
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DC voltage converter 12 V battery to AC voltage 220 V 50 Hz. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
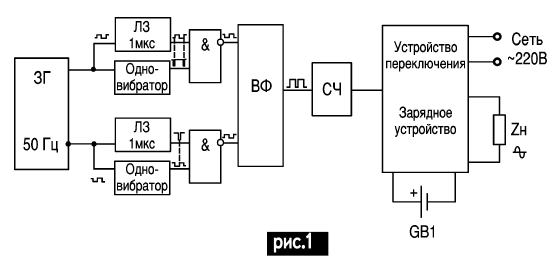
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Voltage converters, rectifiers, inverters Many voltage converters are described in the literature, but almost all of them have serious drawbacks. I have designed a converter devoid of these shortcomings. In doing so, I proceeded from the following criteria: 1. The maximum power delivered to the load must be at least 1 kW. This condition forced us to abandon powerful transistors in the power section (which are a "sore spot" in 100-300 W power converters) and use powerful trinistors. 2. Close to sinusoidal output voltage at the output of the converter is achieved by selecting the capacitance of a capacitor connected in parallel with the load or by using current inverters in the power section. 3. Elimination of "through" currents. This problem is very relevant and lies in the fact that the turn-on time of a transistor or trinistor is less than the turn-off time, i.e. one device turns on and supplies current to the primary winding of the transformer, and the second, which should already be off at this moment, also supplies current to the winding. I solved this problem by reducing the duration of the control pulses by a time sufficient to completely close the trinistor. 4. Automatic shutdown of the device when the battery is deeply discharged is achieved by using a threshold device. 5. Automatic switching on of the converter in the event of a power outage and charging the battery (with disconnection from the charger when fully discharged) in the presence of mains voltage are ensured by using a circuit on a relay and an automatic charger. The functional diagram of the converter is shown in Fig.1.
In the presence of a mains voltage of 220 V, the load is connected to the network, and the battery is connected to the charger. In the event of a mains voltage failure, 12 V battery voltage is supplied to the voltage converter and a load is connected to it. All these operations are carried out by the switching device, which includes an automatic charger. The master oscillator (MG) generates rectangular pulses with a duration of 10 ms and a frequency of 50 Hz. From the outputs of the ZG, the pulses arrive at the delay line (LZ) and the single vibrator. The LZ serves to ensure that the level of the log. "1" comes to the coincidence circuit 1 μs later than the pulse from the single vibrator. The duration of the single vibrator pulse is subtracted from the duration of the MO pulse and must be greater than the duration of the blocking of the used trinistors. The output pulse shaper (WF) generates control pulses to the control electrodes of the trinistors of the power unit (MF). The schematic diagram of the control system for the power part of the voltage converter is shown in Fig. 2, and the voltage diagrams at characteristic points are shown in Fig. 3.
ZG is made on the elements AND-NOT DD1.1, DD1.2. The pulse frequency at its output is set using a frequency meter by selecting the resistor R1. Frequency pulses of 50 Hz are fed through the LZ on the integrating chain R2C2 to the input DD1.4. The pulse delay time is approximately 1 µs. The input 13 DD1.4 receives pulses of a single vibrator DD2.1, the triggering pulses of which are the positive voltage drops of the ZG pulses. The duration of the single vibrator pulses is determined by the elements R3C3. The delay line is used to ensure that the positive voltage drop of the ZG pulse arrives at input 12 DD1.4 later than the negative voltage drop of the one-shot pulse appears at input 13 DD1.4, and there is no negative surge of the pulse based on the VT1 transistor with a duration equal to the response time trigger DD2.1. The pulse duration of the single vibrator is chosen to be approximately 20 μs based on the reliable closing of the trinistors of the power section of the TCH125 type, the on-time of which is 6 μs. When using other types of trinistors, it is necessary to recalculate the values of R3 and C3. A control positive pulse with a duration of 2 μs is removed from the collector of transistor VT9,98. Similarly, an impulse Uу2 is generated, which is in antiphase with the impulse Uу1. The power and value of resistors R8 and R9 are selected in accordance with the type of transistors used: R9 = R8 < 12 V / Iopen, PR8 = PR9 = 144 / R8 = 144 / R9. If several batteries connected in series are used in the voltage converter, the dimensions of the transformer T1 will be significantly reduced, and to obtain the required power at the load, trinistors with a lower current can be selected. The circuit design of the power part of the converter can be most simply solved by using powerful lockable thyristors (Fig. 4).
