
|
|
OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH
Occupational safety instructions for a pipe-laying operator. Full document
Occupational Safety and Health / Standard instructions for labor protection 1. General provisions 1.1. The instructions apply to all departments of the enterprise. 1.2. According to these instructions, the pipe layer operator (hereinafter referred to as the operator) is instructed before starting work (initial instruction), and then every 3 months (repeated instruction). The results of the briefing are recorded in the "Journal of registration of briefings on labor protection issues". In the journal, after passing the briefing, there must be the signatures of the instructing and the driver. 1.3. The owner must insure the driver against accidents and occupational diseases. In case of damage to the driver's health due to the fault of the owner, he (the driver) has the right to compensation for the harm caused to him. 1.4. For non-compliance with this instruction, the driver bears disciplinary, material, administrative and criminal liability. 1.5. Persons at least 18 years of age who have undergone a medical examination and have no medical contraindications are allowed to work independently on a pipelayer; have undergone special training, have the appropriate certificate for the right to operate a pipe layer and practical skills in servicing and operating it; underwent induction training on labor protection, workplace training and fire safety training. 1.6. The driver must: 1.6.1. Know the structure, rules of safe operation and maintenance of the pipe layer. 1.6.2. Comply with internal labor regulations. 1.6.3. Perform only the work that is assigned by the work manager and in which he is instructed. 1.6.4. Keep unauthorized persons out of the work area. 1.6.5. Keep the pipelayer in good condition. 1.6.6. Remember personal responsibility for the implementation of labor protection rules and the safety of colleagues. 1.6.7. Use overalls and personal protective equipment. 1.6.8. Be able to provide first aid to victims of accidents. 1.6.9. Be familiar with the use of primary fire extinguishing equipment. 1.7. The main dangerous and harmful production factors that affect the driver are:
1.8. The driver is provided with overalls and personal protective equipment:
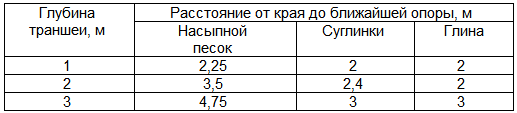
1.9. Before being allowed to work, the driver must receive instructions that reflect the procedure for safely performing work. 1.10. Each pipelayer must have an inventory number and a passport, the data of which is recorded in the equipment reception and accounting log. The magazine is kept by the chief mechanic. 1.11. Before putting into operation, and then every 12 months, pipe layers undergo technical inspection by engineers responsible for their good condition. The results of the inspection are recorded in a technical inspection log, which is kept by the responsible mechanic. 1.12. The date of the next inspection must be indicated on the pipelayer boom. 1.13. It is prohibited to work on a pipelayer whose next inspection period has passed. 1.14. There should be no unauthorized persons at the driver’s workplace (in the cab). Control levers must be kept clean and tidy. 2. Safety requirements before starting work 2.1. Get an assignment from the work manager. 2.2. Familiarize yourself with the entries in the journal of acceptance and delivery of the shift. 2.3. Install the pipe layer on a planned site beyond the boundary of the soil collapse prism. Within the boundaries of the pit collapse prism, fastening, installing and moving a pipe layer is permitted subject to preliminary verification of the fastening strength calculations specified in the PVR, taking into account the magnitude and dynamics of the load. 2.4. Check the technical serviceability of the pipelayer attachments. There should be no cracks on the boom at the points of welding of the support brackets. Particular attention should be paid to the hinge connection of the boom, frame and counterweight (the hinge pins must be securely locked). 2.5. Inspect cargo and boom ropes. Make sure that they are securely fastened to the boom, suspension block, and winch drums and that they are correctly laid in the grooves. 2.6. Check the presence and fastening of the chain drive guard of the power take-off mechanism, as well as the fastening of all parts and assemblies. It is necessary to lubricate the rubbing parts in accordance with the lubrication chart. 2.7. For pipelayers with a hydraulic drive for tilting the counterweight, check: 2.7.1. Fastening of hydraulic drive units, hydraulic cylinder. 2.7.2. The action of the hydraulic drive control lever at idle and when lowering the counterweight frame. 2.7.3. No oil leakage through gaskets and pump covers, or in pipeline connections. Any leaks detected must be repaired. 2.8. The counterweight frame in the guide channels should move easily under its own weight; the upper rollers of the frame should not reach the stop by 25 mm. 2.9. Check the lifting devices, which should have a tag or stamp indicating the load capacity and test date. If defects are detected or the deadline for the next test is violated, they should be replaced. 2.10. You should check: 2.10.1. Engine idling. 2.10.2. The reliability of the brakes. 2.10.3. Oil level in the crankcase of the main and starting engines. 2.10.4. The presence of water in the radiator. 2.10.5. Availability and serviceability of the instrument. 2.10.6. Alarm and lighting. Any minor faults identified should be corrected immediately, and more serious faults should be reported to the work manager. 2.11. Carry out repairs with the engine turned off, the chassis braked and the boom lowered. 2.12. Check with the slinger that he has a certificate authorizing the slinger to perform work. 2.13. Only after inspecting the pipelayer and making sure that it is in good working order is it possible to begin work. 3. Safety requirements during work 3.1. Work on laying pipelines must be carried out in accordance with the PVR. 3.2. When starting the starting engine, you must hold the starting handle without separating your thumb from the others. 3.3. To make it easier to start the engine in winter, the oil must be heated to 60-70°C before filling, and hot water at a temperature of at least 70°C must be poured into the cooling system. 3.4. Before starting work on lowering the pipeline into the trench, it is necessary to check the reliability of the ropes, blocks, soft grips and braking devices of the pipe layer. 3.5. Before lifting the pipeline, you must ensure that the brakes on the cargo winch operate reliably. 3.6. Lift the load only when the hook and the load chain hoist are in a vertical position. 3.7. The height of the pipeline being lifted from the ground by the pipelayer should not exceed 1 m. Before lowering the pipeline, an audible signal should be sounded. 3.8. When several pipe layers are working simultaneously, all actions of the operators must be strictly coordinated. In this case, the pipelayers must work synchronously, without jerking, with the same speeds of the winches. Failure to comply with this rule may result in overloading or overturning of the pipelayer and damage to the rigging equipment. 3.9. The pipelayer is only allowed to lift the maximum load in the first gear of the gearbox. It is necessary to ensure that the mass of the load lifted at a given boom reach does not exceed the load capacity indicator located on the boom. 3.10. All working operations: lifting the hook, changing the boom reach, turning over and lifting the counterweight should be performed slowly, without jerking or jamming, in order to avoid inertial overloads on the pipelayer. 3.11. When lifting and laying the pipeline in a trench, the operator must: 3.11.1. Monitor the condition of the trench edge and stop work even if it collapses slightly. 3.11.2. Constantly monitor the condition of the pipelayer mechanisms and its control devices. 3.11.3. Make sure that the insulated part of the pipeline sinks to the bottom without touching the walls of the trench. 3.11.4. Install the pipelayer hook in a vertical position above the load being lifted. 3.11.5. Monitor the condition of the brakes and winch, check their adjustment, periodically tighten the bolts, nuts and locking devices. 3.11.6. Check the fastening and condition of the ropes, and also ensure that when winding the rope onto the winch drum, it is laid in equal rows (not crossed). 3.11.7. Move the pipelayer along the trench while lowering the pipeline outside the trench prism, but no closer than 2 m from the edge of the trench. 3.11.8. Monitor the work of the slinger, ensure the correctness of the sling. Metal sheets must be applied to the pipes evenly, without twisting, with a rubber mat or other soft gasket placed between the pipe and the sheet to preserve the insulation. 3.11.9. During breaks in work, release the pipelayer hook from the load and lower the boom to the ground. 3.12. It is forbidden: 3.12.1. Move the pipelayer unloaded with the counterweight discarded. 3.12.2. Lift load and boom at the same time. 3.12.3. The presence of unauthorized persons not taking part in this work. 3.12.4. Lift a load that exceeds the maximum lifting capacity of the pipelayer specified in its characteristics for a given boom reach. 3.12.5. Raise the pipeline above the permissible level established for this pipelayer. 3.12.6. Lift a load that is covered with earth or frozen to the ground. 3.12.7. Bring the blocks of the pulley block all the way, as this creates a lot of tension in the rope, causing rapid wear of the rope. 3.12.8. Lift and move the load when the pipelayer is in an unstable position, as well as if it is located on terrain with a slope towards the load of more than 3º. 3.12.9. Work directly under the wires of an active power line of any voltage. 3.12.10. Hold the load on the hook for a long time. 3.12.11. The presence of people in the trench, as well as between the trench and the pipeline during its installation or components of the installed pipeline. 3.13. The pipelayer should be moved at a distance determined depending on the depth of the trench and soil category, taking into account the prism of the trench, but not less than that indicated in Table 1.
3.14. The path along which the pipelayer moves along the trench route must be leveled and planned in advance, and on soft soils and in swampy places, shields or flooring made of boards and beams must be installed. 3.15. When moving a pipelayer along a route or from one object to another, the operator must be guided by the operating rules for tractors; in this case, the power take-off shaft clutch must be disengaged, the counterweight frame must be installed in the transport position - on the clutch. 3.16. When moving a pipelayer with a load on the hook, the boom must be raised and set to a position that corresponds to the minimum reach, and the load must be raised to a height of no more than 50 cm above the ground surface. The pipelayer should be moved in first gear and only on a graded dirt road. 3.17. Work on moving cargo with a pipelayer must be carried out under the direct supervision of the person responsible for its operation. 3.18. When cleaning a pipeline, pipelayers must move along the pipeline with a boom extension of no more than 1-1,5 m. The lifting height of the pipeline should be the minimum required only for the passage of the cleaning machine, and no more than 1 m from the bottom of the pipe to the ground surface. There must be complete coordination between the pipe layer operator and the mechanic on the cleaning machine. The operator should move the pipe layer along the trench only upon a signal from the mechanic on the cleaning machine. 3.19. To protect against dust generated during operation of the cleaning machine, you must use safety glasses and respirators. 3.20. In winter, for normal operation of the pipelayer, a strip of snow at least 4-5 m wide from the edge of the trench must be cleared of snow. When moving along a strip cleared of snow, the folded counter weight of the pipe layer should not touch the snow dumps formed during clearing, in order to avoid the pipe layer turning to the right along the way. 4. Safety requirements after finishing work 4.1. Place the pipelayer in the designated place, turn off the engine, and place the control levers in the neutral position. 4.2. Lower the arrow to the ground; close the fuel supply valves to the engine; thoroughly wipe the engine and all mechanisms of the pipelayer; in winter, drain the water from the radiator and the entire cooling system. 4.3. Fill in the shift log of the pipelayer. 4.4. Fold overalls, personal protective equipment in the place provided for them. 4.5. Wash hands, face with warm water and soap; shower if possible. 4.6. Report to the head of work on all the shortcomings that occurred during work. 5. Safety requirements in emergency situations 5.1. An emergency situation may arise in the event of: a pipe layer overturning; breakage of ropes, slings; failure of winches, etc. 5.2. In the event of an emergency, it is necessary to immediately stop work, fence off the dangerous area and prevent unauthorized persons from entering it. 5.3. Report what happened to the supervisor. 5.4. If an accident occurs, provide first aid to the victim; if necessary, call emergency medical assistance. 5.5. Providing first aid. 5.5.1. Providing first aid in case of electric shock. In case of electric shock, it is necessary to immediately release the victim from the action of electric current by disconnecting the electrical installation from the power source, and if it is impossible to disconnect it, pull it away from the conductive parts by clothing or using insulating material at hand. If the victim has no breathing and pulse, it is necessary to give him artificial respiration and indirect (external) heart massage, paying attention to the pupils. Dilated pupils indicate a sharp deterioration in the blood circulation of the brain. In this state of recovery, it is necessary to start immediately, and then call an ambulance. 5.5.2. First aid for injury. To provide first aid in case of injury, it is necessary to open an individual package, apply a sterile dressing material, which is placed in it, to the wound and tie it with a bandage. If somehow the individual package was not found, then a clean handkerchief, a clean linen rag, etc. must be used for dressing. On a rag that is applied directly to the wound, it is advisable to drip a few drops of tincture of iodine to get a stain larger than the wound, and then apply the rag to the wound. It is especially important to apply the tincture of iodine in this way to contaminated wounds. 5.5.3. First aid for fractures, dislocations, shocks. In case of fractures and dislocations of the limbs, it is necessary to strengthen the damaged limb with a splint, plywood plate, stick, cardboard or other similar object. The injured arm can also be hung with a bandage or handkerchief from the neck and bandaged to the torso. In case of a skull fracture (unconsciousness after a blow to the head, bleeding from the ears or mouth), it is necessary to apply a cold object to the head (a heating pad with ice, snow or cold water) or make a cold lotion. If a fracture of the spine is suspected, it is necessary to put the victim on the board, without lifting him, turn the victim on his stomach, face down, while observing that the body does not bend, in order to avoid damage to the spinal cord. In case of a fracture of the ribs, a sign of which is pain during breathing, coughing, sneezing, movements, it is necessary to tightly bandage the chest or pull it off with a towel during exhalation. 5.5.4. First aid for burns with acids and alkali. If acid or alkali gets on the skin, the damaged areas must be thoroughly rinsed with a stream of water for 15-20 minutes, after which the acid-damaged surface should be washed with a 5% solution of baking soda, and the burnt with alkali - with a 3% solution of boric acid or an acetic solution. acids. If acid or alkali gets on the mucous membrane of the eyes, it is necessary to thoroughly rinse the eyes with a stream of water for 15-20 minutes, then rinse with a 2% solution of baking soda, and if the eyes are damaged by alkali, with a 2% solution of boric acid. In case of burns of the oral cavity with alkali, it is necessary to rinse with a 3% solution of acetic acid or a 3% solution of boric acid, for acid burns - with a 5% solution of baking soda. If acid enters the respiratory tract, it is necessary to breathe a 10% solution of baking soda sprayed with a spray gun, if alkali enters, a sprayed 3% solution of acetic acid. 5.5.5. First aid for bleeding. 5.5.5.1. Raise the injured limb up. 5.5.5.2. Close the wound with a dressing (from a bag) folded into a ball, press it from above, without touching the wound itself, hold for 4-5 minutes. If the bleeding stops without removing the applied material, put another pad from another bag or a piece of cotton on top of it and bandage the wounded area (with some pressure). 5.5.5.3. In case of severe bleeding that cannot be stopped with a bandage, compression of the blood vessels that feed the wounded area is applied by bending the limb at the joints, as well as with fingers, a tourniquet or a clamp. In case of heavy bleeding, you should immediately call a doctor. 5.6. If a fire occurs, start extinguishing with the available fire extinguishing equipment. If necessary, call the fire department. 5.7. In all cases, follow the instructions of the head.
▪ Working with electrical tools. Standard instruction on labor protection ▪ Pipelayer operator. Standard instruction on labor protection ▪ Working on a CITOBORMA type drilling machine. Standard instruction on labor protection
Artificial leather for touch emulation
15.04.2024 Petgugu Global cat litter
15.04.2024 The attractiveness of caring men
14.04.2024
▪ Fixed issue with lack of inspiration ▪ Testing self-driving cars with a remote driver ▪ Giant accumulations of turbulent gas discovered in distant galaxies
▪ site section Batteries, chargers. Article selection ▪ article Honor to the madman who will inspire humanity with a golden dream. Popular expression ▪ white cabbage article. Legends, cultivation, methods of application ▪ article Anti-radio spy. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 See other articles Section
See other articles Section 