Amplifier with common mode mode stabilizer. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Transistor power amplifiers
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
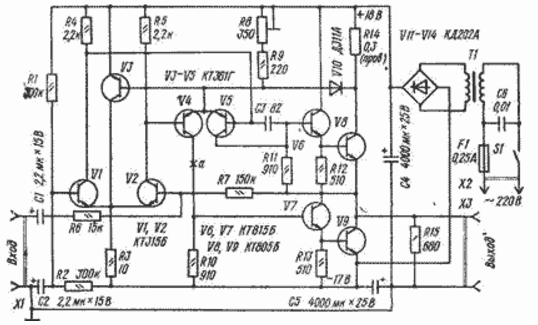
An amplifier with a common-mode mode stabilizer is designed to work with a pre-amplifier-tone block on an operational amplifier. A distinctive feature of the device is the presence of an effective stabilizer of the quiescent current of transistors of differential stages.
The main parameters:
- Rated frequency range, Hz.......10...25 000
- Rated output power, W, at a load with a resistance of 8 Ohm.......12
- Rated input voltage, V ....... 1
- Harmonic coefficient, %, at rated output power at frequency, Hz: 1000.......0,01
- 20 000......0,02
- Relative level of noise and background, dB.......-80
- Input impedance, kOhm.......15
The amplifier contains two differential signal voltage amplification stages on transistors V1, V2 and V4, V5 and an output current amplification stage on transistors V6-V9.
The functions of the mode stabilizer are performed by the transistor V3, the base of which is connected to the emitter circuit of the transistors of the second differential stage, and the collector is connected to the emitter circuit of the transistors of the first stage. The OOS that occurs in this case on the common-mode component of the signal balances the differential stages and increases the resistance to ripples and fluctuations in the supply voltage.
Transistor V3 is fixed on the heat sink of transistor V8 of the output stage, so it also performs the functions of a thermal mode stabilizer. The current through the transistor V3 (40 ... 60% of the current of transistors V1, V2) must be taken into account when calculating the resistance of the resistor R3. By replacing this resistor with a current source, the amplifier can operate at a supply voltage of 12 V up to the limit value for the transistors used. If the supply voltage is greater than 36 V, it is recommended to turn on another transistor of the p-n-p structure (its base is connected to the collector of transistor V4) into the collector circuit of transistor V7 (at point a). The signal level shift that occurs in this case will ensure the thermal balance of the amplifier and the equality of voltages on the collectors of transistors V4, V5.
To balance the amplifier, the non-inverting input (the base of transistor VI) is connected to the midpoint of the voltage divider R1R2. This made it possible to simplify the node for protecting the transistors of the output stage from overcurrent. in this amplifier, it consists of a resistor R14 in the collector circuit of transistor V8 and a diode V10 connecting this circuit to the base of transistor V3.
In addition to those indicated in the diagram, transistors KT361B, KT361G, KT361E, KT209E, KT209K (V1, V2) can be used in the amplifier; KT315B, KT315G, KT315E, KT342A, KT342D (V3-V5); KT626B, (V6, V7); KT816B, KT816V, KT818B (V8, V9). The static current transfer coefficients of transistors V6, V7 and V8, V9 should be as close as possible. With such a replacement, the polarity of the power supply, electrolytic capacitors and the V10 diode must be reversed.
It is not difficult to adapt the amplifier to work on a load with a resistance of 4 ohms (output power at a supply voltage of 35 V will increase to 18 W). To do this, the resistance of the resistor R6 must be reduced to 6,8 kOhm. R7 - up to 68 kOhm, R9 - up to 90 Ohm, R10 and R11 - up to 680 Ohm. The input impedance after such changes will drop to 6,5 kOhm
Setting up the amplifier comes down to setting the quiescent current of the output stage with a tuned resistor R8. If the signal limitation does not reach at the same time (due to the unequal amplification of the output stage arms), resistors R10, R11 are selected (in the arm, where the limitation occurs earlier, the resistance of the resistor should be increased, and in the other it should be reduced by the same amount). Due to the unavoidable imbalance of the second differential stage, it is not recommended to change the resistance of the resistors by more than ± 20% (from the ratings indicated in the diagram).
 See other articles Section Transistor power amplifiers.
See other articles Section Transistor power amplifiers.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive solar mega power plant
20.10.2013
In the Arizona desert near Phoenix, industrial tests of the most powerful solar power plant Solana have ended.
Solana is one of the largest solar power plants in the world and can deliver up to 280 MW. But, besides this, the power plant has a unique feature: it can accumulate solar heat and generate electricity within 6 hours after sunset. The new heat storage technology is a huge step forward for solar energy, as uneven power generation is one of the main disadvantages of solar energy.
The Solana power plant is an array of 2700 parabolic mirrors, the troughs of which occupy a surface of 7,7 square meters. km. Mirrors concentrate sunlight on tubes in which a liquid heat carrier - synthetic oil - circulates. The coolant heated by sunlight enters the steam boilers and heats the water, which, in turn, turns into steam and turns 140-MW turbines.
Solana is equipped with a thermal energy storage system: special containers where heated oil is stored. This allows the production of clean energy at maximum capacity for six hours. In normal operation, the power plant is able to meet the energy needs of consumers during peak hours in the morning and early evening. At present, Solana at its peak capacity can provide energy to about 70000 households. In the future, 4 more similar power plants will appear in Arizona, and the total generated capacity will increase to 750 MW, which is enough to power 185 households.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ wifi on sheep
▪ Solar-powered desalination plant
▪ radioactive thunderstorm
▪ Reconnaissance drone RQ-4D Phoenix
▪ Friday Lock smart door lock
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Application of microcircuits. Article selection
▪ article Models of rocket gliders. Tips for a modeler
▪ article In what country does the groom give the bride white slippers? Detailed answer
▪ article Slinger. Standard instruction on labor protection
▪ article Transfer function: how to measure? Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Ukrainian proverbs and sayings. Large selection
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: