
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING A photo watchman with a pulsating beam. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Security devices and object signaling In many cases, such a sensor is needed that could work both in complete darkness and in sunlight, remaining invisible to the intruder. Several schemes immediately come to mind, and the first is the one where rays invisible to humans are used. The rest of the circuit should work normally.
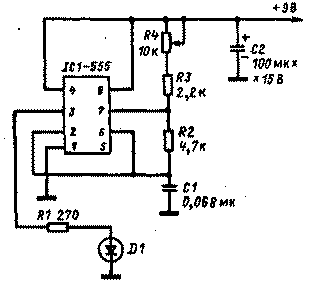
The simplest method (in terms of design) in this case would be to use a continuous beam of light illuminating the photocell. In 99% of cases, this method works well, but in the remaining 1% of cases, a robber comes across who, either from experience or from the information received, knows where the photocell is, and by directing his light source at it, can go unnoticed. Here we need a more perfect photo guard. The light beam in such a photoguard can be made pulsating by modulating it with a low frequency, while the photodetector can be made sensitive only to a certain beam modulation frequency. The scheme shown in fig. 1 interrupts an invisible infrared (IR) beam of light at 1500 Hz. Here D1 is an element of type XC-880-A, Radio Shack 276-143. The beam falls on the photodetector of IR rays, the role of which is played by a phototransistor in the circuit in Fig. 2.
Schema work. Let's start with the light transmitter in Figure 1. An oscillator operating at a frequency of 555 Hz is assembled on a type 1500 timer. An infrared LED is connected to its output, pulsing at the frequency of the generator. The oscillator frequency is determined by the values of resistors R2, R3, R4 and capacitor C1. Variable resistor R4 fine tunes the transmitter to the frequency of the photodetector. The specific operating frequency of the successor is not so important, since it is easy to adjust the frequency of the phototransmitter to it. Resistor R1 limits the current through the LED. By reducing it, you can increase the light output of the LED, but before that you need to make sure that the current through the LED does not exceed the maximum allowable. The photodetector circuit shown in Figure 2 is a bit more complex than the simple phototransmitter circuit, but is actually a simple circuit too. An infrared light detector transistor Ql (Radio Shack 276-142) receives a pulsed beam from a phototransmitter and sends a small amplitude AC voltage signal to a double T-bridge circuit. If you look closely, you can see that the input and output of the T-bridge are connected to the base and collector of transistor Q2. The whole complex forms a resonant amplifier, the maximum gain of which falls on the resonant frequency. At this frequency, the resistance of the T-bridge is maximum, and therefore the negative feedback induced through it is minimal. Due to this property, transistor Q2 amplifies only the 1500 Hz signal coming from the phototransmitter. Further, the signal with a frequency of 1500 Hz is amplified by transistor Q3 to a level sufficient for the detector to operate with a doubling of the voltage on diodes D1 and D2. A constant voltage from its output through the resistor R2 opens the transistor Q4, which closes the terminals B and C through itself. Schema assembly. Choose the design of the device at your discretion. When placing the transmitter LED and the receiver phototransistor, make sure that they are not exposed to direct light. This can best be achieved by placing the phototransistor together with the parts in a light-tight housing. Drill a hole less than 1 cm in diameter in one side of the box and place the phototransistor 2,5 cm opposite it. With this arrangement of the phototransistor, the signal from the transmitter will reach it with an unloaded side light. If the transmitter LED is placed in the same way, the reliability of the circuit will increase. Use of the device. Determine the place where the criminal is most likely to pass. Position the receiver and transmitter accordingly to guard the area. The device works best when the distance between transmitter and receiver is less than 5 m. It is always best to experiment to find the best position for the device. After finding a place for both parts of the device, turn on the power of each, and connect a DC voltmeter to the cathode of the diode D1 of the receiver. The second output of the voltmeter is connected to a common wire. Following the readings of the voltmeter, tune the transmitter using resistor R4 to the frequency of the receiver according to the maximum readings of the voltmeter, while the voltage at the cathode of the diode D1 should be at least 1,5 V and reach 5 V with decreasing distance between transmitter and receiver. Terminals B and C can be connected to any NC alarm system. The main thing here when you turn it on is to observe the polarity. To work with any existing alarm, you can also turn on an electromagnetic relay between terminal B and the plus of the receiver's power supply. Whichever photoguard scheme you choose, the importance of proper photocell placement cannot be underestimated. Poorly placed sensors may not miss an intruder, but they will cause a number of false positives. It is difficult to think of anything else that lowers the overall effectiveness of any alarm as much as a false alarm. They scared the wolves so that no one believed when they actually came. Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
Artificial leather for touch emulation
15.04.2024 Petgugu Global cat litter
15.04.2024 The attractiveness of caring men
14.04.2024
▪ Universal wireless sensor node STEVAL-MKSBOX1V1 for the Internet of Things ▪ Technique is controlled by thoughts ▪ Navigator looking for parking
▪ section of the site Electrical safety, fire safety. Article selection ▪ article Linen lift. Tips for the home master ▪ article Why is one of Jim Beam bourbons called the devil's share? Detailed answer ▪ article Cashier of the trading floor. Job description
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: