 Free technical library
Free technical library
All-wheel drive all-terrain vehicle. Drawing, description

Directory / Tools and mechanisms for agriculture
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
The all-terrain vehicle is made according to a scheme that has proven itself well on the Kirovets tractor. It has the same "breaking" frame and drive to both axles. What does it give? First, permeability. The frame, constantly bending, follows the terrain, as it were. All four drive wheels are constantly in contact with the ground. This eliminates the overload of individual wheels and their slippage on uneven ground. Secondly, maneuverability. The articulated frame is sensitive to even slight deviations of the steering wheel and allows you to turn around almost on the spot. Thirdly, constructive simplicity. In this scheme, you can use exactly the same front and rear axles. The engine mount is also simple.

The frame consists of two main parts connected in the middle by a hinge with a vertical axis of rotation. Its front part is a rigid welded assembly, on which the bridge, engine, fuel tank, control pedals and driver's seat are installed. The left bearing arch of the frame also serves as a silencer.
A hinge with a vertical axis of rotation consists of two forks connected by powerful fingers. The pins are bolted to the rear fork lugs, while the front fork pivots around them in thrust and needle bearings.

Chassis (in the top view, the engine and seat are conditionally not shown) (click to enlarge): 1 - fuel tank, 2 - engine, 3 - steering column mounting bracket, 4 - exhaust pipe, 5 - central engine mounting bracket, 6 - casings differentials, 7 - steering column, B - steering rod. 9, 10 - limiters of the "break" angle of the frame, 11 - limiter-bolt of fastening the body 12 - steering worm drive, 13 - casing of the front propeller shaft, 14 - connecting link. 15 - casing of the rear propeller shaft, 18 - body mounting loop, 17 - gear lever. 18 - gas pedal, 19 - lower engine mount bracket, 20 - clutch pedal, 21 - kickstarter, 22 - muffler intake pipe, 23, 29 - axle shaft flanges. 24 - footboard. 25 - supporting frame arc (silencer), 26 - exhaust pipe. 27 - steering rocker. 28 - supporting arc of the frame. 30 - brake cable, 31 - brake drum, 32 - rear driveshaft. 33 - steering gear bracket, 34 - front propeller shaft. 35 - chain drive casing, 36 - rear engine mount bracket. 37 - brake handle
To prevent the wheels from rubbing against each other when the frame "breaks" around the vertical axis, the hinge has stops installed respectively on the front and rear forks: a slightly curved and flattened tube for rigidity and two studs at the ends of the channel brackets. The rear part of the frame - a bridge, a brake and a removable body are attached to it - is movable, its hinge is with a horizontal axis of rotation. But it is arranged somewhat differently: a fixed casing with an internal thread is riveted to the rear fork, into which a bronze bushing is screwed. It is she who serves as a plain bearing for the movable casing of the rear of the frame.
In the sleeve, this casing is held by a pin screwed into the reinforcing lining. It is also the limiter of the "break" angle of the frame relative to the longitudinal axis of the all-terrain vehicle. The angle value depends on the length of the groove cut in the fixed casing and sleeve.
The VP-150M engine is installed across the movement so that it takes up less space, and the air-cooled fan has the most favorable conditions for operation.

Articulation of the drive sprocket with the differential and the front propeller shaft (click to enlarge): 1 - bevel gear, 2 - differential casing, 3, 7 - tapered roller bearings, 4 - spacer, 5 - shim, 6, 12 - M6 studs, 8 - cuff, 9 - bearing housing, 10 - M4 bolt, 11, 18 - casing halves, 13 - inner flange, 14 - rivet Ø 0 mm, 3 - driven sprocket, 15, 16 - M20 screws, 4 - lining, 17 - hinges of the steering gear bracket, 19 - nut M 21x14, 1,5 - outer flange, 22 - front propeller shaft.
The mounting brackets are located as follows: the central and most powerful one is on the differential casing, under the engine cylinder, the lower one is on the right axle beam, under the crankcase, and the rear one is on the chain transmission casing.
A metal fuel tank with a capacity of 5,5 liters is attached to the engine crankcase; fuel flows into the carburetor by gravity.
The controls are placed on the beams of the front axle: on the left is the clutch pedal, on the right is the gas. Footrests are installed next to the pedals for the convenience of the driver.

Installing the brake drum (click to enlarge): 1 - rear driveshaft, 2 - outer flange, 3, 8. 12 - M6 studs, 4 - brake drum, 5 - inner flange, 6 - M14 nut, 7 - brake disc, 9 - housing of the bearing unit, 10 - cuff, 11, 15 - tapered roller bearings. 13 - shim, 14 - spacer, 16 - differential housing, 17 - bevel gear.
Gears are shifted by hand using a lever with a ball at the end, welded to the gear sector.
The engine is started by a kick starter with a handle instead of a folding pedal.
The exhaust gases from the cylinder through the corrugated pipe enter the left frame carrier tube as a muffler and exit the exhaust pipe under the seat.
The transmission of the all-terrain vehicle is symmetrical about the vertical axis of the "break" of the frame. The torque from the engine is transmitted by a chain to the cardan shafts, and from them through bevel gears and differentials - to the axle shafts of the axles. Cardan shafts are machined from a bar. In the middle they have necks for sealing cuffs, and at the ends there are slots. Cardans with crosses (including for the connecting link) were taken from the Ural motorcycle. They rotate in bronze bushings, which are lubricated from time to time through thin oiler tubes brought out.
With external splines, the cardan shafts enter into the outer flanges connecting them to the shanks of the drive gears of the bevel gears. The rear shaft is equipped with a brake from the Vyatka scooter: the brake disc is studded to the bearing assembly housing, and the drum is attached to the flanges. The control cable from the disc is brought to the steering column.
The axle differentials on the all-terrain vehicle are of a traditional design: with two satellite gears (from the Moskvich-412 car). The side gears are homemade, and the bevel gear is taken from a Ural motorcycle.
Rusk, unlike the "Moskvich" one, does not have a spherical surface facing the differential case, but a cylindrical one, for simplicity.
Bridges are attached to the frame with bolts, inserts and shims. Only on the rear axle, the bolts still hold the body mounting loops, and on the front axle, the brackets for the gas and clutch pedals.
The steering consists of a detachable handwheel, a vertical column, a steering worm gear, two rockers and an adjustable rod. The gear ratio of the drive is 1: 4, which allows you to "break" the frame not only in motion. but also in the parking lot. The force from it is transmitted by a rod to the rocking chair attached to the fork of the rear of the frame, and causes it to deviate in one direction or another.
The wheels are also structurally simple and completely identical. The bearing element of each of them is an aluminum hub, to the ends of which discs of the same material are screwed.
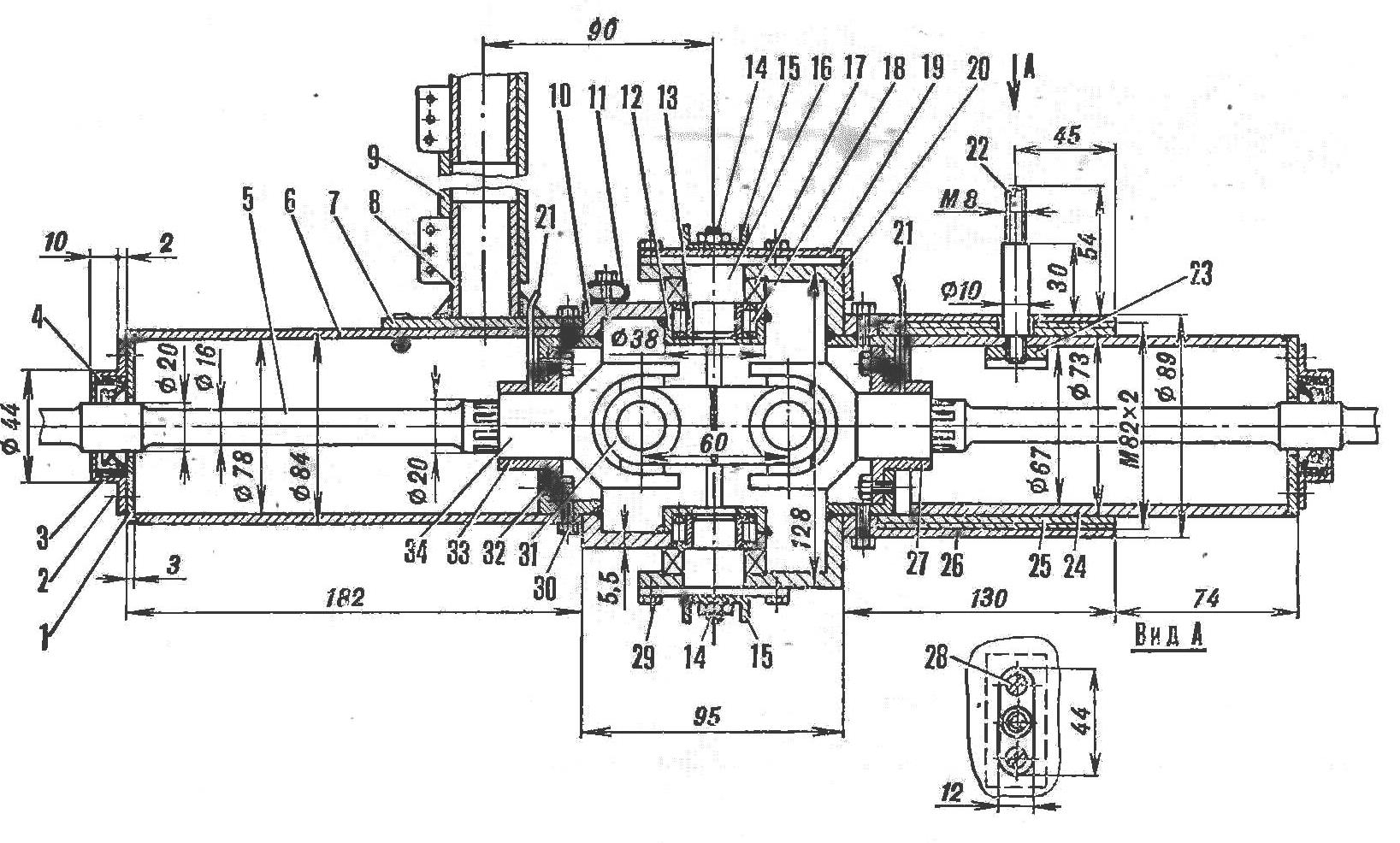
The design of the frame "break" hinges (click to enlarge): 1 - plug, 2 - M3 screw (4 pcs.), h - cuff body, 4 - cuff, 5 - front propeller shaft, 6 - front casing, 7 - lining, 8 - seat post. 9 - seat height adjuster, 10 - front fork, 11 - frame "kink" angle limiter tube, 12 - needle bearing housing, 13 - bushing. 14 - stud-limiter of the angle of the "break" of the frame, 15 - brackets of the studs-limiters, 16 - pin-axle of the "break" of the frame, 17 - thrust ball bearing. 18 - needle bearing, 19 - steering rocker, 20 - rear fork, 21 - oilers, 22 - limiter-body mounting bolt, 23 - reinforcing lining, 24 - movable casing, 25, 27, 33 - bronze bushings-bearings, 26 - fixed casing, 28 - M5 screw (2 pcs.), 29 - bolt Mb for fastening the axle pin (6 pcs.), 30 - M6 bolt (8 pcs.), 31 - connecting link, 32 - Mb bolt (4 pcs. ), 34 - cardan
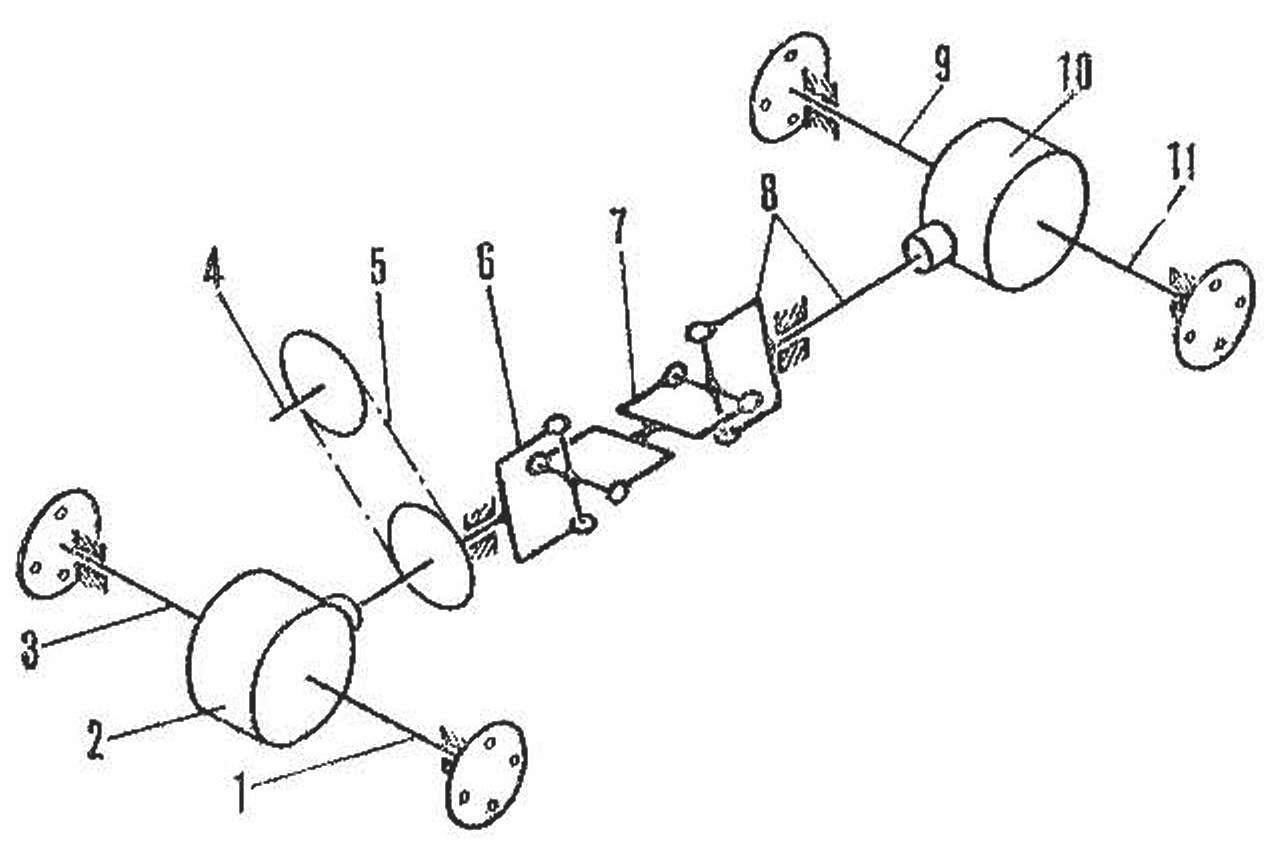
Transmission diagram: 1, 3 - front axle shafts, 2, 10 - differentials, 4 - engine output shaft, 5 - chain drive, 6 - front driveshaft, 7 - connecting link, 8 - rear driveshaft, 9, 11 - axle shafts rear bridge.

Rear axle (click to enlarge): 1 - wheel flange, 2 - oil seal, 3 - cover, 4 - bearing housing, 5 - axle shaft bearing. 6 - cuff, 7 - retaining ring, 8 - bridge beam, 9 - axle shaft. 10, 17 - differential casing flanges, 11 - cover, 12 - driven bevel gear, 13 - M8 tie rod, 14 - cracker, 15 - satellite pin, 16 - satellites. 18 - hairpins Mb. 19 - differential bearing. 20 - half shaft bearing housing, 21 - gasket, 22 - differential housing halves, 23 - frame bearing arc, 24 - plug, 25 - adjusting gasket. 26 - liners, 27 - M8 coupling bolt, 28 - body mounting loop
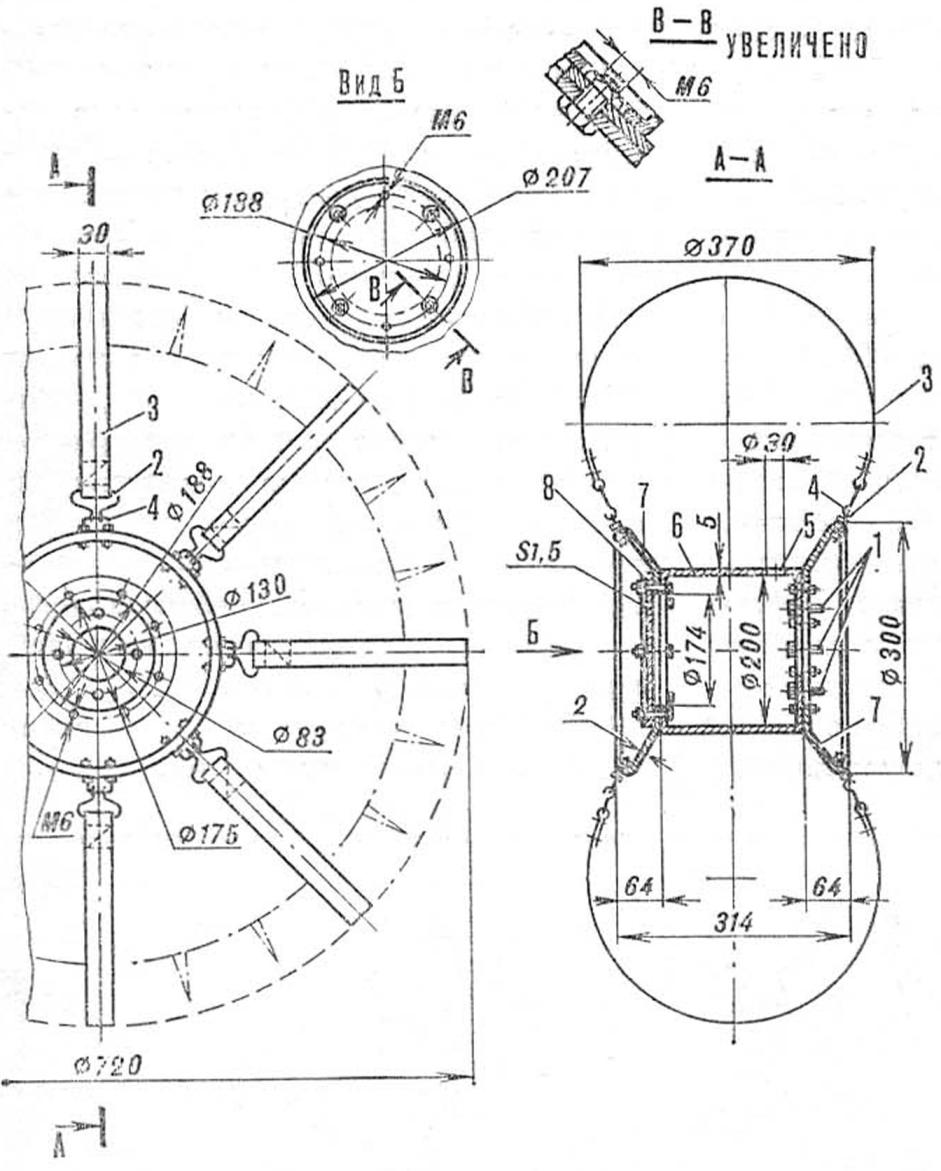
Wheel (click to enlarge): 1 - M8 bolts for fastening to the axle shaft flange, 2 - hook (wire Ø 3 mm). 3 - canvas belt, 4 - bracket (wire Ø 4 mm), 5 - hole for the valve. 6 - hub, 7 - discs. 8 - cover.

Body: 1 - front bracket, 2 - side brackets, 3 - rivets Ø 3 mm, 4 - M4 screws
Eight tarpaulin belts are attached to the disks with wire hooks and brackets, holding the tire - two chambers measuring 720 X 310 mm, nested one inside the other and protected by a tarpaulin tape with tucks-lugs.
The outer end of the hub is closed with a cover that protects its cavity from contamination, and the inner end is equipped with four bolts for fastening the wheel to the axle shaft flange.
The body is assembled from a welded steel frame and fiberglass panels. Provide the necessary rigidity to the floor
three channels with brackets for installation on the frame of the all-terrain vehicle.
The weight of the body is only 6,5 kgf, but its dimensions are such that they allow an adult to sit without experiencing any particular inconvenience.
Technical care for the all-terrain vehicle is almost minimal. It is enough to monitor the level of fuel in the tank, the gear oil in the bridges and the air pressure in the tires. Yes, occasionally lubricate bronze bushings-bearings through oilers - that's all.
Author: A.Gromov, A.Timchenko
 We recommend interesting articles Section Tools and mechanisms for agriculture:
We recommend interesting articles Section Tools and mechanisms for agriculture:
▪ Hand mower
▪ Single-row mechanical seeder
▪ light in the greenhouse
 See other articles Section Tools and mechanisms for agriculture.
See other articles Section Tools and mechanisms for agriculture.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive New multi-standard TV audio processors and audio demodulators
30.01.2004
ST MICROELECTRONICS has released a new family of multi-standard TV audio processors and audio demodulators SW82x7.
They support audio standards such as Dolby, ProLogic, SRS TruSurround XTTM, and many more. This allows the use of chips for analog and digital television, digital video recorders, DVD equipment, etc.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Smart air purification system in the car
▪ GaN-on-silicon LEDs
▪ 60-inch LCD TVs from Foxconn and Sharp
▪ Self-driving Volvo cars on Swedish roads
▪ Eewrite Janus tablet with E Ink and LCD screens
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Audio and video surveillance. Selection of articles
▪ article by Daphne Du Maurier. Famous aphorisms
▪ article Do crocodiles attack humans? Detailed answer
▪ European spruce article. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
▪ article Types and characteristics of solar panels. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Touch Memory - electronic identifier. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese










 See other articles Section
See other articles Section 