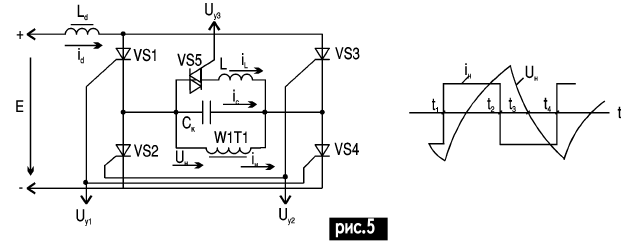
The load of the inverter is the primary winding of the transformer T1. The 220 V load is connected to the secondary winding of the transformer. The transformer is calculated according to the methodology that has been repeatedly published in the educational literature. A capacitor is connected in parallel with the load to obtain a voltage shape close to sinusoidal. Its capacity depends on the load, it is determined experimentally. In the presence of a control pulse Uу1, thyristors VS1 and VS4 are turned on and VS2 and VS3 are turned off. The winding of the transformer w1 is connected with the left end to the positive power bus, and with the right end to the negative one, and the current in flows, as shown in Fig. 4. In the absence of Uy1 and the presence of Uy2, VS1 and VS4 are turned off, the voltage and current of the winding w1 change direction. When locking VS1 and VS4 at the moment t2, despite the arrival of the unlocking pulse to VS2 and VS3, the load current iн due to the presence of the inductance Lн will tend to maintain its direction. In order to open the way for the load current after locking VS1 and VS4, the thyristors are shunted with diodes VD10 - VD40. Therefore, the load current in at t2 A more complex circuit solution for constructing the power part of the converter is the use of a current inverter shown in Fig.5.
Current inverters with an inductive-thyristor controller are widely used in industry, for example, in uninterruptible power supplies, their power reaches hundreds of kilowatts. The output voltage waveform is close to sinusoidal, which allows them to be used without filters on the AC side. Due to the large inductance of the smoothing inductor Ld, the inverter current id (source current E) can be considered perfectly smoothed. A positive pulse Uy1 opens thyristors VS1 and VS4, a positive pulse Uy2 opens thyristors VS2 and VS3. The input current of the inverter id, due to the periodic switching carried out by the thyristors, is converted in the diagonal of the bridge into an alternating current of a rectangular shape. Capacitor Sk - switching. It serves to create a blocking voltage on transistors. To eliminate the strong dependence of the voltage on the load on the magnitude of the load, an adjustable AC voltage converter with an inductive load (elements VS5, L) was used. The current it consumes has the 1st harmonic, the phase shift of which relative to the voltage is always equal to π/2. The amplitude of the 1st current harmonic depends on the control angle α, which is equal to the phase shift of the control pulses on VS5 relative to the moment of voltage change Un. Therefore, this voltage converter circuit is considered as a controlled inductance. By adjusting iL by changing the angle α using the control circuit, it is necessary to set the same current iL, at which the shift angle β between the current iн and voltage Un remained unchanged, then the voltage on the load will be constant when the load current changes. Formulas for calculating Sk, Ld, L. For normal switching, the shift angle β between voltage and current must be β≥ωtoff, where ω = =2πf = 314 s-1 angular frequency; toff - thyristor turn-off time; tgβ = bc/(ynsosϕn tgϕn), where bc = ωC is the conductance modulus of the capacitor Sk; yn = 1/zn load conductivity modulus. Active load power Рн = Еid = =Unincosϕ. Reactive power of the capacitor Qc = = U2нωСк. Reactive load power Qн = Рнtgϕн. Reactive power consumed by the inverter Qi = Qc - Qн. Load voltage Un = 0,35πE[1 + (ωCk /yn cosϕn - tgϕn)2]1/2. Capacitance Ск = Рн(tgβ + tgϕн)/ωU2н. Choke inductance Ld≥ {E[1 - cos(β + π/6)]cosϕ}/72fPнcosβ if β<π/6. Ld≥ E2sin2β/144fPnsos2β if β≥π/6; Inductive load L≥1,4Uнsin(α- π/2)/ωiL ≥ 1,4Uн.ωiL, where α is the triac control angle VS5, iL = Iw1maxsin(α - π/2). For current iL, triac VS is also selected. A schematic diagram of the control of the triac VS5 is shown in Fig.6. This circuit is built on a DD2.1 single vibrator, which produces pulses with a duration of no more than 10 ms (the capacitance of capacitor C1 is selected). The single vibrator is started by impulses from the control circuit (Fig. 2). The duration of the pulses is regulated by the resistor R1. From the collector of the transistor VT2, the control pulses of the triac Uу3 are taken. The value and power of the resistor R3 depend on the opening current of the selected triac VS5 in the power section: R3 < E/I open; РR3==E2/R3. If the required load power does not exceed 200 ... 300 W, the power part of the converter can be made on transistors according to the diagram in Fig. 7. The absence of the effect of "through currents" is ensured by the circuit design of the control system according to Fig.2. Author: A.N.Mankovsky
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Instead of drilling teeth - remineralization with electricity ▪ Samsung WB2200 60x optical zoom camera
▪ site section Digital technology. Article selection ▪ article by Walter Lippman. Famous aphorisms ▪ article What kind of pornographic scene is in Woe from Wit? Detailed answer ▪ article Internal labor regulations ▪ article ZCH with telegraph filter. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese



 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: