 Free technical library
Free technical library
Section 1 General Rules
Insulation of electrical installations. Coefficients of use of the main types of insulators and insulating structures (glass and porcelain)

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Rules for the installation of electrical installations (PUE)
 Comments on the article Comments on the article
1.9.44. The utilization factors k of insulating structures made up of insulators of the same type should be determined as
k = ki · kk
where ki is the coefficient of use of the insulator;
kk is the utilization factor of a composite structure with parallel or series-parallel branches.
1.9.45. The utilization coefficients k and suspension disc insulators according to GOST 27661 with a poorly developed lower surface of the insulating part should be determined from Table. 1.9.20 depending on the ratio of the length of the creepage distance L of the insulator and the diameter of its plate D.
1.9.46. The coefficients of use k and suspension plate insulators of a special design with a highly developed surface should be determined from Table. 1.9.21.
1.9.47. The utilization coefficients k and pin insulators (linear, support) with a poorly developed surface should be taken equal to 1,0, with a highly developed surface - 1,1.
1.9.48. The coefficients of use k and external insulation of outdoor electrical equipment, made in the form of single insulating structures, including outdoor support insulators for a rated voltage of up to 110 kV, as well as suspension rod-type insulators for a rated voltage of 110 kV, should be determined from Table. 1.9.22 depending on the ratio of the length of the creepage distance of the insulator or insulating structure L and to the length of their insulating part h.
1.9.49. The coefficients of use kk of single-circuit garlands and single support columns, made up of the same type of insulators, should be taken equal to 1,0.
1.9.50. The coefficients of use kk of composite structures with parallel branches (without jumpers), made up of the same type of elements (double-circuit and multi-chain supporting and tension garlands, two- and multi-column columns), should be determined from Table. 1.9.23.
1.9.51. The coefficients of use of kk-shaped and V-shaped garlands with single-circuit branches should be taken equal to 1,0.
1.9.52. The utilization coefficients kk of composite structures with series-parallel branches, made up of insulators of the same type (garlands of the or type, support columns with a different number of parallel branches in height, as well as substation devices with extensions), should be taken equal to 1,1.
1.9.53. The utilization factors k and single-circuit garlands and single support columns, made up of different types of insulators with utilization factors ki1 and ki2, should be determined by the formula
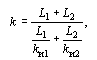
where L1 and L2 are the length of the creepage distance of the construction sections from insulators of the corresponding type.
Similarly, the value of ki should be determined for structures of the specified type with the number of different types of insulators greater than two.
1.9.54. The configuration of suspension insulators for areas with various types of pollution should be selected according to Table. 1.9.24.
Table 1.9.20. Utilization coefficients ki of suspension disc insulators with a poorly developed lower surface of the insulating part
| Lи/D |
kи |
| From 0,90 to 1,05 inclusive |
1,00 |
| From 1,05 to 1,10 inclusive |
1,05 |
| From 1,10 to 1,20 inclusive |
1,10 |
| From 1,20 to 1,30 inclusive |
1,15 |
| From 1,30 to 1,40 inclusive |
1,20 |
Table 1.9.21. Utilization coefficients ki for special suspension plate insulators
| Isolator configuration |
kи |
| Diptera |
1,20 |
| With extended rib extension on the bottom surface |
1,25 |
| Airfoil (conical, hemispherical) |
1,0 |
| Bell-shaped with a smooth inner and ribbed outer surfaces |
1,15 |
Table 1.9.22. Coefficients for the use of single insulating columns, support and suspension rod insulators
| Lи/h |
less 2,5 |
2,5-3,00 |
3,01-3,30 |
3,31-3,50 |
3,51-3,71 |
3,71-4,00 |
| kк |
1,0 |
1,10 |
1,15 |
1,20 |
1,25 |
1,30 |
Table 1.9.23. Utilization coefficients kk of composite structures with electrically parallel branches (without jumpers)
| Number of parallel branches |
1 |
2 |
3-5 |
| kк |
1,0 |
1,05 |
1,10 |
Table 1.9.24. Recommended applications for suspension insulators of various configurations*
| Isolator configuration |
Characteristics of contaminated areas |
| Poppet with ribbed bottom surface (Lи/D ≤ 1,4) |
Areas with 1-2nd C3 for any type of pollution |
| Disk-shaped smooth hemispherical, Disk-shaped smooth conical |
Areas with 1-2nd C3 for any type of pollution, areas with saline soils and industrial pollution not higher than 3rd CXNUMX |
| Plate porcelain |
Areas with 4th C3 near cement and oil shale processing enterprises, ferrous metallurgy enterprises, enterprises for the production of potash fertilizers, chemical plants producing phosphates, aluminum plants in the presence of workshops for the production of electrodes (anode mass workshops) |
| Porcelain rod normal execution (Lи/h ≤ 2,5) |
Areas with 1st C3, including those with hard-to-reach overhead lines |
| cymbal dipteran |
Areas with saline soils and industrial pollution (2-4th C3) |
| Disc-shaped with a strongly protruding rib on the lower surface (Lи/D > 1,4) |
Coasts of the seas and salt lakes (2-4th C3) |
| Porcelain rod special version (Lи/h > 2,5) |
Areas with 2-4th C3 for any type of pollution; areas with hard-to-reach overhead lines (2nd-3rd C3) |
| Rod polymer normal execution |
Areas with 1-2nd C3 for any type of pollution, including areas with hard-to-reach overhead lines |
| Rod polymer special version |
Areas with 2-3nd C3 for any type of pollution, including areas with hard-to-reach overhead lines |
* D - diameter of the disc insulator, cm; h - height of the insulating part of the rod insulator, cm; Li is the length of the creepage distance, see
 See other articles Section Rules for the installation of electrical installations (PUE). See other articles Section Rules for the installation of electrical installations (PUE).
 Read and write useful comments on this article. Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics: Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
A New Way to Control and Manipulate Optical Signals
05.05.2024
The modern world of science and technology is developing rapidly, and every day new methods and technologies appear that open up new prospects for us in various fields. One such innovation is the development by German scientists of a new way to control optical signals, which could lead to significant progress in the field of photonics. Recent research has allowed German scientists to create a tunable waveplate inside a fused silica waveguide. This method, based on the use of a liquid crystal layer, allows one to effectively change the polarization of light passing through a waveguide. This technological breakthrough opens up new prospects for the development of compact and efficient photonic devices capable of processing large volumes of data. The electro-optical control of polarization provided by the new method could provide the basis for a new class of integrated photonic devices. This opens up great opportunities for ... >>
Primium Seneca keyboard
05.05.2024
Keyboards are an integral part of our daily computer work. However, one of the main problems that users face is noise, especially in the case of premium models. But with the new Seneca keyboard from Norbauer & Co, that may change. Seneca is not just a keyboard, it is the result of five years of development work to create the ideal device. Every aspect of this keyboard, from acoustic properties to mechanical characteristics, has been carefully considered and balanced. One of the key features of Seneca is its silent stabilizers, which solve the noise problem common to many keyboards. In addition, the keyboard supports various key widths, making it convenient for any user. Although Seneca is not yet available for purchase, it is scheduled for release in late summer. Norbauer & Co's Seneca represents new standards in keyboard design. Her ... >>
The world's tallest astronomical observatory opened
04.05.2024
Exploring space and its mysteries is a task that attracts the attention of astronomers from all over the world. In the fresh air of the high mountains, far from city light pollution, the stars and planets reveal their secrets with greater clarity. A new page is opening in the history of astronomy with the opening of the world's highest astronomical observatory - the Atacama Observatory of the University of Tokyo. The Atacama Observatory, located at an altitude of 5640 meters above sea level, opens up new opportunities for astronomers in the study of space. This site has become the highest location for a ground-based telescope, providing researchers with a unique tool for studying infrared waves in the Universe. Although the high altitude location provides clearer skies and less interference from the atmosphere, building an observatory on a high mountain poses enormous difficulties and challenges. However, despite the difficulties, the new observatory opens up broad research prospects for astronomers. ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Water treatment with cellulose and air
25.04.2020
Combining a highly water-absorbing organic material with a solar energy-storing polymer results in an inexpensive material that quickly makes liquid from any body of water drinkable.
When it comes to converting large volumes of salty or polluted water into potable water, evaporation followed by condensation usually comes to mind. However, it is not easy and costly to implement this method in practice: installations and energy are needed to carry out the phase transition of water into a vapor state. Natural solar heat for these purposes is not enough.
Linköping University in Sweden has found a way to use the sun's energy to clean dirty water bodies. To do this, scientists have created a hybrid material, which is a highly porous airgel, 90% air. As part of the airgel, glucose and a special polymer PEDOT: PSS were combined. Cellulose is one of the most abundant organic compounds on earth. It is the main component of plant cell walls and effectively absorbs water. Polymer PEDOT:PSS, also organic, absorbs sunlight energy well. Especially the polymer likes "warm" infrared radiation.
The scientists glued the airgel to a "cushion" of porous foam floating on the surface of the water and estimated the rate of evaporation of the liquid. It turned out that the thermal energy of the native star, collected by the PEDOT:PSS polymer, heated and turned water into steam 4-5 times faster than without the use of airgel.
The evaporated liquid condensed on a plate located above the hybrid material and then flowed down a special trough into a collection container. The impurities and salts that were removed from the water remained in the airgel. The material can be washed and reused many times.
|
 Other interesting news: Other interesting news:
▪ GIGABYTE GB-BNi5G4-1050Ti barebone system
▪ Blue SN550 NVMe SSDs
▪ Cat face expression
▪ AMD AM1 platform (Kabini)
▪ Integrated amplifier at 1 THz
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library: Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ site section Parameters of radio components. Article selection
▪ article ENT diseases. Crib
▪ article Who published the first newspaper? Detailed answer
▪ article Plot. Travel Tips
▪ article Electronic ignition unit for a car on a thyristor. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Identifier of zener diodes. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article: Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024
|







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 See other articles Section
See other articles Section 