Transistor switch with overload protection. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Clocks, timers, relays, load switches
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
Transistor switches are used as terminal devices of electronic control systems. With their help, a DC power network is remotely connected to various electromagnetic mechanisms. In these mechanisms, malfunctions are possible in the form of a short circuit between the turns of the winding, which leads to an increase in the load current in excess of the norm and may be the cause of the failure of the transistor switch. Therefore, the transistor switch must combine the functions of switching and protection [1].
There are many similar devices [2,3]. For some electronic systems, for example, automotive, preference is given to transistor switches with "latch" protection [4].
Such protection eliminates the possibility of overheating of the elements of the transistor switch when the load current is exceeded.
The circuit in Fig. 1 is an example of such a device. It does not have additional resistance in the collector circuit of the terminal transistor, as is the case in [5], due to which the voltage on the load when the device is turned on approaches the voltage of the power source.

(click to enlarge)
Device parameters:
- Supply voltage......+12 V
- Rated switching current.......2 A
- Voltage drop across the switch.......0,5 V
- Breaking current ....... 2,3 A
The transistor switch consists of a start-up switch on transistors VT1, VT2, resistors R1 ... R4 and capacitor C1, a preliminary stage on transistor VT3 and resistors R6, R7, a power switch on transistor VT4 and resistor R5 and a protection circuit on a zener diode VD1 and resistor R8.
The device works as follows. When the supply voltage is applied to the device, the transistors VT1, VT3 and VT4 are closed, the transistor VT2 is open with a positive potential coming through the resistor R3 to its base, and shunts the base-emitter junction of the transistor VT3. When a control signal appears at the input of the device (when the SA1 switch is closed), the transistor VT1 opens, shunts the base-emitter junction of the transistor VT2, the latter closes, and the capacitor C1 is charged through the circuit: control input resistor R4 - junction b-e VT3. In this case, the voltage at the base of the transistor VT4 is enough to open it to saturation. In the absence of a short circuit, the voltage at the VT4 collector becomes maximum, and its collector current enters the load. The zener diode VD1 breaks through, this is enough to keep the transistor VT3 open.
If there is a short circuit or overload in the load circuit, the voltage at the collector VT4 becomes less than the breakdown voltage of the zener diode VD1, and the transistors VT3, VT4 close, turning off the load. To resume operation of the device after the cause of the overload has been eliminated, it is necessary to disable and re-enable SA1.
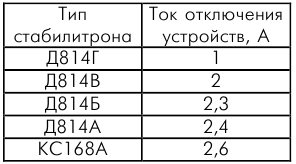
Changing the protection threshold is achieved by selecting the type of zener diode, as indicated in the table:
The device is assembled on a double-sided printed circuit board (Fig. 2).

References:
- Microelectronic electrical systems / Under the editorship of Yu.I.Konev. - M.: Radio and communication, 1987. - 143 p.
- Optoelectronic keys with current protection//Radio. - 1990. - No. 8. - P.57.
- A. s. 1473682 USSR.
- Polyak D.G., Yesenovsky-Lashkov Yu.K. Electronics of automobile control systems. - M.: Mashinostroenie, 1987, S. 106,107.
- Esaulov N. Adjustable electronic fuse//Radio. - 1988. - No. 5. - P.31-32.
Author: O.L. Sidorovich
 See other articles Section Clocks, timers, relays, load switches.
See other articles Section Clocks, timers, relays, load switches.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Toshiba TC3567x series chips supporting Bluetooth 4.1 LE
23.07.2016
Toshiba announced the release of TC35678FSG, TC35678FXG and TC35679FSG chips supporting Bluetooth Low Energy (LE) 4.1 wireless interface. According to the manufacturer, they have the lowest energy consumption in their class, consuming half the energy compared to their predecessors.
The supply voltage of new microcircuits can lie in the range of 1,68-3,6 V. At a voltage of 3,0 V, the current in transmit mode is 3,6 mA, in receive mode - 3,3 mA, and in sleep mode it does not exceed 100 on the. As stated, a beacon with such a microcircuit can work from one CR2032 element for more than a year.
The TC35678FXG and TC35678FSG models feature 256 KB of flash memory. Between themselves, these microcircuits differ in design: TC35678FXG is available in a QFN60 package with dimensions of 7 x 7 mm, which made it possible to increase the number of GPIO lines from 16 to 32, and TC35678FSG - in a QFN40 package with dimensions of 5 x 5 mm. Same package selected for TC35679FSG.
Toshiba's new Bluetooth 4.1 LE chips are designed for wearable electronics, medical devices, smartphone accessories, remote controls and toys. Their trial samples are already available. The manufacturer expects to start serial deliveries of TC35678FXG at the end of this year, and deliveries of two other products - at the beginning of 2017.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ The computer was taught to distinguish male text from female
▪ Helioboat
▪ Transcend USB 3.0 Flash Drives 128GB and 256GB
▪ Worm is enough for one tape
▪ First 200V DirectFET Transistor from IR
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Home workshop. Article selection
▪ article by Ivana, who does not remember relatives. Popular expression
▪ Article What color is Mars? Detailed answer
▪ article Sassafras red. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
▪ article Repair and modernization of the electric fan SMF-3RDEA. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Cuts friction. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese



 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: