Battery discharge signaling devices. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
It is known that discharging a battery to a voltage level below the allowable voltage for each specific type leads to a decrease in its resource or can completely damage it. To prevent this from happening, it is necessary to periodically monitor the voltage on the battery, which is inconvenient, given that this requires a voltmeter.
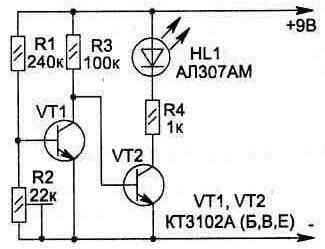
Rice. 5.20. indicator light
The voltage level signaling circuits have been repeatedly published in magazines, however, the devices proposed in this article have fewer details and are characterized by low consumption.
The construction of the following circuits is based on the voltage level indicator on the transistor (VT1) operating in the microcurrent mode. At the same time, the transistor has a very high gain and when the supply voltage changes by 0,1 V, it switches from the locked state to the open one.

Rice. 5.21. Sound indicator
On fig. 5.20 shows a diagram that allows you to show (by the glow of the HL1 LED) a decrease in the voltage level on the batteries below the permissible norm. The LED can be of any type. The voltage level at which the signaling device is triggered is adjusted by resistor R2 (it is more convenient to use a multi-turn one, such as SP5-2).
But sometimes it is better to have an audible alarm, since the glow of the LED can be overlooked in time.

Rice. 5.22. The topology of the printed circuit board of the sound indicator (the piezo emitter is installed on the side of the printed conductors above the board)
On fig. 5.21 shows a diagram of an audible signaling device on a HF1 piezoelectric emitter (ЗП-1 or any similar). The level of the controlled voltage can be from 2 to 30 V, but when using a circuit with a voltage of more than 9 V, it is necessary to select the value of the resistor R5 so that the circuit, with a sufficient volume of the piezo sound, consumes no more than 1 ... 2 mA in the alarm mode . The sound frequency depends on the capacitor C1, and it can be changed.
Coil L1 contains 600 turns of PEV wire with a diameter of 0,08 mm (0,1 or 0,12 mm), wound on two rings glued with glue, size K10x6x3 mm, made of ferrite 600NM1 or 1000NM1. The topology of the printed circuit board is shown in fig. 5.22.
Publication: cxem.net
 See other articles Section Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells.
See other articles Section Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive foam paper
06.06.2000
Styrofoam is widely used for packaging fragile products - a porous plastic used to make packaging inserts for boxes with equipment and balls or flakes poured into such boxes to soften shocks. However, the synthesis of styrofoam consumes a non-renewable raw material - oil, gases that are dangerous for the Earth's ozone layer are used in its production, and the used packaging practically does not decompose, accumulating in nature.
The German inventor Friedrich Pries from Hamburg founded a small company that produces foamed packaging material from waste paper using the technology he developed. Waste paper is finely cut, then ground into individual fibers, which are mixed with starch.
Granules are pressed from this mass. They are subjected to high pressure in a sealed apparatus with superheated water vapor, and then the pressure is abruptly released. The granules foam, forming porous balls that absorb shocks better than styrofoam.
Packing inserts are also obtained, only the paper pulp is preliminarily poured into molds. This material is cheaper than styrofoam and quickly decomposes in a landfill by microbes and fungi.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Zeptoseconds measured
▪ Smart collar
▪ Silent planes on owl wings
▪ Diagnosing a cold before symptoms appear
▪ A new type of artificial leather
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the Antenna website. Article selection
▪ article Phillips screwdriver. History of invention and production
▪ article Who discovered Alaska? Detailed answer
▪ article Plum prickly. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
▪ article Gas-discharge lighting - from the accumulator. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ Periscope article. physical experiment
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese



 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: