Automatic backlight device with house number. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Lighting
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
The figure shows the appearance of an automatic lamp that works when the working surface is darkened.
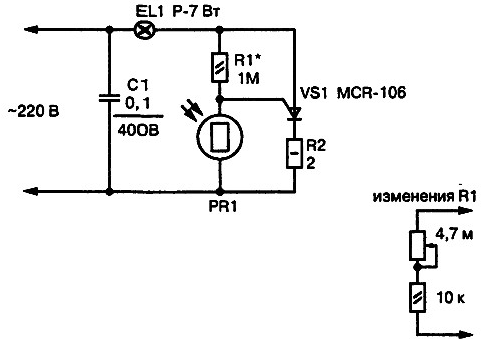
The practical application of the device is in the automatic switching on of the illumination of the plate with the name of the street and the house number. The incandescent lamp is installed inside the plastic case of the plate with the house number, and the elements of the device are installed in the wall of the house in a closed case protected from moisture. In normal lighting (when it is light outside), the lamp does not light. At dusk, the level of natural light drops and the incandescent lamp lights up, illuminating the sign. The photoelectric sensor is a photoresistor, which receives an external light flux through the lens.
PR1 - RFT-01 brand photoresistor, used as a photosensor in Arctur-004 turntable rotation controller. Instead, as a photoresistor, it is also permissible to use photoresistors installed in OEP-1 optocouplers. When the photoresistor is illuminated (bright sunlight), its resistance drops to 12 kOhm and shunts the transition "control electrode - cathode" of the thyristor VS1. In this case, the thyristor closes and de-energizes the incandescent lamp EL1. For such illumination, a low-power lamp is sufficient. It is impossible to use a more powerful incandescent lamp in the device because of the danger of overheating and melting of the plastic case of the plate.
With a 1 W incandescent lamp (to illuminate refrigerators, sewing machines and illuminate other household appliances), the device was operated for two days (with the EL1 lamp constantly turned on), while the temperature around the lamp bulb did not rise above +35 ° С, which is quite acceptable . If the sensor is not sufficiently illuminated (which happens at night), the resistance of the photoresistor is high (more than 1 MΩ). The current passing through the limiting resistor R1 is sufficient to open the thyristor.
Establishment. To increase the photosensitivity of the node, you can replace the fixed resistor R1 with an equivalent circuit, as shown in Fig. 2.12 (below), by entering the sensitivity adjustment into the electronic assembly. So, by changing the resistance of the resistor R1, an increase or decrease in the current through R1 is achieved, respectively. For the same reason, there will be potential changes at the midpoint of the voltage divider R1PR1. With an increase in current through R1 (a decrease in its resistance), the sensitivity of the node to external darkness increases many times over. Now the lamp works faster at dusk (turns on the backlight).
With a decrease in the current through the resistor R1 (increase in its resistance), the opposite will happen - the lamp becomes more sensitive to external lighting and turns off the backlight even with a small impact on the working surface of the light flux photosensor. Any variable resistor is used in the process of setting the sensitivity threshold (after adjustment, having measured its equivalent resistance, R1 is replaced by a constant one). To retain the ability to adjust, a multi-turn variable resistor SPZ-1BV or a similar compact tuning resistor is suitable.
The phasing of the connection to the 220 V network is not important for the device.
About details. Thyristor VS1 is used of the MCR-106-8 type (marked MCR-106 in the diagram). It can be replaced with other Motorola thyristors. This designation is not given by chance, since the thyristor for this circuit can be chosen and another one, guided by reference materials on the electrical characteristics of thyristors and triacs from Motorola (located in the appendix to the book).
Capacitor C1 of the MBM type or similar for an operating voltage of at least 300 V. When the load power increases by more than 60 W, it is necessary to install a thyristor on the heat sink.
The electrical circuit can be assembled independently for use in other designs as a simple photo relay. In doing so, the following points are taken into account.
Thyristor VS1 is replaced by a domestic triac KU208G.
The fixed resistor R2 is excluded from the circuit, a jumper is installed instead. Resistor R1 is replaced by another with a dissipation power of 2 W and a resistance of 12-18 kOhm. Or an equivalent circuit (if sensitivity and threshold adjustment of the photorelay is required) with the same total resistance. Photoresistor PR1 is the same as in the basic circuit. When replacing it with a different type, the resistance of the resistor R1 will have to be selected additionally and within other limits.
 See other articles Section Lighting.
See other articles Section Lighting.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Wheelchair control with the mind
11.03.2016
Researchers at the Duke University School of Medicine (USA) have developed a device to control the movement of a wheelchair using only mental commands and have successfully tested it on monkeys.
To date, several scientific groups in the world have developed brain-machine interfaces to control prostheses using the activity of neurons in the cerebral cortex. However, it remained unclear whether this method could be used to control a wheelchair as it moved continuously through space.
Biologists from Duke University began experiments that could answer this question back in 2012. They injected two rhesus monkeys with hundreds of tiny microfibers in the cortex, responsible for movement and sensation. Then, placing the monkeys in wheelchairs, the researchers showed them bunches of grapes, forcing the monkeys to strive for the desired goal. The macaques did not move, so the drive was purely mental. The researchers recorded the resulting signals from nearly 300 brain neurons. Having accumulated a vast array of data, they programmed a computer system - a decoder - to translate brain signals into digital commands to control a special robotic wheelchair.
At the next stage, the monkeys tried to reach the goal by mentally controlling the wheelchair. They showed good learning ability, over time greatly improved their ability to navigate and got to the treat more and more efficiently and quickly.
Thus, the experimenters were able to prove that the activity of the cerebral cortex can be used to control the movement of a wheelchair and the brain can be taught this.
Interestingly, along with the brain signals responsible for various types of movement, the researchers unexpectedly identified a signal corresponding to an estimate of the distance to the target, which was not present at the beginning of the experiment. It came about during the course of study.
This work is of great importance for people with severe disabilities who have lost mobility and muscle control due to illness. Such technology can restore mobility to them.
Since the equipment can control up to 2000 neurons, the researchers plan to scale up the experiment to improve the fidelity and accuracy of the monkey device before moving on to developing a human version.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Panasonic Lumix DC-S1H mirrorless camera
▪ Pregnant women should talk less on cell phones
▪ Toshiba HK3E2 Solid State Drives
▪ Disney Hair Copy Technology
▪ The value of the graviton mass was specified
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ radio section of the website. Article selection
▪ article The smile of the augurs. Popular expression
▪ article Which famous admiral suffered from seasickness all his life? Detailed answer
▪ article Accountant for accounting of cash transactions. Job description
▪ article Smoking substances. Simple recipes and tips
▪ article Small-sized switching power supply, 12 volts 2 amperes. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: