
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Digital receive frequency meter. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
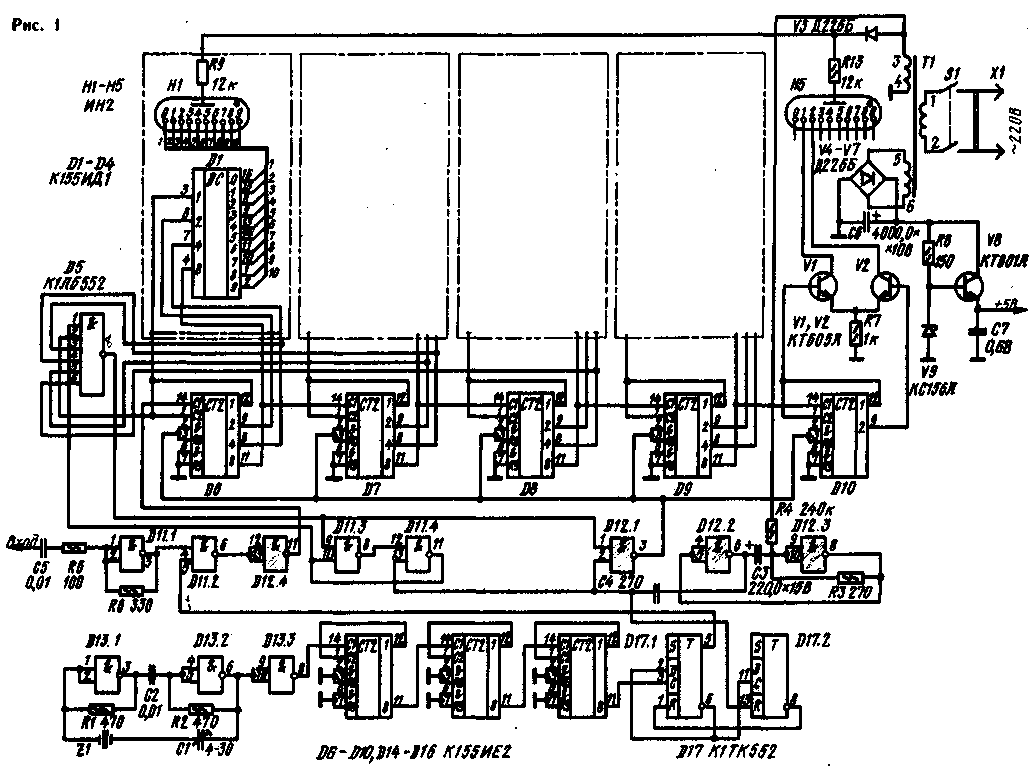
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Measuring technology The development of digital technology and integrated circuits have made it quite realistic to solve such complex technical problems as measuring and digital indication of the tuning frequency of broadcasting receivers. It is known that in a superheterodyne radio receiver, the signal frequency is usually equal to the difference between the frequency of the local oscillator and the intermediate frequency. And since this difference is constant and equal to 465 kHz, then to determine the tuning frequency of the radio receiver, it is enough to measure the local oscillator frequency, for example, using a frequency meter with a digital display, and subtract the intermediate frequency from it. The resolution of such a digital device is chosen depending on the required indication accuracy and the local oscillator frequency instability. For household broadcast receivers in the LW and MW bands, the local oscillator frequency instability is approximately 100 Hz. and in the KB range - 1 kHz, therefore, for these ranges, a reading accuracy of 1 kHz is quite sufficient. This is exactly what it is in the reception frequency meter offered to the attention of readers, made in the form of a separate set-top box, powered by an alternating current main. The device uses a five-digit digital indicator. The operating frequency range is from 150 kHz to 10 ... 12 MHz, which corresponds to the broadcasting ranges of LW, MW and HF. Schematic diagram of the radio tuning frequency meter is shown in fig. 1. The local oscillator voltage of the radio receiver is fed to the input of the limiting amplifier, made on the D11.1 chip. At the output of this device, a sequence of almost rectangular pulses is formed, the repetition rate of which corresponds to the measured frequency of the local oscillator. The sensitivity of the limiting amplifier is about 100 mV. The essence of measuring the local oscillator frequency is to count the number of pulses arriving at the measuring device in a certain time interval. In the described meter, it is equal to 1 ms, so the local oscillator frequency is measured with an accuracy of 1 kHz (the price of the least significant digit). The time interval is set by a device consisting of a quartz oscillator on D13.1 and D13.2 microcircuits, tuned to a frequency of 1 MHz, and a frequency divider on D14-D16 microcircuits, which reduces it to 1 kHz. In addition to the elements already mentioned. the measuring device includes a multivibrator made on the elements D12.2 and 012.3. element "2AND-NOT" D11.2, match node D5. triggers D17.1, D17.2 and a similar device assembled on elements D11.3, D11.4. pulse counter on chips D6-D10. decoders D1-D4 and digital indicators H1-H5. Since the most significant digit of the counter is incomplete, it was possible to save one high-voltage decoder by replacing it with transistors V1. V2. The microcircuits and transistors of the meter are powered by a stabilized rectifier made on diodes V4-V7, transistor V8 and zener diode V9, indicator lamps - from an unstabilized half-wave rectifier based on diode V3. The measurement begins with the receipt of the starting pulse of the multivibrator D12.2, D12.S. setting the counter D6-D10, the trigger D17.2 and the trigger, executed on the elements D11.3, D11.4, to the zero state. Trigger D17.1 is an account trigger. In the "0" state of the trigger D17.2, a high level of logic "1" allows the account of the trigger D17.1, and the first pulse coming to its input from the frequency divider D14-D16. puts it in state "1". This logical unit through the element "2I-NOT" D11.2 allows counting of the local oscillator pulses coming from the amplifier-limiter D11.1 to the input of the counter D6-D10. Exactly 1 ms after the arrival of the first pulse, the second pulse arrives at the input of trigger D17.1, which puts it in the zero state and prohibits further counting of pulses coming from the local oscillator. At the same time, the trigger D17.2 goes into a single state, preventing the trigger D17.1 from changing its state in the future from pulses entering its input from the frequency divider. This completes the measurement cycle. Since the time during which the counting of the local oscillator pulses by the counter D6-D10 is allowed is, as already mentioned, 1 ms. then their number corresponds to the local oscillator frequency in kilohertz. To indicate the tuning frequency of the radio receiver, the number corresponding to the intermediate frequency must be subtracted from the number of local oscillator pulses. A match node is used for this purpose. D5 and a trigger made on elements D11.3, D11.4. With the start of counting the local oscillator pulses, the counter reading D6-D10 begins to increase, and when the value to be subtracted is reached, the coincidence node generates a pulse that re-translates the counter to the zero state. This impulse translates into a single state and the trigger on the elements D11.3, D11.4. which prohibits further generation of pulses by the coincidence node. To get rid of the interference resulting from the power supply of the H1-H5 lamps from a half-wave rectifier. applied synchronization of the multivibrator (D12.2, D12.3) with the mains frequency. As a result, measurements are taken during the negative half-cycles when the lamps are not lit. A tuning frequency meter is connected to the radio receiver through an emitter follower, the circuit of which is shown in fig. 2. To reduce the effect on the local oscillator, the connection between its circuits and the emitter follower should be rather weak. The easiest way to do this is to connect the repeater to the already existing taps of the local oscillator coils.
The power transformer can be used from the Ocean-205 radio receiver by rewinding its secondary winding. Two new windings should contain 2700 turns of PEL 0.08 wire (pins 3-4} and 170 turns of PEL 0,41 wire (pins 5-6). Chips D11-D13 - 155LA3. A properly assembled device practically does not need to be configured. It is only necessary to check the frequency of the crystal oscillator and, if necessary, adjust it using capacitor C1. Tuning can be done when receiving a station of known frequency. For this purpose, it is convenient to use reference frequencies and time signals transmitted at frequencies of 5, 10 and 15 MHz. Authors: I. Voyanov, V. Belikov, Sofia; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Beetles are the most tenacious creatures ▪ Promising graphene photomatrices
▪ section of the Radio Control website. Article selection ▪ article A Chekist must have a cool head, a warm heart and clean hands. Popular expression ▪ Tire fitter article. Standard instruction on labor protection ▪ article car. Accumulators, chargers. Directory ▪ article Rotation changes shape. physical experiment
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: