
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING New life for old watches. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Clocks, timers, relays, load switches In many families, old or simply old clocks have been preserved - wall, floor, fireplace, "clocks" - quite decent in appearance, but with a mechanism that has long served its purpose and cannot be repaired. To "revive" such watches, the author proposes to install a stepper motor (SM) and a small electronic unit in them. The watch will not just "go", its course will be stabilized by a quartz resonator. In mechanical watches, the anchor mechanism most often fails, synchronizing the movement of the hands with the oscillations of the pendulum, or balancer. Only an experienced watchmaker can repair it. Such repairs are quite expensive, especially if the watch has long been discontinued and there are no spare parts for it. However, the part of the mechanism directly connected with the arrows, as a rule, remains intact. By installing a stepper motor (SM) in such watches, you can turn them into electromechanical ones that can work properly for many more years. Quite detailed information about the device and the principle of operation of the stepper motor can be found in the article by L. I. Ridiko "Stepper motor controller", located on the Internet at < telesys.ru/projects/proj077/index.shtml> They are widely used in computer drives, printers , scanners, copiers and many other devices. Almost any watch drive will do. Even motors with a rated operating voltage of 24...28 V develop sufficient torque for such an application when supplied with 5 V. Most often there are stepper motors, the rotor of which rotates in increments of 15 ° (24 steps per revolution). Among them are FB-20-4-1, DSh-0.25A, SDV 15/100. Less often come across engines with a step of 11 ° 15' (32 steps per revolution), for example, DShM-50 / 8-0.47. The rotor of a very convenient and compact engine DSHI-200-1-1 makes a full revolution in 200 steps. If the purpose of the outputs of the existing stepper motor is unknown, you should measure the resistance between them with an ohmmeter (each with each). Considering that all windings have approximately the same resistance, it is not difficult to determine their number and connection scheme from the measurement results. Diagrams of some common step motors are shown in fig. 1, a-c. Alternately applying voltage to the windings of the stepper motor and watching in which direction and at what angle the rotor turns, the sequence of switching windings (Phase 1 - Phase 4) is determined, which ensures uniform rotation of the rotor in one direction. When switching windings in reverse order (Phase 4-Phase 1), the rotor must rotate in the opposite direction. It remains to calculate the number of steps for which the rotor of the stepper motor makes a complete revolution.
The shaft of the stepper motor is easiest to connect with the axis of the second hand of the clock. However, the hand itself will have to be removed from the dial, since after the alteration it will move in jumps of 2 ... 2,5 s. The connection is made as shown in Fig. 2. A cylinder 1 made of plastic (organic glass, textolite, ebonite, etc.) is mounted on the axis of the second hand 2, the outer diameter of which is equal to the diameter of the shaft 4 of the SD. Cylinder 2 and shaft 4 are connected by a tightly fitted spring 3 of suitable inner diameter. With such a connection, there is no need to strictly observe alignment. If there is no second hand in the watch or their design does not allow to attach a stepper motor to its axis, rotation can be transferred to the axis of any of the numerous gears of the clock mechanism. It is only necessary, having counted the number of teeth in pairs, to determine the gear ratio between the shaft of the stepper motor and the axis of the second or minute hand and, accordingly, select the frequency of the pulses applied to the stepper motor. In order not to create an unnecessary load on the engine, it is better to remove one or more gear pairs between the axis to which its shaft is connected and the anchor mechanism of the clock. It is also necessary to remove the drive available in the clock - spring or weight. The movement usually has a friction clutch that allows the hands to be moved by hand, which is easy to find by the characteristic three-beam steel spring. It needs to be blocked. Otherwise, slippage of the friction clutch under the action of the impulse mechanical load created by the stepper motor is not ruled out, as a result of which the watch will noticeably lag behind. The easiest way to do this is to solder the spring to the gear, along which it slides when the arrows are switched. The control pulse generator, the circuit of which is shown in fig. 3 is designed for a stepper motor with 24 rotor steps per revolution, which rotates the axis of the second hand of the clock. The desired speed (1 min-1) will be obtained if the pulses at the output of the master oscillator on the elements DD1.1 and DD1.2 have a frequency of 10 kHz. Achieving the accuracy of the course, the frequency is regulated within a small range by a tuning capacitor C1. For a stepper motor with a different step value, it will be necessary to proportionally change the resonant frequency of the quartz resonator. For example, at 32 steps per revolution, quartz with a frequency of 1000-32 / 24 \u1333,3d 5.1 kHz is required. The desired result can also be achieved by changing the frequency divider circuit. In this case, it consists of a trigger DD6, counters DD7, DD9, DD11, DD13-DD2 and DD24000000 with a total conversion factor of XNUMX. second hand.
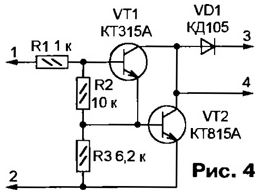
The necessary switching sequence of the windings of the SD M1 is provided by the shift register DD8, the outputs of which are connected to the windings through the multiplexer DD10 and the same transistor switches A1-A4, assembled according to the circuit shown in Fig. 4. The DD10 multiplexer shortens the current pulses in the stepper motor windings by half. The amplitude of the pulses is limited by the resistor R9 in the common winding circuit. These measures increase the efficiency of the device. If element D3.3 is replaced by a single vibrator triggered by the edge of the pulse from the output of element DD4.3 and forming a short enabling pulse, the average current consumed by the motor can be reduced even more. At the time of power-up, the logic voltage levels at inputs 9 and 10 of register DD8 are high. This corresponds to the mode of parallel writing to the register of the code applied to its inputs 3-6. Therefore, with the receipt of the first pulse at the input 11 of the register, its output 15 will be set high, and the outputs 12-14 will be set to a low level. The Phase1 circuit will be connected to a common wire, and current will flow through the corresponding winding of the stepper motor M1. The engine will take the first step. The same pulse will set the DD5.2 trigger to a low level at output 5 and high at output 6. The HL1 LED will start blinking at a frequency of 0,5 Hz. A low level at input 10 DD8 will put the register into code shift mode in the direction from the least significant bit to the most significant one. If the SA1 switch is set to the "Run" position, the low level at the input 2 of the element DD4.1 will prohibit the passage of high-frequency pulses through it from the output of the counter DD13. Pulses with a nominal frequency of 24/60 Hz from the output 8 of the counter DD2 are fed to the input of the register through the elements DD3.2 and DD4.3. When the switch SA1 is switched to the "Forward" or "Back" position, the passage of pulses of the nominal frequency to the input of the register DD8 will be prohibited, and the increased frequency will be allowed, which will lead to an accelerated movement of the arrows in the corresponding direction. Author: A.Marievich, Voronezh
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Fujitsu TeamPoS 7000 S Series Modular Controller for Retail ▪ Bacteria help plants survive heat ▪ Multi-Voltage Power Supply Controllers for LCD Monitors ▪ AVerTV Mobile 510 - Android TV tuner that works without internet
▪ section of the Electrician website. PUE. Article selection ▪ article How did a Jewish girl win an Aryan children photo contest? Detailed answer ▪ article Work in a career. Standard instruction on labor protection
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese



 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: