
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
Electronic ballasts. Miniature electronic ballasts based on the IR53HD420 chip. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
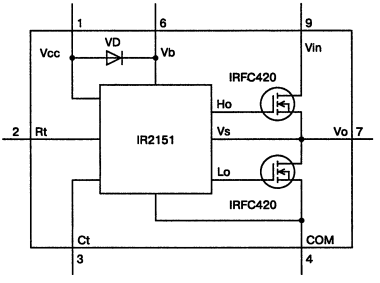
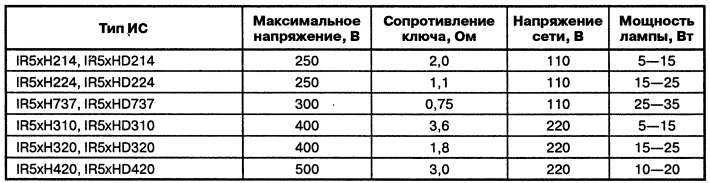
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Ballasts for fluorescent lamps Attention! The design is galvanically connected to the electrical network. Potentially life threatening due to possible electrical shock. Therefore, in the manufacture, testing, adjustment and operation, one should remember the strict observance of electrical safety measures. The design must be made in such a way as to exclude accidental contact with bare terminals of conductors or parts. When checking the operation of the structure, you should not touch any of its parts or circuits with your hands, and solder the parts to be replaced only when the mains plug is removed from the socket. Consider miniature electronic ballastmade on a hybrid microcircuit IR53HD420 (IR51HD420), which has built-in power transistors and a voltage boost diode. Subminiature electronic ballasts based on the IR51HD420 hybrid chip are designed to work with single lamps with a current of up to 0,3 A and are widely used with compact fluorescent lamps. Structural diagram of IR53HD420/IR51HD420 is shown in fig. 3.20. The IR53Hxxx / IR51Hxxx family with integrated power transistors includes several microcircuits with different parameters, the main characteristics of which are given in Table. 3.4.
Table 3.4. Chip characteristics
Note to table. 3.4. HD - with integrated booster diode; H - without diode. The main parameters of IR51HD420 are similar to IR2151, IR2153. The two n-channel HEXFET transistors (IRFC51) integrated in the IR420HD420 have following parameters:
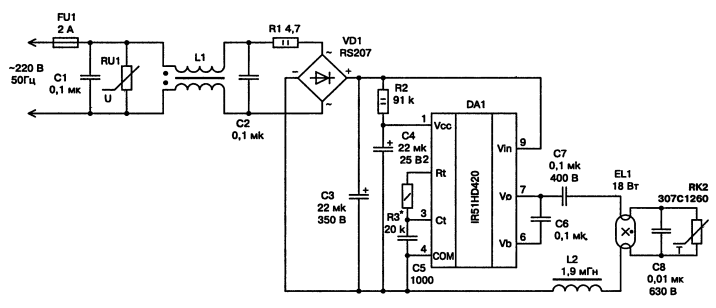
Schematic diagram of a miniature electronic ballast is shown in fig. 3.21.
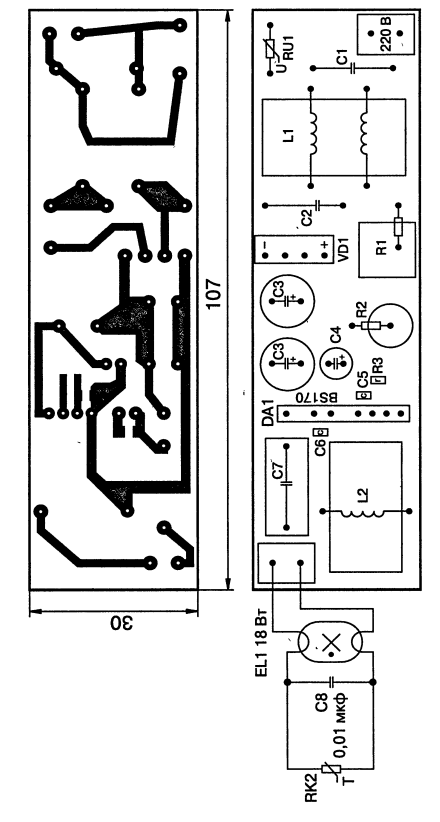
Principle of operation similar to the electronic ballast on the IR2153, which we have already discussed above. The mains filter inductor L1 is wound on a K20x12x6 M2000NM ferrite ring with a two-core network wire (or MGTF folded in half) until the window is completely filled. Good noise suppression results in combination with miniature dimensions are provided by specialized EPCOS filters: B84110-B-A14, B84110-A-A5, B84110-A-A10, B84110-A-A20. The inductor of the electronic ballast L2 is made on a W-shaped magnetic core made of M2000NM ferrite. Core size Sh5x5 with a gap δ = 0,4 mm under all three working surfaces of the W-shaped core. The size of the gap in our case is the thickness of the gasket between the contacting surfaces of the halves of the magnetic circuit. To make a gap, it is necessary to lay gaskets made of non-magnetic material (non-foiled fiberglass or getinax) 0,4 mm thick between the mating surfaces of the halves of the magnetic circuit and fasten with epoxy glue. The value of the inductance of the inductor (with a constant number of turns) depends on the value of the non-magnetic gap. With a decrease in the gap, the inductance increases, with an increase, it decreases. Winding L2 - 180 turns of PEV-2 wire with a diameter of 0,25 mm. Interlayer insulation - varnished cloth. Winding - turn to turn. Diode bridge VD1 - imported RS207, admissible direct current 2 A, reverse voltage 1000 V. Can be replaced by four diodes with the appropriate parameters. The IR51HD420 hybrid chip can be replaced with IR53HD420, IR51H420, IR53H420. Council. When using IR51H420, IR53H420, you need to take into account that these microcircuits do not have a built-in voltage boost diode (between pins 1 and 6), and it should be installed. The diode used in this case must be of the ultra-fast class (superfast) with the following parameters: reverse voltage 400 V; permissible direct direct current - 1 A; reverse recovery time - 35 ns. Fits 11DF4, BYV26B/C/D, HER156, HER157, HER105-HER108, HER205-HER208, SF18, SF28, SF106-SF109. The diode should be located as close to the chip as possible. R3, C5, Sat - SMD elements for surface mounting (C6 for 60 V). Capacitors C1, C2, C7 - K73-17. C1, C2 - for 630 V, C7 - for 400 or 630 V; C3 - electrolytic (two 10 microfarads in parallel) imported for a nominal voltage of at least 350 V; C4 - electrolytic for 25 V; C8 - polypropylene K78-2 for 1000 V. Varistor RU1 from EPCOS - S14K275, S20K275, replace with TVR (FNR) 14431, TVR (FNR) 20431 or domestic CH2-1a-430 V. R1 - wire 2,2-4,7 Ohm with a power of 1-2 W, can be replaced with a thermistor (thermistor) with a negative temperature coefficient (NTC - Negative Temperature Coefficient) - SCK 105 (10 Ohm, 5 A) or from EPCOS - B57234 -S10-M, B57364-S100-M. RK2 is a posistor, the same as in the electronic ballast on IR2153. The ballast is assembled on a printed circuit board made of foil fiberglass and placed in an aluminum shielding casing. The printed circuit board and arrangement of elements is shown in fig. 3.22. The tuning recommendations are similar to those discussed in the section on the electronic ballast on the IR2153.
Author: Koryakin-Chernyak S.L.
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024 The threat of space debris to the Earth's magnetic field
01.05.2024 Solidification of bulk substances
30.04.2024
▪ Found a new property of graphene ▪ Carbon 3D frame will improve lithium-ion battery anodes
▪ site section Field strength detectors. Article selection ▪ article Burn - does not mean to refute. Popular expression ▪ article Who and when designed and built a flying submarine? Detailed answer ▪ article Star anise is real. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: