
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Philips DVDQ50 DVD player switching power supplies. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
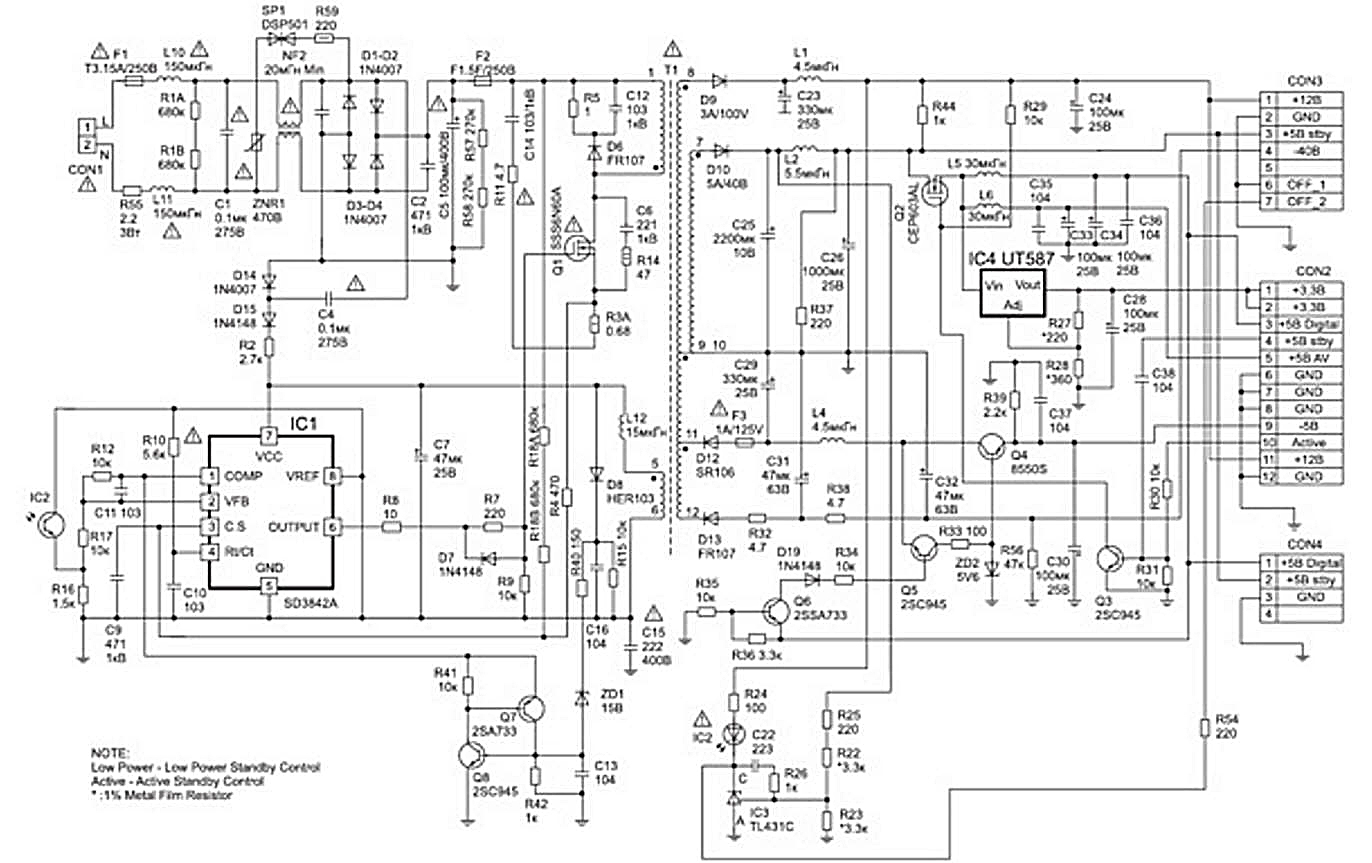
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Power Supplies PHILIPS is one of the world leaders in the production of DVD players. Let's consider the DVDQ40 and DVDQ50 models, which are very similar in circuit and design solutions. They are equipped with the same switching power supplies (UPS). For EU countries, this block is called EPM (Part No. 3122 427 22920 or 22930), and for other countries - Billion (Part No. 3139 248 70851). In the CIS countries, you can find a complete set of the player with both one and the other block. This article provides a detailed description of the Billion UPS and some features of its analogue - EPM. Switching power supplies Billion and EPM, as well as a DVD player, have two modes of operation: operational (operational) and standby (standby). The UPS provides the DVD player components with the appropriate voltages in each of these modes (see Table 1). This provides group, and for some channels also separate voltage stabilization. Both UPSs provide galvanic isolation of the rest of the DVD player from the mains. Billion Switching Power Supply (Part No. 3139 248 70851) The basis of the Billion UPS is a flyback pulse converter (inverter), which is assembled on an MIS transistor with an N-channel Q1 (SSS6N60A), a pulse transformer T1 EERL-28 and a PWM controller IC1 (SD3842A). The SD3842A chip is an analogue of the more common UC3842A chip. It is a PWM controller for switching power supplies that controls an external key on a field-effect transistor with an MIS structure. These microcircuits can be manufactured in different types of packages. The Billion power supply uses a chip in a DIP-8 package. The functional diagram of this microcircuit is shown in Fig. 1, and the purpose of the conclusions in table. 2. Note. The designation of the pins of the microcircuit in table. 2 corresponds to the schematic diagram of fig. 2. The SD3842A chip has the following features:
Table 1. DVDQ50 UPS Output Voltages
Table 2. Pin assignment of the SD3842A (UC3842A) PWM controller chip in the DIP-8 package
Consider the operation of the Billion UPS according to the schematic diagram, which is shown in fig. 2. The purpose of the main elements of the Billion UPS is given in Table. 3. The UPS mains rectifier is assembled on diodes D1-D4. An interference suppression filter is installed at its input, and a filter capacitor C5 is installed at the output. All of these chains are quite simple and do not require additional explanations. The ZNR1 varistor and the SP1 spark gap protect the UPS and the entire device from overload in case of a significant increase in the mains voltage, for example, during a lightning discharge (lightning). Resistor R55 limits the charge current of capacitor C5, thereby protecting the rectifier bridge diodes from overload when the device is connected to the network. DC voltage 290...310 V (for mains ~220 V), obtained at the output of the mains rectifier, provides power to the pulse converter. Operation of the UPS converter in operating and standby modes Current limit output switch Q1 In these modes of operation of the UPS, the output. 8 of the microcircuit, a voltage of 5 V is formed and the converter operates at a fixed frequency (approximately 58 kHz), which is determined by the values of the parts of the timing chain C10 R10. The positive pulses generated by the microcircuit with the pin. 6 IC1 through resistors R8 and R7 are applied to the gate of transistor Q1 and open it. Since the transistor has an inductive load (winding 3-1 T1), its current will gradually increase, creating an increasing positive voltage on the current sensor R3A, which is fed to the pin through the limiting resistor R4. 3 (CS input) chips. From the functional diagram of MS IC1 SD3842A (see Fig. 1) it can be seen that to the pin. 3 is connected to the non-inverting input of the current sensor comparator (CURRENT SENSE COMPARATOR). The inverting input of this comparator receives a control voltage from the error amplifier (ERROR AMP). When the sawtooth voltage from the current sensor exceeds the error control voltage, a log level will appear at the output of the comparator. "1", which, controlling the subsequent logic circuits of the microcircuit, will ensure the locking of the upper and unlocking the lower transistor of the totem output of the microcircuit. The voltage at the output of IC1 SD3842A (pin 6) will decrease to zero and the output switch Q1 (see Fig. 2) will close. The process described above provides a current limiting of the output switch Q1 in each period of operation of the circuit, which protects the switch from current overload.
Secondary power supply circuits The following voltages are formed in the secondary circuits of Billion UPS using pulse rectifiers:
Moreover, the first three of these voltages provide power to the corresponding circuits of the player both in standby and in operating modes. In operating mode, on the output. 10 connector CON2 receives an Active signal with a log level. "1", which opens the key transistor Q30 through the divider R31 R3. Since the collector of this transistor is connected directly to the gate of the power switch Q2, it will also open, and a voltage of 5 V through this switch and additional decoupling filters will enter the power circuits of the digital and analog parts of the device. From the drain of transistor Q2, power will also be supplied to the 3,3 V stabilizer, which is made on the IC4 chip (UT587). The required output voltage (3,3 V) of this stabilizer is set by a voltage divider across resistors R27 and R28. In addition, the 5 V voltage from the drain of Q2 is supplied to the emitter of the pnp transistor Q6. Due to the bias from the divider R35 R36, the key on the transistor Q6 opens and ensures the unlocking of the key Q5, which, in turn, ensures the operation of the -5 V parametric voltage regulator on the transistor Q4 and the zener diode ZD2. Group stabilization of UPS output voltages Group stabilization of the output voltages of the UPS is carried out due to the control loop of the OOS, which includes the stabilization stage (controlled zener diode) IC3 (KIA431A) and optocoupler IC2 (TCET1108G). The LED anode of optocoupler IC2 is connected to a secondary voltage of 12 V, and the cathode is connected to the output of controlled zener diode IC3, i.e. the current through the LED is determined by the output voltage of the zener diode IC3. Table 3. Purpose and types (ratings) of the main elements of Billion UPS
Assume the UPS output voltages are rising. The voltage at the regulating input of the zener diode IC3 will also increase, which comes there from a source of 5 V through the divider R25 R22 R23. The output voltage of IC3 rises, which means that the diode current of the optocoupler IC2 decreases, which will increase the junction resistance of the optocoupler transistor and decrease the DC voltage at the pin. 2 IC1 chips. This voltage is amplified and inverted by the error amplifier inside the microcircuit, which leads to an increase in the voltage at the output of this amplifier (pin 1 in Fig. 1). As already noted, the error voltage inside the microcircuit is supplied to the inverting input of the comparator (CURRENT SENSE COMPARATOR), and the sawtooth voltage from the current sensor is supplied to the non-inverting input of this comparator. Now, to turn off the power switch, a slightly larger value of this voltage is required, which means that the output field effect transistor Q1 will be open for a longer time. This will lead to a decrease in the duty cycle of the pulses at the output of the microcircuit and, consequently, to a decrease in the output voltages of the UPS to nominal values. Similarly, but up to the "vice versa", the circuit works in the case of a decrease in the output voltages of the power supply converter. Start mode When the DVD player is connected to the network, the UPS capacitor C7 is charged from the network through an interference suppression filter and a start-up circuit consisting of capacitor C4, diodes D14, D15 and resistor R2. When the voltage across the capacitor C7 and pin. 7 of the IC1 microcircuit exceeds the threshold value (16 V), the UVLO circuit of the microcircuit is activated and the voltage from the capacitor C7 through this circuit is supplied as a power supply to the main components of the microcircuit. With pin. 8 IC1 reference voltage of 5 V is applied to the timing circuit R10 C10 and to the phototransistor collector of optocoupler IC2. The UPS starts up, voltage pulses occur in the TPI T1, which, from the pin. 5 T1 through the inductor L12 and diode D5 recharge the capacitor C7, and the power supply smoothly enters one of the stable operating modes (working or standby). There may be several reasons why there may be no or insufficient recharging of the capacitor C7:
intermittent mode If for some reason the capacitor C7 is not recharged, the voltage on it and on the pin. 7 IC1 will decrease. When it falls to the lower threshold level (10 V), the UVLO circuit in IC1 will turn off the power to a number of nodes in this chip. The voltage on the pin will also disappear. 8, which was fed to the timing circuit, the phototransistor of the optocoupler IC2 and the UPS will turn off. Its power consumption will be reduced to a minimum level. Capacitor C7 will again be charged through the trigger circuit to the upper threshold voltage (16 V), i.e. another start attempt will occur. If the reason for the lack of recharging of the capacitor C7 has not disappeared, then start attempts will be repeated. This mode of operation of the UPS is called intermittent. It protects the UPS and the entire machine from possible overload. This mode is usually accompanied by a characteristic sound - "tsik", which emits a pulse transformer T1. Voltage overload protection circuit The basis of this circuit is a bi-stable cell on transistors of different conductivity Q7 and Q8. This scheme was widely used in domestic televisions. For example, in the USU-15 touchscreen device of the popular 3USCT TV, there were eight such cells. It has two stable states: both transistors are off or both transistors are open to saturation. In addition, the circuit contains a separate pulse rectifier on the diode D8 and a threshold device on the zener diode ZD1. During normal operation, the voltage at the output of the rectifier D8 is less than 15 V. The Zener diode ZD1 and the cell transistors are locked. When the UPS voltages rise above normal, the voltage at the output of the rectifier D8 will exceed the level of 15 V, the zener diode ZD1 opens and the trigger voltage is supplied to the base of Q8. Transistor Q8 turns on, enabling transistor Q7 to turn on. At the same time, due to the fact that the collector current of each of these transistors is the base current of the other transistor, the cell will remain in the open state, shunting the pin. 1 chip IC1 and blocking its work. Some malfunctions of the Billion UPS and recommendations for its repair 1. If the fuse F1 is blown, then the protective varistor ZNR1, bridge diodes and power transistor Q1 should be checked for breakdown. Somewhat less often, the capacitor of the smoothing filter C5 and the capacitors of the noise suppression filter break through. With this defect, the current sensor R3A and the limiting resistor R55 may burn out. 2. The totem output of the PWM controller chip (pin 6) usually fails for the following reasons:
3. The UPS may not start for the following main reasons:
4. The UPS may go into intermittent mode for the following reasons:
5. In the absence of one or more output voltages of the power supply, check the switching switches, stabilizers and rectifiers. All these chains have been discussed in sufficient detail above. Features of switching power supply EPM Unfortunately, the author could not find the diagram of this UPS. Therefore, we will make a small review of this block according to the available information. To designate positional part numbers, PHILIPS very often uses letters that are not familiar to us (C325, IC501, etc.), but only numbers. More specifically, four-digit numbers. For example: 7101, 2107 etc. Such designations, out of habit, make it extremely difficult both to read the circuit diagrams and to search for details on the boards. Let's decipher these notations. The first digit from the left (the most significant digit of the four-digit number) indicates the type of part. Although there are exceptions, the following 1st digit code is generally used:
The next, second digit is the functional node to which this element belongs. Here the system is more difficult to trace, but for the EPM UPS parts that are located in the primary circuit, the 2nd digit is 1, and for the secondary circuit parts it is 2. The third and fourth digits are the part number. The basis of the EPM UPS is a flyback pulse converter (inverter), which is assembled on a PWM controller 7101 of the TY720xx series, an output high-voltage MOS transistor 7125 and a pulse transformer with position number 5131. The conversion frequency of 125 kHz is set by a capacitor 2107, which is connected to pin. 5 microcircuit 7101. The optocoupler has a position number 7102, and 7201 is a controlled zener diode of the TL431 type. Resistors 3126, 3127 and 3128 are used as the output transistor current sensor. Line rectifier diodes are numbered 6112-6115. In general, the circuit and operation of this UPS resembles the circuit and operation of the Billion UPS, so the repair procedure for this unit is similar to the previous one. Literature
Author: Igor Bezverkhny
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ User identification by badge ▪ Subcutaneous fingerprint scanner ▪ Loneliness damages the brain
▪ section of the site Household electrical appliances. Selection of articles ▪ Jeans article. History of invention and production ▪ article What are shooting stars? Detailed answer ▪ article Head of the postal car. Job description ▪ superman article. Focus Secret
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: