the direction of budgetary funds for the implementation of the main functions of the state and the solution of issues of local importance. The first level of the functional classification of budget expenditures of the Russian Federation is the sections that determine the expenditure of budgetary funds for the performance of state functions. The second level of functional classification of expenditures of budgets of the Russian Federation - subsections that specify the direction of budgetary funds to perform the functions of the state in the context of sections. The classification of target items of expenditures of the federal budget forms the third level of the functional classification of expenditures of the budgets of the Russian Federation and reflects the financing of federal budget expenditures in specific areas of activity of the main managers of federal budget funds within the subsections of the functional classification of expenditures of the budgets of the Russian Federation. The classification of types of budget expenditures forms the fourth level of the functional classification of expenditures of the budgets of the Russian Federation and details the directions of financing budget expenditures by target items (Table 2). Table 2 Distribution of expenditures by functional classification for 2007 (thousand rubles)
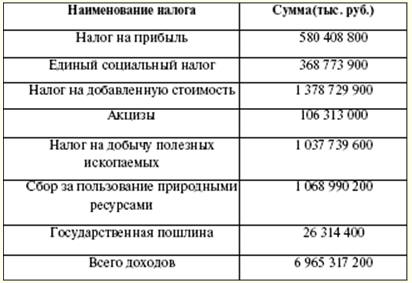
The economic classification of expenditures of budgets of the Russian Federation is a grouping of expenditures of budgets of all levels of the budgetary system of the Russian Federation according to their economic content. The classification of sources of financing budget deficits of the Russian Federation is a grouping of borrowed funds attracted by the Russian Federation, constituent entities of the Russian Federation and municipalities to cover the deficits of the corresponding budgets. The departmental classification of federal budget expenditures is a grouping of expenditures that reflects the distribution of budgetary funds among the main administrators of the federal budget funds. The type of expenditure is supported by the source of financial coverage. If a new type of expenditure appears, the sources and procedure for financing new types of budget expenditures should be determined, including if it is necessary to transfer financial resources for new types of expenditures to budgets of other levels. The structure of budget expenditures includes capital and current expenditures. Capital spending is intended to invest in newly created legal organizations and support existing ones. The form of support is budget credits. Capital expenditures are determined by the economic budgetary classification of expenditures. Current spending is associated with the provision of subsidies and subventions to lower budgets. In addition to the provided budget loans, there are other forms of spending budget funds (appropriations, transfers, payment under a government contract, inter-budget transfers, etc.). The practice of creating reserve funds as part of the budget is widespread. The size of the fund should not exceed 3% of the total cost. The purpose of creating such funds is to use a reserve stock for unforeseen expenses (losses from natural disasters, restoration work from accidents that have occurred). Thus, the Reserve Fund of the President of the Russian Federation is formed as part of the federal budget. Its volume should not be more than 1% of the established amount of expenses. Only the President of the Russian Federation has the right to dispose of the funds of this fund. However, spending the funds of the fund for personal purposes, for elections and other events is prohibited. This fund is created for emergency expenses. The total amount of income in 2007 amounted to 6 rubles. The structure of the revenue part consists of tax and non-tax revenues. The list of tax revenues depends on the legally fixed taxes and fees (Table 964). At the same time, there is a distribution of the share of tax sources between the budgets of different levels. This year, income tax, value added tax, excises, mineral extraction tax, unified social tax, water tax, collection for the use of aquatic biological resources are determined. The first place in terms of revenues to the budget is occupied by the value added tax, the fee for the use of natural resources, and the tax on the extraction of minerals. Customs payments have a large share of income. Establishment of new types of taxes, their cancellation or change is possible only by making appropriate changes to the tax legislation of the Russian Federation. The federal legislative authorities may establish new types of non-tax revenues, cancel or change the existing ones after the federal executive authorities submit their opinion and only by amending the Budget Code of the Russian Federation. Table 3 Tax receipts to the federal budget in 2007
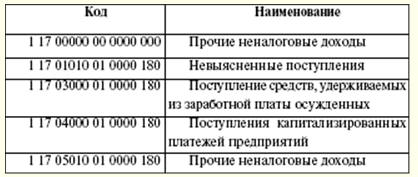
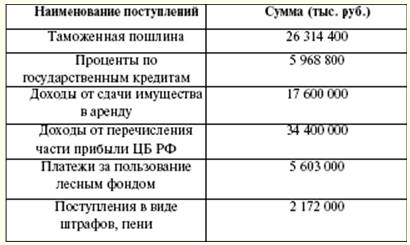
Non-tax revenues of the federal budget (Table 4) are formed from: 1) income from the use of state-owned property, income from paid services provided by budgetary institutions; 2) remaining after taxes and other obligatory payments and fees for the issuance of licenses to carry out activities related to the production and circulation of ethyl alcohol, alcoholic and alcohol-containing products, part of the profits of unitary enterprises established by the Russian Federation; 3) customs duties and customs fees; 4) fees for the use of water bodies; 5) fees for the use of aquatic biological resources; 6) payments for negative impact on the environment; 7) the profit of the Bank of Russia remaining after the payment of taxes and other obligatory payments (according to the standards established by federal laws); 8) income from foreign economic activity; 9) other income. Table 4 Non-tax revenues to the budget in 2007
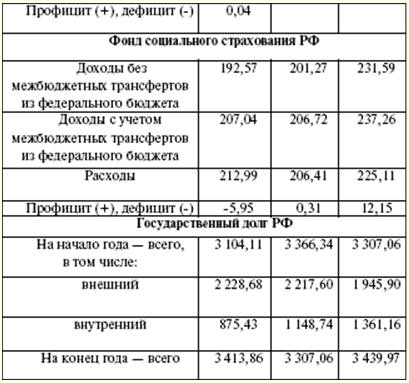
The income of the federal target budget funds is taken into account in the income of the federal budget. Receipts are made at established rates and are distributed among the federal target and territorial target budget funds. In the course of consideration of income and expenditure items, a deficit may appear. In such cases, the sources of financing the budget deficit are approved. Funding sources are approved by the legislature in law for the next financial year. Credits from the Bank of Russia, as well as the acquisition by the Bank of Russia of debt obligations of the Russian Federation, subjects of the Russian Federation, municipalities during their initial placement cannot be sources of financing the budget deficit. The sources of financing the federal budget deficit are: 1) internal sources: a) loans received by the Russian Federation from credit institutions in the currency of the Russian Federation; b) government loans carried out by issuing securities on behalf of the Russian Federation. State borrowings of the Russian Federation are loans and credits attracted from individuals and legal entities, foreign states, international financial organizations, for which debt obligations of the Russian Federation arise as a borrower or a guarantor of repayment of loans by other borrowers; c) budget loans received from the budgets of other levels of the budget system of the Russian Federation; d) proceeds from the sale of state-owned property; e) the amount of excess of revenues over expenditures on state stocks and reserves; f) change in the balances of funds on the accounts for the accounting of federal budget funds; 2) external sources: a) government loans made in foreign currency by issuing securities on behalf of the Russian Federation; b) loans from foreign governments, banks and firms, international financial organizations, provided in foreign currency, attracted by the Russian Federation. The drafting of budgets is preceded by the development of forecasts for the socio-economic development of the Russian Federation, constituent entities of the Russian Federation, municipalities and sectors of the economy, as well as the preparation of consolidated financial balances, on the basis of which the executive authorities develop draft budgets. The whole process begins with the Budget Message of the President of the Russian Federation, which is sent to the Federal Assembly no later than March of the previous year. The Government of the Russian Federation is engaged in the design of budgets, and at the local level - the executive bodies of local authorities. The draft budget is prepared by the Ministry of Finance. For the formation of the draft budget, the Message of the President of the Russian Federation, the forecast of socio-economic development, the forecast of the consolidated financial balance, and the plan for the development of the economic sector in the given territory are used. In addition, the calculations use information on the current tax legislation, the estimated amount of financial assistance from the budgets of other levels of the budget system of the Russian Federation, the types and amounts of expenditures from one level of the budget system to another, and the standards of financial costs for the provision of state or municipal services. Budgeting depends on the calculation of important indicators of GDP per capita, inflation. The development plan for the state or municipal sector of the economy includes: 1) a list and a summary plan of the financial and economic activities of federal state-owned enterprises; 2) a list and a summary plan of the financial and economic activities of state or municipal unitary enterprises; 3) a program for the privatization of state or municipal property and the acquisition of property into state or municipal property; 4) information on the maximum staffing of state or municipal employees and military personnel for the main administrators of budgetary funds. Simultaneously with the draft budget for the next financial year, the following are drawn up: 1) forecast of the consolidated budget of the relevant territory for the financial year; 2) targeted investment program for the financial year; 3) a development plan for the state or municipal sector of the economy; 4) the structure of the state or municipal debt and the program of internal and external borrowings; 5) assessment of budget losses from the provided tax benefits; 6) assessment of the expected execution of the budget for the current financial year. In addition, the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation is developing indicative budget indicators for the medium term, a draft federal law on the budget. At the same time, a medium-term forecast of socio-economic development and a forecast of the Consolidated Financial Balance are being prepared. The formation of the federal budget begins with the selection by the Government of the Russian Federation of a plan-forecast of the functioning of the Russian economy for the next financial year. Based on the chosen plan-forecast, the federal budget expenditures are distributed (Table 5). Table 5 Parameters of the budget system of the Russian Federation (billion rubles)
The indicators affecting the budget spending are considered in detail. These include the relationship between the subsistence minimum and the minimum wage, the minimum old-age pension, the minimum scholarships, allowances and other payments, proposals on the procedure for indexing the wages of public sector employees and state pensions, the financial allowance of federal civil servants, the monetary allowance of military personnel for a year and for an average period. After that, the project is sent to specific recipients of funds. Based on the characteristics of the budget, in the future, the distribution of the maximum amounts of funding for the financial year takes place according to the functional and economic classification of expenditures and to the recipients of budget funds. At this stage, proposals are being considered for structural and organizational reforms in the sectors of the economy and the social sphere, the abolition of some regulatory legal acts. All uncoordinated issues are resolved by an interdepartmental government commission headed by the Minister of Finance. Documents accompanying the draft budget: 1) preliminary results of the socio-economic development of the Russian Federation for the past period of the current year; 2) forecast of the socio-economic development of the Russian Federation for the next financial year; 3) the main directions of budgetary and tax policy for the next financial year; 4) a plan for the development of the state and municipal sectors of the economy; 5) forecast of the Consolidated Financial Balance for the territory of the Russian Federation for the next financial year; 6) forecast of the consolidated budget of the Russian Federation for the next financial year; 7) basic principles and calculations on the relationship between the federal budget and the consolidated budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation; 8) projects of federal targeted programs and federal programs for the development of regions; 9) draft federal targeted investment program; 10) draft state armament program; 11) a draft program for the privatization of state and municipal enterprises; 12) calculations under the articles of the classification of federal budget revenues, sections and subsections of the functional classification of expenditures of the budgets of the Russian Federation and the federal budget deficit for the next financial year; 13) international treaties of the Russian Federation; 14) draft program of state external borrowings of Russia; 15) a draft program for the provision by the Russian Federation of state loans to foreign states; 16) draft structure of the state external debt of the Russian Federation by types of debt and broken down by individual states; 17) a draft structure of the state internal debt of the Russian Federation and a draft program of internal borrowings; 18) proposals for indexing the minimum amounts of scholarships, allowances and social payments, the salaries of federal civil servants, the monetary allowance of military personnel, as well as proposals for indexing (increasing) the remuneration of employees of public sector organizations; 19) a list of legislative acts, the effect of which is canceled or suspended; 20) calculations of the projected volume of the Stabilization Fund. The preliminary specified draft is sent to the President of the Russian Federation and to the Government of the Russian Federation. A draft federal law on the federal budget for the next financial year shall be considered submitted on time if it is delivered to the State Duma by August 26. After reviewing the main indicators of the budget, preparing accompanying documents, the project is submitted for consideration by the legislature. If at this stage disagreements arose between the bodies entitled to legislative consideration of the budget, then, in addition to the above documents, draft budget estimates from each such body are submitted for consideration. The draft budget is sent to the Duma committee responsible for considering the budget. The result of the work carried out by the Committee is its conclusion. If the project is not approved, then there are two ways to transport the project: either it is reviewed by the Duma, or it is sent to the Government for revision. A more or less corrected draft is sent to the Federation Council, Duma offices, and the Accounts Chamber. Procedure for Considering a Draft Federal Law on the Federal Budget The representative body represented by the State Duma of the Russian Federation considers the draft federal law on the federal budget for the next financial year in four readings. In the first reading, laws on the budgets of state non-budgetary funds, the minimum pension, the tariff rate of the first category of the Unified Tariff Scale for the remuneration of employees of public sector organizations, the procedure for indexing and recalculating state pensions, the minimum wage. In case of deviation from federal laws, changes must be made to tax legislation, legislative acts on the rates of insurance contributions to state non-budgetary funds. The first reading considers the framework of the budget itself. The forecast of the socio-economic development of the Russian Federation, the directions of the budget and tax policy, the principles and calculations on the relationship between the federal budget and the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, the draft program of state external borrowing (as external financing of the budget deficit), federal budget revenues by groups, subgroups and classification articles are discussed. budget revenues of the Russian Federation, the federal budget deficit in absolute terms and as a percentage of federal budget expenditures for the next financial year and the sources of covering the federal budget deficit, the total volume of federal budget expenditures. The Government of the Russian Federation, the Budget Committee, and the Accounts Chamber take part in the first stage of reading. The work of these subjects consists in the formation and reading of reports and co-reports, on the basis of which the Duma makes a decision on the bill. If the budget is rejected in the first reading, the draft is submitted to the conciliation commission to clarify the main characteristics of the federal budget or is returned to the Government for revision. If the Duma decides to reject the draft twice at the first reading, a global question arises of distrust in the Government of the Russian Federation. In the event of one rejection by the Duma of the draft federal budget, it is finalized by the Government of the Russian Federation in accordance with the instructions and proposals submitted by the Committee on Economic Policy of the State Duma. The revision period is 20 days. Secondary consideration of the budget in the first reading should not exceed 10 days. In the second reading, federal budget expenditures are approved by sections of the functional classification of expenditures of the budgets of the Russian Federation within the total volume of federal budget expenditures approved in the first reading, and the size of the Federal Fund for Financial Support of the RF Subjects. The review period is 15 days. At the second stage of consideration, it is possible to adjust budget expenditures according to their functional classification. Questions on this situation are considered by the Budget Committee. If the State Duma rejects in the second reading the draft federal law on the federal budget, then it submits the said bill to the conciliation commission. In the third reading, federal budget expenditures are approved by subsections of the functional classification of expenditures and by the main administrators of the federal budget funds. The distribution of the funds of the Federal Fund for Financial Support of the Subjects of the Russian Federation by subjects of the Russian Federation, the main indicators of the state defense order, and the federal budget expenditures for financing federal targeted programs are considered. In the third reading, there is the last opportunity to correct the future budget by subsections of the functional classification of expenditures and by the main administrators of the federal budget funds. Unanswered questions are sent to the conciliation commission. 25 days are allotted for the third reading. The committee considers the introduced amendments within 10 days, after which it submits its opinion. The final fourth reading is held within 15 days. At this stage, no amendments are made, but a vote is taken for the bill. The developed bill is submitted to the Federation Council. The approved law is sent to the President of the Russian Federation within 5 days. If the federal law on the federal budget for the next financial year is rejected by the Federation Council, the said federal law is submitted to a conciliation commission to overcome the disagreements that have arisen. The Commission submits an approved federal law for reconsideration by the State Duma. The State Duma is reconsidering the federal law on the federal budget for the next financial year in one reading. The decision of the Federation Council may be rejected if 2/3 of the number of deputies of the State Duma voted "for". The last instance of consideration and approval of the law on the federal budget is the President of the Russian Federation. In case of rejection by the President of the Russian Federation, the law is submitted to the conciliation commission to overcome the disagreements that have arisen. The execution of the budget is provided by the Government of the Russian Federation. Cash services for the execution of budgets of the budget system of the Russian Federation are carried out by the Federal Treasury. For cash services for the execution of budgets, the Federal Treasury opens accounts with the Central Bank of the Russian Federation. All cash transactions for the execution of budgets are carried out by the Federal Treasury through these accounts and are reflected in the reports on the cash execution of budgets submitted by it to the financial authorities. Execution of income budgets: 1) transfer and crediting of income to a single account of the budget; 2) distribution of regulatory revenues; 3) return of excessively paid amounts of income to the budget; 4) accounting for budget revenues and reporting on budget revenues. Expenditure budgets are executed within the actual availability of budgetary funds. If the law on the budget has not entered into force since the beginning of the financial year, the Government of the Russian Federation must spend budgetary funds to continue financing investment objects and provide financial assistance to budgets of other levels. The main condition is that these expenses in the past year were carried out for similar purposes (but not more than 1/12 per month of the previous appropriations). Rates of transfer of regulatory taxes to the budgets of other levels, standards for centralization of revenues credited to the budgets of other levels to finance centralized activities, other tariffs and rates are determined by the law on the budget for the previous financial year. If the budget has not entered into force three months after the start of the financial year, the Government of the Russian Federation continues to spend and distribute income, with the exception of investment, the provision of funds on a repayable basis and subsidies to private legal entities, and the formation of reserves. If the budget law enters into force after the beginning of the financial year, it is about introducing amendments and additions to the budget law, clarifying the budget indicators, taking into account the results of budget execution for the period of interim budget management. The Stabilization Fund of the Russian Federation is a part of the federal budget funds, formed by the excess of the oil price over the base oil price, subject to separate accounting, management and use in order to ensure the balance of the federal budget when the oil price drops below the base one. The base oil price is the Urals crude oil price equivalent to US$197,1 per 1 ton (US$27 per barrel). The stabilization fund is formed at the expense of income received from the excess of the price, and income received from the placement of the fund's resources. In accordance with the RF BC, the additional income of the Stabilization Fund is determined by: 1) the product of the actual revenues to the federal budget of the export customs duty on crude oil in the current month by the ratio of the difference between the export customs duty rate for crude oil in the current month and the estimated rate of the said duty at the base oil price to the export customs duty rate in effect in the current month duties on crude oil; 2) the product of the actual revenues to the federal budget of the tax on the extraction of minerals (oil) in the current month by the ratio of the difference between the current rate of the tax on the extraction of minerals (oil) and the estimated rate of the said tax at the base price of oil to the current one in the current month at the rate of tax on the extraction of minerals (oil). The balances of federal budget funds at the beginning of the financial year, as well as free balances of federal budget funds required by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, are credited to the Stabilization Fund. Based on the results of its consideration of the report on the execution of the federal budget for the previous financial year, the Government of the Russian Federation specifies the amount of balances of federal budget funds to be used in accordance with the federal law on the federal budget for the corresponding financial year. Funds from the Stabilization Fund can be used to finance the federal budget deficit when the price of oil falls below the base price, as well as for other purposes if the accumulated volume of funds from the Stabilization Fund exceeds RUB 500 billion. The volumes of use of the Stabilization Fund's resources are determined by the federal law on the federal budget for the corresponding financial year, the draft of which is submitted by the Government of the Russian Federation. The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation publishes on a monthly basis information on the balance of the Stabilization Fund at the beginning of the reporting month, the amount of funds received by the Stabilization Fund and the use of the Stabilization Fund in the reporting month. The funds of the Stabilization Fund are set aside in foreign currency: dollars, euros, British pounds sterling. The funds are held in the accounts of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, and the Central Bank pays interest for the use of funds. Replenishment of funds is carried out by acquiring debt obligations of foreign states. These include debt securities of the governments of Austria, Belgium, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, the United Kingdom and the United States. Paper requirements: 1) the issuer of debt obligations must have a long-term credit rating of at least AAA according to the classification of Fitch Rating or Standard & Poor's rating agencies. Early redemption of debt obligations by the issuer is not provided; 2) the norms of the minimum and maximum terms to maturity of issues of debt obligations, established by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, are mandatory; 3) the rate of coupon income paid on coupon debt obligations, as well as the nominal values of debt obligations, are fixed; 4) the face value of debt obligations is expressed in US dollars, euros and British pounds sterling, payments on debt obligations are made in the currency of the face value; 5) the volume of issue of debt obligations in circulation is at least 1 billion US dollars for debt obligations denominated in US dollars, at least 1 billion euros for debt obligations denominated in euros, and at least 0,5 billion . pounds sterling - for debt obligations denominated in pounds sterling; 6) issues of debt obligations are not issues intended for private placement. Author: Novikova M.V. << Back: Fundamentals of budget policy >> Forward: Municipal budget
▪ Forensic medicine and psychiatry. Crib ▪ Foreign literature of the XVII-XVIII centuries in brief. Crib
The existence of an entropy rule for quantum entanglement has been proven
09.05.2024 Mini air conditioner Sony Reon Pocket 5
09.05.2024 Energy from space for Starship
08.05.2024
▪ On the lift across the street ▪ External graphics cards for Thunderbolt 3 laptops
▪ site section Parameters of radio components. Article selection ▪ Cupid article. Popular expression ▪ article How did some children's games appear? Detailed answer ▪ article Loading and unloading master. Job description ▪ article Powerful regulator. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering ▪ article Simple switching regulator. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese




 See other articles Section
See other articles Section 