 Free technical library
Free technical library
Stabilized voltage converter on the YX8018 chip. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Voltage converters, rectifiers, inverters
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
The YX8018 chip is widely used in low-cost LED lawn lamps, where an unstabilized boost converter is built on it. It provides power to the lighting LED (or LEDs) from a Ni-Cd battery. The current through the LED (from fractions to several milliamps) is set by the inductance of the storage choke in the converter. Therefore, there is no need to stabilize the voltage.
A feature of the YX8018 and similar microcircuits is the presence of a control input, with which you can also turn on the switch of the voltage converter. It is this input that is used in LED lawn lights to turn them on automatically at nightfall. The same input can be used to build a stabilized boost converter.
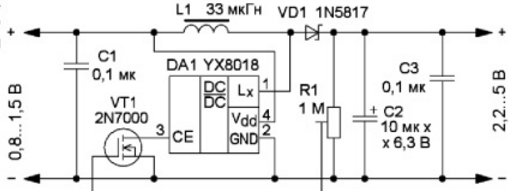
Fig. 1
A diagram of such a converter on the YX8018 chip is shown in fig. 1. It can be used to power a single Ni-Cd, Ni-Mh battery or a galvanic cell of various electronic devices that require a supply voltage of 2 to 5 V. In the initial state, at the CE input (pin 3) of the microcircuit, there is a voltage close to the voltage nutrition. This is due to the presence of a built-in resistor connecting this pin to the power plus. Therefore, the converter turns on, the voltage pulses at its output L (pin 1) rectifies the diode VD1, and the smoothing capacitors C2 and C3 are charged - the output voltage rises.
When the voltage at the gate of the transistor VT1 reaches the threshold value (about 2 V), the resistance of the transistor channel will decrease and the voltage at its source (and the CE input of the microcircuit) will also decrease - the converter will turn off. The output voltage will begin to decrease, which will lead to the closing of the field effect transistor and turning on the converter.

Fig. 2
Thus, the converter periodically turns on and off, maintaining the output voltage set by the tuning resistor R1. The operating frequency of the converter is about 200 kHz, and the on / off frequency depends on the output current and the capacitance of the capacitor C2 (the greater the current and the lower the capacitance of the capacitor, the greater the frequency) and can be from several hertz to tens of kilohertz. The dependences of the output voltage of the converter (2,7 V) on the input voltage for different values of the load current are shown in fig. 2.
The amplitude of the ripples is about 10 mV, it remains practically unchanged and, to a small extent, depends on the output voltage and the parameters of the field-effect transistor. The pulsation frequency depends on the operating frequency of the converter and the on/off frequency of the converter and can vary over a wide range. Thermal stability is determined primarily by the parameters of the field effect transistor. In this case, the voltage temperature coefficient is negative and amounts to several millivolts per degree Celsius.

Fig. 3
All elements can be mounted on a single-sided printed circuit board made of foil fiberglass, its drawing is shown in fig. 3. A tuning resistor SP3-19 was used, an oxide capacitor was imported, the rest were K10-17. Instead of the 1N5817 diode, low-power pulse or detector germanium diodes or Schottky diodes can be used. The inductor is wound on a ferrite ring with a diameter of 6 ... 9 mm from the transformer of the electronic ballast of a compact fluorescent lamp and contains 5 turns of wire PEV-2 0,4.
The output voltage in the range of 2,2.5 V is set with a tuning resistor, it can be replaced with a resistive divider with a total resistance of at least 1 MΩ. To reduce ripples with a frequency of 200 kHz between capacitors C2 and C3, a choke, for example EC24, with an inductance of 470 ... 1000 μH, must be installed in the positive power line.
Author: I. Nechaev
 See other articles Section Voltage converters, rectifiers, inverters.
See other articles Section Voltage converters, rectifiers, inverters.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Electricity from mushrooms and wooden floor
01.04.2021
Wood consists of fibers of cellulose and hemicellulose polymers in a lignin matrix. Cellulose in the composition of wood can be amorphous and crystalline. The presence of the latter makes wood a piezoelectric material - a material in which electric charges arise under the action of deformation. When cellulose crystallites are compressed, the centers of gravity of positive and negative charges diverge in space, and charges arise on the surface of the crystallite to maintain electrostatic equilibrium. The piezoelectric properties of wood have been known since the fifties, but no one has made commercial materials and devices for generating electricity from it - due to the low piezoelectric modulus and the deformability of wood, this was considered unprofitable.
Swiss scientists led by Ingo Burgert from ETH Zurich managed to enhance the piezoelectric properties of wood. Burgert and his colleagues have long been able to change the properties of wood and obtain various functional materials on its basis. For example, last year they turned balsa wood into a luminous material by dissolving lignin and replacing it with a solution of luminescent quantum dots. To make wood a good piezoelectric, you also need to dissolve the lignin, then the wood will become looser, and it will be easier to deform it. In order to carry out the dissolution gently, without damaging the cellulose framework, Burgert and his colleagues proposed an unexpected solution - they treated the wood with mushrooms from the basidiomycete department.
The scientists again took the light wood of the balsa tree (Ochroma pyramidale) with a density of 94,8 kilograms per cubic meter as the basis for the material. Three types of fungi were used to dissolve lignin: Phanerochaete chrysosporium, Ganoderma adspersum, and Ganoderma applanatum. The wood was cut into thin plates, dried at a temperature of 100 degrees during the day, a freshly prepared mushroom culture was applied to the surface and left in a humid atmosphere for a period of 4 to 12 weeks.
To control how much lignin the fungi had time to absorb, wood samples were thoroughly cleaned and dried again for a day, and then weighed. The fastest loss of lignin was provided by the fungi Ganoderma applanatum. The optimal processing time Burgert and his colleagues considered eight weeks (corresponding to a weight loss of 45 percent mainly due to lignin) - with longer processing, the wood became too loose and significantly lost strength. Fourier IR spectroscopy confirmed that the fungi preferentially absorbed lignin, and a slight loss of hemicellulose was also observed. But the cellulose frame of wood remained practically unchanged after treatment - this was clearly visible not only in the IR spectra, but also in the images of scanning electron microscopy.
Lignin-free wood had better compressibility. As a result, the displacement of the centers of gravity of the charge in cellulose crystallites occurred with a greater amplitude, and the piezoelectric effect also increased. A cube of treated wood measuring 15 x 15 x 13,2 millimeters generated a voltage of 0,87 volts and a current of 13,3 nanoamps. This is fifty-five times more than unmodified wood under the same conditions. By connecting nine such cubes in series, the authors obtained electricity sufficient to power a light emitting diode.
From the new material, the authors propose to make a floor covering that will produce electricity under the weight of human steps. Such a coating could be placed in the homes of the elderly and powered by sensors that are activated if a person falls. There are more exotic ideas for using piezoelectric wood floors in dance and aerobics rooms. Note that so far Burgert and his colleagues have obtained a piezoelectric material only from balsa wood - light and with a large number of pores. In the future, they are going to adapt the method for denser and heavier types of wood.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Cats can heal people
▪ Creation of an artificial uterus
▪ quantum spin liquid
▪ Smart pillow
▪ Rabbits threaten heritage
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ site section Electrician's tool. Article selection
▪ article Blood insult. Popular expression
▪ article Where and why two million people lined up in a chain 600 km long? Detailed answer
▪ article Preparer of padding and flooring materials, engaged in cutting upholstery fabrics. Standard instruction on labor protection
▪ article Wiring products. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Repair of electric shaver Kharkiv. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese



 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: