AC solid state relays 1 A / 400 V. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Reference materials
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
Features
- switched voltage 240V
- switching current 1 A
- control current 10 mA
- dimensions 37x24x11 mm
Application
- replacement of electromagnetic relays
- industrial automation
- powerful interface |
Pin assignment
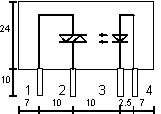 |
Recommended wiring diagram
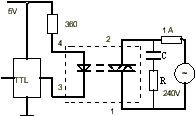
RC damping circuit
R=0.1uF, C=100 Ohm |
ELECTRICAL PARAMETERS ( T = 25 C )
| Parameter name |
Ref. |
Unit. |
minutes. |
Significant.
a type. |
Max. |
Measurement mode |
| Input voltage |
Uin |
В |
1.0 |
1.2 |
1.5 |
Iin=10mA |
| Residual voltage in open comp. |
Ures |
В |
- |
1.0 |
2.0 |
Iin=10mAIout=1A |
| Leakage current in closed state. |
Iut |
μA |
- |
0.1 |
100 |
Uin=0.8V Uout=400V |
| Insulation voltage |
Uiz |
В |
1500 |
- |
- |
T=1min |
| Insulation resistance |
Riz |
Om |
- |
11
10 |
- |
- |
| through capacity |
Spr |
pF |
- |
3.0 |
- |
- |
| Response time |
Tsr |
ms |
- |
4.0 |
- |
- |
MAXIMUM PERMISSIBLE OPERATION MODES
| Mode Options |
Ed. amend. |
Min. |
Max. |
Note |
| Switching voltage (avg.) |
В |
50 |
240 |
- |
| Switching current (avg.) |
А |
0.25 |
1.0 |
- |
| Switching current pulse |
А |
- |
10.0 |
Timp.=500ms |
| In. on-state current |
mA |
10 |
25 |
- |
| In. off state current |
mA |
0.0 |
0.25 |
- |
| Critical slew rate e.g. |
V/µs |
5 |
- |
- |
| Slave. temperature range |
С |
-60 |
85 |
- |
Author: Zeshkov Yu., Pervouralsk, Sverdlovsk region; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
 See other articles Section Reference materials.
See other articles Section Reference materials.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Traffic noise delays the growth of chicks
06.05.2024
The sounds that surround us in modern cities are becoming increasingly piercing. However, few people think about how this noise affects the animal world, especially such delicate creatures as chicks that have not yet hatched from their eggs. Recent research is shedding light on this issue, indicating serious consequences for their development and survival. Scientists have found that exposure of zebra diamondback chicks to traffic noise can cause serious disruption to their development. Experiments have shown that noise pollution can significantly delay their hatching, and those chicks that do emerge face a number of health-promoting problems. The researchers also found that the negative effects of noise pollution extend into the adult birds. Reduced chances of reproduction and decreased fertility indicate the long-term effects that traffic noise has on wildlife. The study results highlight the need ... >>
Wireless speaker Samsung Music Frame HW-LS60D
06.05.2024
In the world of modern audio technology, manufacturers strive not only for impeccable sound quality, but also for combining functionality with aesthetics. One of the latest innovative steps in this direction is the new Samsung Music Frame HW-LS60D wireless speaker system, presented at the 2024 World of Samsung event. The Samsung HW-LS60D is more than just a speaker system, it's the art of frame-style sound. The combination of a 6-speaker system with Dolby Atmos support and a stylish photo frame design makes this product the perfect addition to any interior. The new Samsung Music Frame features advanced technologies including Adaptive Audio that delivers clear dialogue at any volume level, and automatic room optimization for rich audio reproduction. With support for Spotify, Tidal Hi-Fi and Bluetooth 5.2 connections, as well as smart assistant integration, this speaker is ready to satisfy your ... >>
A New Way to Control and Manipulate Optical Signals
05.05.2024
The modern world of science and technology is developing rapidly, and every day new methods and technologies appear that open up new prospects for us in various fields. One such innovation is the development by German scientists of a new way to control optical signals, which could lead to significant progress in the field of photonics. Recent research has allowed German scientists to create a tunable waveplate inside a fused silica waveguide. This method, based on the use of a liquid crystal layer, allows one to effectively change the polarization of light passing through a waveguide. This technological breakthrough opens up new prospects for the development of compact and efficient photonic devices capable of processing large volumes of data. The electro-optical control of polarization provided by the new method could provide the basis for a new class of integrated photonic devices. This opens up great opportunities for ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Sound controls the light
04.02.2015
At the beginning of the last century, the Soviet physicist Leonid Mandelstam theoretically showed that sound vibrations in a transparent substance can scatter light passing through this substance. Sound waves cause local changes in the density of the medium and, as a result, change the refractive index. As a result of such scattering, part of the light energy is lost. Independently of Mandelstam, the American physicist Leon Brillouin arrived at the same results. As a result, the interaction of sound and light in transparent media was called the Mandelstam-Brillouin effect.
However, we do not notice that loud music scatters the light from a light bulb, as, for example, the light of car headlights scatters in the fog. The effect will become noticeable only if instead of an ordinary light bulb we take a source of monochromatic radiation - a laser. The fact is that the laser beam is an electromagnetic radiation with one wavelength, which determines its "color". The red beam has one wavelength, the green beam has another.
Now let's take a fiber optic data line. The principle of its operation is that information is transmitted by changing the intensity of a light beam propagating along a transparent glass thread. A single fiber optic strand can be used simultaneously to transmit data over hundreds of channels, simply by using light beams of different wavelengths. Each channel corresponds to a specific laser wavelength. It is quite similar with the transmission of data over radio waves, except for one thing: if we increase the power of the radio transmitter, then the signal power and the range of its reception increase. If we increase the laser power to transmit a signal over an optical fiber, the transmission deteriorates - more and more of the signal will begin to be lost due to Mandelstam-Brillouin scattering. Therefore, there is a threshold signal power, which does not make sense to exceed, otherwise the transmitted light will simply be reflected back.
What did physicists from the University of Illinois do? On a thin fiber optic strand, they fixed a small glass sphere. This design is called a ring optical resonator. A laser beam from a fiber optic filament enters the resonator and, due to multiple internal reflection, remains in it, as in a trap. The key point in the experiment was the second laser beam, with a frequency that differs from the original one by a certain amount. The difference in the frequencies of the laser beams corresponded to the frequency of the acoustic vibrations of the sphere material. This made the optical fiber and resonator system transparent to the first beam.
What is most surprising, such a system turned out to be transparent to rays from only one side. It turned out to be a kind of optical turnstile - the light passes from one side, and cannot pass from the other. Such an interesting property arises due to the complex interaction of two light rays and acoustic waves in a material - the Mandelstam-Brillouin scattering effect. Only in this case, instead of preventing the passage of the beam through the fiber, he, on the contrary, provided him with a free corridor.
The discovery of such properties will make it possible to create miniature optical isolators and circulators, which are needed for fiber optic systems and, in the future, for quantum computers. Now these devices are based on the magneto-optical Faraday effect, and magnetic fields and materials are used to transmit light in only one direction. The discovery made will just help to get rid of unnecessary magnetic fields. In addition, it can be used to change the group velocity of a light beam - what physicists call "fast" and "slow" light, it is needed to store quantum information.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Exciton laser on bacteria
▪ Creation of electrically conductive nanostructures using water and air
▪ Oblivion molecule
▪ Gas stove is more harmful than passive smoking
▪ Azulle Access3 keychain computer with Intel processor
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Reference materials. Article selection
▪ Bungalow article. Tips for the home master
▪ Article What is the difference between a legal entity and an individual? Detailed answer
▪ article Operator (driver) of a crane-manipulator. Standard instruction on labor protection
▪ article Advantages of electronic transformers for halogen lamps. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Overhead power lines with voltage above 1 kV. The intersection of overhead lines with water spaces. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese



 See other articles Section
See other articles Section 