
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Regeneration of galvanic elements. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells Galvanic cells intended for powering electronic watches and calculators (the so-called "tablet cells") are no longer in short supply. But still, sometimes there is a problem of extending their service life or restoring performance. It is for such cases that the device described here is designed. The diagram of the charger is shown in Fig.1. It works according to a well-known principle - charging a recoverable galvanic cell with an asymmetric current.
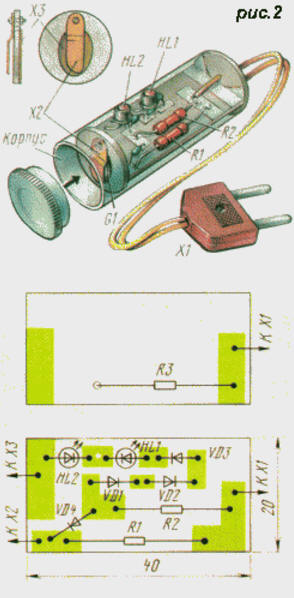
The charging current of the G1 element connected to the contacts X2 and X3 flows through the diode VD4. The average value of this current is determined mainly by the values of the resistors R2, R3 and in our case does not exceed 2.5...3 mA. And the discharge current of the element, flowing through the resistor R1 and the LED HL2 opened in the opposite direction, is approximately 0,15 mA. The LEDs HL1 and HL2 serve as indicators of the state of the restored element, the diodes VD1-VD3 are the limiters of the degree of its charge. The cell is charged during the positive half-cycle of the mains voltage. If the element is highly discharged, then the voltage on it, as a rule, does not exceed 1 V. Therefore, the voltage across the series-connected diode VD7 (0.7 V), LED HL2 (2 V) and element G1 will be 3.7 ... 4 V. In the same time, the total voltage across the series-connected diodes VD1, VD2, VD3 (0.7 V each) and the HL1 LED (2 V) will be approximately 4.1 V. This means that the current in this case will flow (mostly) through the element, and the HL2 LED will glow much brighter than the HL1 LED. And since they have different glow colors, it is easy to determine what state the element is in. In this case, the HL2 LED should glow brighter - green. As the element is restored, the voltage on it will increase, which means that now most of the current will flow through the HL1 LED, its brightness will begin to increase, and the brightness of the HL2 LED, on the contrary, will weaken. By the end of the cell regeneration cycle, the red LED will increase in brightness and the green LED will barely glow. In principle, the duration of the recovery cycle of the element can be arbitrarily long - you should not be afraid of the failure of the element, since the charging current flowing through it is small. When constructing such a device, the main attention should be paid to safety - after all, the element being restored is galvanically connected to the network. A possible design and installation of parts of the proposed device for regenerating electronic watch batteries are shown in Fig. 2. Its cylindrical body, which protects the user from electric shock or destruction of the element (rarely, but it happens!), Is a plastic medicine container with an inner diameter of 20 and a depth of 48 mm. Of course, another case of suitable size will do, but it must be made of insulating material, for example, a container from under the film. In this case, it will be necessary to adjust the dimensions of the printed circuit board and the insert with contacts for the regenerated element accordingly. The printed circuit board is made of double-sided foil fiberglass 2 mm thick. It should fit snugly into the body and securely linger in it. A hole is made in the bottom of the case for a network wire, the length of which is only a few centimeters. This is done on purpose so that it is convenient to install the element into the device when the wire plug (X1) is inserted into the mains socket. In the side wall of the case, in accordance with the location of the LEDs, two viewing "windows" with a diameter of 4 mm are drilled.
The basis of contacts X2 and X3, fixing the restored element, is an insert with a diameter of 20 mm made of one-sided foil fiberglass 2 mm thick. An oval hole 9x13 mm in size was cut out in it and a hole 2 mm in diameter was drilled for the screw (or rivet) of the spring contact X2. The contact function is performed by a plate with a diameter of 20 mm made of tinned foil or tin, soldered to the foil side of the insert. With this plate, the insert is soldered to the current-carrying pad on the printed circuit board, to which the anode terminal of the HL2 LED is connected. This is how a negative contact is formed for the element being restored. The positive contact (X2), cut out of brass, should rotate around the screw (or rivet) with little effort, and on the foil side it is connected to the cathode terminal of the VD4 LED. The element to be restored is inserted into the oval hole of the insert with the minus side down (in the middle or closer to the edge), depending on its dimensions, and pressed with a spring contact. Then the case is closed with a plastic cover, after which the device can be connected to the network.
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ New features of the SPWF01SA.11 WiFi module ▪ The phone is controlled by sight ▪ Satellite to print solar panels in space ▪ Created an artificial pancreas ▪ New video discs store up to four hours of video on each side
▪ section of the site Data transfer. Article selection ▪ article Human security in the information space. Basics of safe life ▪ article What is UEFA? Detailed answer ▪ article Alfalfa townsville. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: