 Free technical library
Free technical library
Inflating the ball without a needle. Tips for the home master

Directory / Builder, home master
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
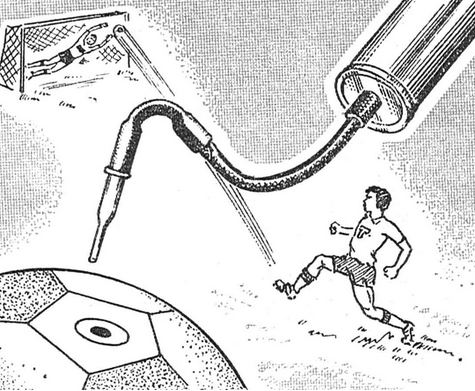
If you don’t have a special needle for pumping up a nipple volleyball or soccer ball, use ... an ordinary pharmacy pipette with an extended nose. Cut off its rubber part a little and put it on the pump hose, and insert the glass part into the nipple hole of the ball.
The ball is pumped up with such a "needle" much faster.
Author: N. Zhirkov
 We recommend interesting articles Section Builder, home master:
We recommend interesting articles Section Builder, home master:
▪ Arched structure for a greenhouse or conservatory
▪ Drilling is more reliable with a compass
▪ Polyethylene sewing - with the help of a newspaper
 See other articles Section Builder, home master.
See other articles Section Builder, home master.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive New electronics will withstand radiation and heat
28.06.2012
Engineers from the University of Utah have developed microscopic mechanical devices (MEMS) that can withstand the most powerful radioactive radiation and heat. According to scientists, the devices they have created can control robots or computers even inside a reactor or in deep space.
Ionizing radiation quickly damages traditional electronics, so you have to use numerous redundant circuits and powerful protection, as was the case, for example, with the robots that worked at the emergency Fukushima nuclear power plant. But even the protected robots sent to monitor the damaged reactors stopped working after a few hours. The thing is that powerful ionizing radiation breaks through "extra" conductive channels in semiconductors, which disables electronics.
For the first time, scientists have managed to develop a unique technology that continues to work in the presence of even the most powerful ionizing radiation. The new devices are 25x25 micron logic elements that perform the simplest logical operations: "on" or "off". Microscopic mechanical devices can even work inside a nuclear reactor
During the experiments, new devices were immersed in the core of a university reactor for two hours, and MEMS continued to work as if nothing had happened. MEMS have not been destroyed by ionizing radiation because they do not use semiconductor channels. These are simple microscopic switches with tungsten electrodes that touch each other and make or break a circuit.
In terms of "traditional" applications, MEMS have certain drawbacks, for example, they are 1000 times slower than silicon electronics and, moreover, less durable (due to the presence of moving parts). However, when it comes to extreme operating conditions, MEMS is unmatched. So, during the experiments, microscopic mechanical devices worked for hours in a vacuum at a temperature of 277 degrees Celsius and even in the core of a 90-kW research reactor. Even the most reliable and protected silicon electronics in such conditions failed after a few minutes. Under normal conditions, MEMS worked for about 2 months, completing more than one billion cycles without failure. Currently, scientists plan to improve this figure by a million times.
The use of MEMS opens up completely new possibilities for monitoring the operation of nuclear power plants, internal combustion engines and creating probes that can penetrate the most dangerous places without requiring powerful and heavy protective systems.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Xiaomi Star Trang Telescope compact telescope
▪ Good deed ransomware virus
▪ Eternal implant the size of a grain of sand
▪ From now on, all Hollywood studios support Blu-ray
▪ Hydrogen Mercedes
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ website section Television. Article selection
▪ article The devil pulled the tongue. Popular expression
▪ article Why Liverpool, having won the Champions League, could only defend the title by exception? Detailed answer
▪ article Buchu mountain. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
▪ article Entertaining experiments: some possibilities of the field-effect transistor. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Rebus proverbs and sayings
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 See other articles Section
See other articles Section 