
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Powerful AC breaker. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Miscellaneous electrical devices For various purposes, sometimes a device is required, which is a two-terminal network that periodically turns off the supply voltage of the load operating in a 220 V network. In this case, in the on state, the resistance of the "closed key" should be minimal. Using modern high-power MOSFETs, the problem can be solved relatively simply. A device that does not create interference during operation (Fig. 1) can be included in the gap of any of the power wires, which is very convenient if it is not possible to make changes to the wiring of the power wiring. In the above version of the circuit, an EL1 incandescent lamp is used as a load. The device is capable of operating with a load of power from 12 to 1200 W and, depending on your requirements, allows you to discretely change the ratio of the glow time and the pause in the lamp operation. The design can be used for illumination, in security systems, with heaters, for various experiments or for other purposes. A flashing LED [1-3] is used as a master oscillator, which makes it impossible to adjust the frequency of its oscillations, but greatly simplifies the circuit. Pulses with a close to rectangular shape are fed to the counting input CN of the DD1 microcircuit. Switching of the decimal counter-decoder K561IE8 (import analogue of CD4017) occurs according to the decays of the negative polarity pulses arriving at pin 14 DD1. At the moment the supply voltage is applied, the decimal counter-decoder is reset by a reset pulse of positive polarity supplied to the input R (pin 15) DD1. At the same time, the level of log. "0" is set at the output "3" (pin 1), the remaining outputs (pins 1-9) of the IC will be log "0". For fast charging and discharging of large gate-source capacitances of parallel-connected field-effect transistors VT3, VT4, in this case, a sufficiently powerful control cascade is required, implemented as a push-pull emitter follower on bipolar transistors VT1, VT2. When, with the arrival of the next counting pulse, a log "2" is set at the output of the microcircuit to which one of the VD6-VD1 diodes is connected, a voltage of 1 ... full opening. Open field-effect transistors with their low resistance of the source-drain channels will shunt the output of the VD12 diode bridge, which will lead to the ignition of the EL13 lamp to full heat. At this moment, the recharging of the oxide capacitor C4 does not occur, the current through the zener diode VD1 connected in series and the HL2 LED will stop, the LED will turn off, the voltage across the capacitors C3, C4 will slowly decrease. Diode VD7 prevents the discharge of C4 through R4-R6. In the case when the log. "1" appears on the output of the IC DD1, to which none of the decoupling diodes VD2-VD6 is connected, on the bases VT1, VT2 relative to the common wire, the voltage will be close to zero, respectively, "0" will be on gates VT3, VT4, the field-effect transistors will close, the lamp will go out. Through the resistors R4-R6 and the diode VD7, the storage capacitor C4 will quickly recharge, a current will appear in the circuit VD1, HL2, the LED will light up. The flashes of the flashing HL1 LED are practically invisible due to its low operating current. Capacitor C2 eliminates high-frequency "noise" at the input of the microcircuit, which ensures its clear switching with each voltage level difference at the anode terminal of the flashing LED. The resistance and power of the resistors R4-R6 are selected based on the fact that it is necessary to ensure fast charging of the capacitor C4 and ensure the device can operate in a wide range of supply voltages. The varistor R7 protects the closed field-effect transistors from breakdown during surges in the mains supply voltage, for example, when turning on or off a powerful inductive load (refrigerator) or during a thunderstorm. Details. You can take any fixed resistors: C1-4, C2-23, C2-33, MLT. The varistor is suitable for the type FNR-14K431, FNR-20K431, FNR-10K471 or the domestic 1 V CH1-560 common among radio amateurs. Imported oxide capacitor C4 (analogous to K50-35, K50-24) with a capacity of 1000 ... 2200 microfarads, preferably with the lowest possible leakage current. Diodes VD2VD7 can be installed in any of the series KD102, KD510, KD521, KD522, D223, 1N4148. Zener diode VD1 can be installed D814D, KS207V, KS212Zh, KS508A, KS512A, 1N4742, BZX / BZV55C12. The flashing HL1 LED will suit the red color of the glow L36BID, L36BSRD / B, L56BID, L796BID, BR34D, L.R3330 or another of the mentioned series. The HL2 LED is replaced by any similar one, for example, L383SRWT, L1503SGT, L1503SRD, L934SGC, L934SRD., L63YD, AL307, KIPD21, KIPD35 series. Imported 8A diode bridge KBU08M is replaced by KBU8J, KBU8K, RS806, more powerful KBPC1006, BR106, KBPC1010, BR1010. With a load current of 6 A, it must be installed on a heat sink with an area of at least 100 cm2. The rectifier bridge can also be made up of 4 diodes of types 8EWS08S, H.A08TB60, D247A, D248A, D233A. The KT315G transistor is replaced by any of the KT3102, KT503, KT6111, KT645, SS9013, SS9014, 2SC1008, 2SD1020 series; KT361G is replaced by KT3107, KT502, SS9015, 2SA642, 2SA1150, 2SB1116. It is desirable to take field n-channel MOSFETs with the lowest possible open channel resistance, for a maximum drain-source voltage of at least 400 V. The BUZ210 used in the device have a drain-source resistance of no more than 0,6 Ohm in the open state. When two such transistors are connected in parallel and at the indicated maximum load power of 1200 W, the voltage drop across the open power switch will be about 3,6 V and the power dissipation will be about 20 W. In such a situation, the transistors are installed on a common aluminum heat sink with an area of at least 200 cm2. Instead of BUZ210, you can use BUZ213, BUZ216, 2SK1723, 2SK899, IR.P450, KP779A. To reduce power losses and to reduce the size of the heat sink, you can use a large number of similar field-effect transistors connected in parallel. With a maximum load power of up to 100 W, you can install one field-effect transistor without a heat sink. The pinout of field-effect transistors, made in a standard TO220 plastic package, is given in Fig. 2.
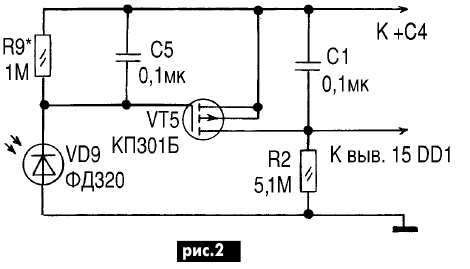
If the device is a little more complicated, for example, as shown in Fig. 3, then the supply voltage to the load will be automatically supplied only after dark. The sensitivity of the photorelay node depends on the resistance of the resistor R9. A low-power p-channel field-effect transistor with an insulated gate can be any of the KP301 or KP304A, 2P304A series. The photodiode can be taken like FD252, FD256, FD265. You can also install a suitable photoresistor SF3-2B, SF3-7A, SF3-16.
The "program" for the ignition of the EL1 lamp can be set by changing the connection of the diodes VD2-VD6 to the outputs DD1. In the variant given in the diagram of Fig. 1, for one cycle of operation of the IC, the lamp operates in the 2P-1V-2P-3V-2P-1V mode, where "B" is on, "P" is a pause. The output "0" of the microcircuit (pin 3) in any options for connecting decoupling diodes must remain free. During operation of the device, the voltage across the capacitor C4 should not fall below 11 V. Before installing the HL2 LED, its pinout must be specified. The given circuit design version of a powerful interrupter device operating in an alternating current circuit does not have to be repeated in strict accordance with the diagrams in Figs. 1 and 3. For example, a flashing LED generator can be replaced with a micropower generator on a CMOS version of the 555 timer (KR1006VI1), for example, ICL7555. When working with a low-power load, you can increase the resistance of resistors R1,5-R2 by 4-6 times. You can make other changes, guided by your experience and the real need for further improvement of the proposed device. References:
Author: A.L. Butov
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Sockets and switches from old fishing nets ▪ Tourism helps treat dementia
▪ section of the site Electronic directories. Article selection ▪ article Starting towing device. Tips for a modeler ▪ article Which animals do Finnish farmers cover with reflective paint? Detailed answer ▪ article Occupational safety of employees of housing and communal services ▪ article Powerful regulator. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering ▪ article HF signal generator. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: