Increased battery life. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
Many battery powered devices require that the output voltage be maintained at a constant level, regardless of whether the battery voltage is below or above this level. This requirement is easily met when the battery voltage exceeds 15 V [1]. But for low-voltage batteries, the solution to the problem can be very difficult. By providing a floating battery negative terminal that is normally grounded when powered positively, it is possible to simplify the construction of a positive diode reverse converter.
The voltage of the battery supplying the proposed device can be in the range from 3 to 30 V (see figure). The switching regulator model LT 1072 controls the transfer of power from the input to the output. The output Vsw of the regulator is the collector of an npn transistor connected in a common emitter circuit; thus, the flow of current into the regulator is ensured at a low potential at this pin. The generation frequency of the circuit, equal to 40 kHz, is determined by the built-in generator. When the key on this transistor is turned on, the battery voltage is applied to the inductor L1 and energy is stored in its core. However, when the switch is turned off, current flow through the LT 1072 stops. As current continues to flow through the inductor, diode D1 becomes forward biased, allowing the energy stored in the inductor to be transferred to the output.
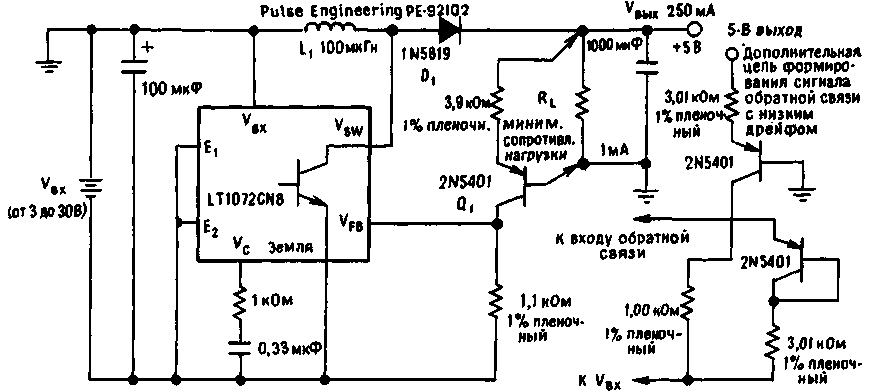
(click to enlarge)
Output voltage regulation is achieved by applying a voltage of up to 1,25 V to the control input (Vfb). The IC is controlled relative to the common output; thus, level shifting should be done from the 5V output. Transistor Q1 serves this purpose, providing an output voltage temperature drift of only -2 mV/°C. This value is usually sufficient for logic power supplies, but can be corrected by an additional carefully selected diode-resistor circuit. The minimum required load current is in any case 1 mA. If more current is needed, the LT 1072 regulator can be replaced with an LT 1070 or LT 1071 IC.
Literature
- William, J. and Huffman B. "Some thoughts on DC-DC converters", Linear Technology Corp., Application Note 29, Feb. 1989.
Author: Brian Huffman; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
 See other articles Section Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells.
See other articles Section Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Plenoptic cameras for Nokia devices
10.05.2013
The Finnish company Nokia is going to invest in Pelican Imaging startup to jointly develop plenoptic cameras for mobile gadgets. Now, Chris Pickett, CEO of Pelican Imaging, says the camera could be part of at least one new smartphone next year.
According to him, plenoptic cameras for smartphones will use 16 independent sensors located on the module in the form of a 4x4 grid, while a module with one sensor is traditionally installed in mobile devices. Each of them will recognize only one color, which will improve image quality and eliminate noise. In addition, the distance between the subsensors will be used to determine the depth and location of objects relative to each other.
Thanks to special software, users will end up with a JPEG file with less noise in the image and the ability to change focus, the volume of which will be about 20% larger than usual.
"Our technologies with Nokia are not mutually exclusive. We can take elements of what they do and improve on what we do. As a result, this will lead to some pretty interesting capabilities that are actually starting to work today," added the technical Pelican Imaging Director Kartik Venkataraman.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Scientists have discovered diamonds from a dead protoplanet in a meteorite
▪ Flexible sensors
▪ Car GPS-navigator Garmin nuviCam LMTHD
▪ New Schottky diodes from VISHAY
▪ Step-down voltage regulator LM26001
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the website Audiotechnics. Article selection
▪ article The Whore of Babylon. Popular expression
▪ article Who Invented Opera? Detailed answer
▪ article MHD generator. Children's Science Lab
▪ article Features of the installation of electrical wiring. General provisions. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Power amplifier for QRP transceiver. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: