
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Automatic charger for car batteries. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
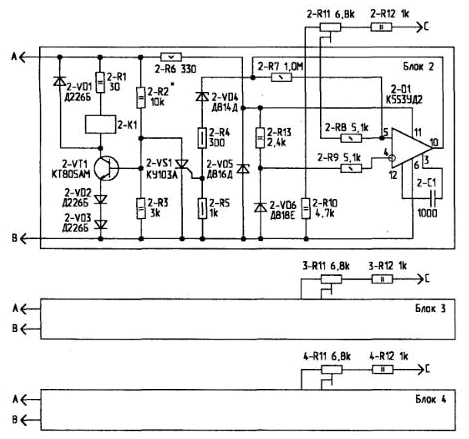
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells In order to maximize the "life" of rechargeable batteries (AB), it is advisable to charge them according to the law. Woodbridge. those current, the value of which decreases exponentially. In principle, it is possible to provide such a mode of changing the charging current, but the circuit turns out to be rather complicated. It is much easier to provide a stepwise decrease in the charging current, which I propose in this charger. In practice, it is enough to limit ourselves to two stages of current reduction, and the third stage is the termination of the charge. At the same time, the electrolyte in the battery does not boil, which favorably affects the service life of the batteries. The circuit with a quenching capacitor in the circuit of the primary winding of a power transformer is taken as a basis. In it, the value of the charge current is set by choosing the capacitance of the quenching capacitor. On the other hand, it is also impossible to recharge batteries, since this also adversely affects their service life. In practice, it was found that at the beginning of charging for about 3 hours (depending on the degree of discharge of the battery), the voltage on the battery is kept at 5 V and only at the end of charging smoothly increases to 13,2 V. The increase in battery voltage is used to assess the battery charge and reduce the charging current or completely stop charging. The circuit has three sections of quenching capacitors. There are two charging modes: manual (turning the capacitors on and off using switches) and automatic (turning off the sections one by one when the voltage rises). In manual mode, it is possible to charge 6-volt and 24-volt batteries. In manual mode, using the switches, you can set one of the following charge currents (for a 12-volt battery):
In automatic mode, at low voltage on the battery, three relays (2-K1.3-K1 and 4-K1) are first turned on and all three sections of capacitors are connected with their contacts. When the voltage on the battery increases as a result of the charge, three threshold devices (PD) are sequentially triggered, made according to the same schemes (Block 2, Block 3, Block 4). relays 4-K1, 3-K1, 2-K1 are released in turn and the corresponding capacitors are turned off. PU is made on an operational amplifier using a thermally compensated zener diode 2-VD6 as an exemplary voltage driver. The large gain of the op-amp allows you to obtain a high accuracy of the response threshold. If the voltage on the battery is below the threshold of the PU, then the output of the op-amp is low voltage, and the opening voltage is not supplied to the control electrode of the thyristor 2-VS1. At rest, the transistor switch 2-VT1 is open, and the relay 2-K1 is turned on. When the voltage at the battery increases and exceeds the exemplary one, a high level appears at the output of the op-amp, the zener diode 2-VD4 breaks through, and an opening voltage is supplied to the control electrode of the thyristor 2-VS1. An open thyristor shunts the 2-R3 resistor and the input circuit of the transistor switch, which closes, and the 2-K1 relay releases. There are no scarce radio components in the AZU. As a power transformer 1-T1 for powering automation, you can use any transformer with a power of 30 ... 50 W with a voltage on the secondary winding of 24 ... B included in series). A converted transformer is used as a power transformer 25-T36. TS30. in which all secondary windings are removed and new ones are wound with PEV wire 6,3 mm, 1 turns on each coil (two layers of 2 turns). After assembling the transformer, the windings are connected in series, and the output is about 270 V. In principle, a ready-made power transformer is suitable, providing an output voltage of 3,0 V (60 V) at a power of about 30 watts. In this case, the capacities of the quenching capacitors may differ. In the ACS, relays of the type are used. RKS3 (passport RS4 501.200) with powerful contacts and winding resistance 180 Ohm. Diodes 1-VD5.1-VD8 of the charging rectifier are installed on heat sinks with an area of 200 cm2, transistors 2-VT1, 3-VT1, 4-VT1 - on heat sinks with an area of 10 cm2, and zener diodes 2-VD5, 3-VD5, 4-VD5 - on heat sinks with an area of 10 cm2. Diodes 1-VD1...1-VD4 can be applied KD202 with any letter; 1-VD5, 1-VD8 - any with IMAX=10A (D243. D246, etc.) AZU is assembled in a metal case with dimensions of 400x200x300 mm.
Setting up a properly assembled AZU actually comes down to setting thresholds. PU1, PU2 and. Buzzer using trimmer resistors 2-R11, 3-R11 and 4-R11. To do this, the PU inputs are connected to a laboratory power source with smooth adjustment of the output voltage in the range of 12 ... - In for PU16) and adjusted resistors 13,5-R14,0, 2-R14,5, 1-R4, the necessary response thresholds are set (before setting, the adjusted resistors are brought to the maximum response threshold). As tuning resistors, it is better to use PPZ-type potentiometers. In my device, I set the following thresholds for switching:
In the event of a power failure in the network and its appearance, all three sections may first turn on, but subsequently the AZU will be set to the mode that it was before the power failure. It should be noted that this AZU must be used only with the battery connected. A short circuit at the output of the AZU does not lead to its failure. Therefore, to check its performance in manual mode, you can simply short-circuit the output of the AZU. In this case, the currents will be slightly higher than with the battery connected. In automatic mode, in case of poor contact at the battery terminals, the output voltage rises sharply (more than the threshold), and the AZU turns off the battery charging. The AZU itself does not fail, but the AB does not receive a full charge. To ensure good contact, it is desirable to use wires with cap collars and a bolt tie. Author: D.S.Babyn, town. Kelmentsy, Chernivtsi region
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ MAX17509 Dual Channel 16V 3A DC/DC Regulator ▪ Gaming laptop Maingear Pulse 17 ▪ New small craft tracking technology
▪ section of the Electrician website. PUE. Article selection ▪ article by Natalie Clifford Barney. Famous aphorisms ▪ article In which restaurant did Colonel Sanders eat the worst chicken of his life? Detailed answer ▪ Hydrangea article. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: