 Free technical library
Free technical library
Endless water lift. Tips for the home master

Directory / Builder, home master
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
Free wind energy has long served man. The question of its use is urgent even now, especially with the ever-increasing shortage of natural fuel. There is a "demand" for it in personal subsidiary farms, as evidenced by letters from readers received by the editorial office.
So, Evgeny Pavlovich Osipov from the village of Nikolaevka, Bashkir Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic, writes: “I am a carpenter by profession, I have my own plot of land. During the day, the whole family works, and in the evening in the summer time we do not have time to stock up on water from the well. "Leave the electric pump on when no one is home because of the risk of fire. It would be best to build a low-power wind pump installation."
In this and the 3rd issue, a description of a wind-driven water lift for low-yield wells of household plots is published. E. Makarova from Karaganda received an author's certificate for it No. 866265. The design uses the original principle of delivering water to the top with the help of an "endless" absorbent tape, from which it is then squeezed out by a roller with a counterweight.
Wind is the engine of this installation; propeller with blades - propeller. On the shaft of the latter, there is a water "conveyor": an endless belt of porous material, the lower part of which is lowered into the well. The screw turns, the tape stretches up, raising the absorbed water. The squeezing roller selects it - the water flows down the drain pipe into the supply container. The verticality of the tape - sagging - is provided by a tension mechanism located at its very bottom, constantly immersed in water.

Rice. 1 (click to enlarge). Water lifting unit: 1 - propeller, 2 - drive mechanism, 3 - drain pipe, 4 - tower of the installation, 5 - stabilizer, 6 - control pipe, 7 - supply tank, 8 - supply pipe, 9 - tension mechanism, 10 - tape - "conveyor", 11 - well
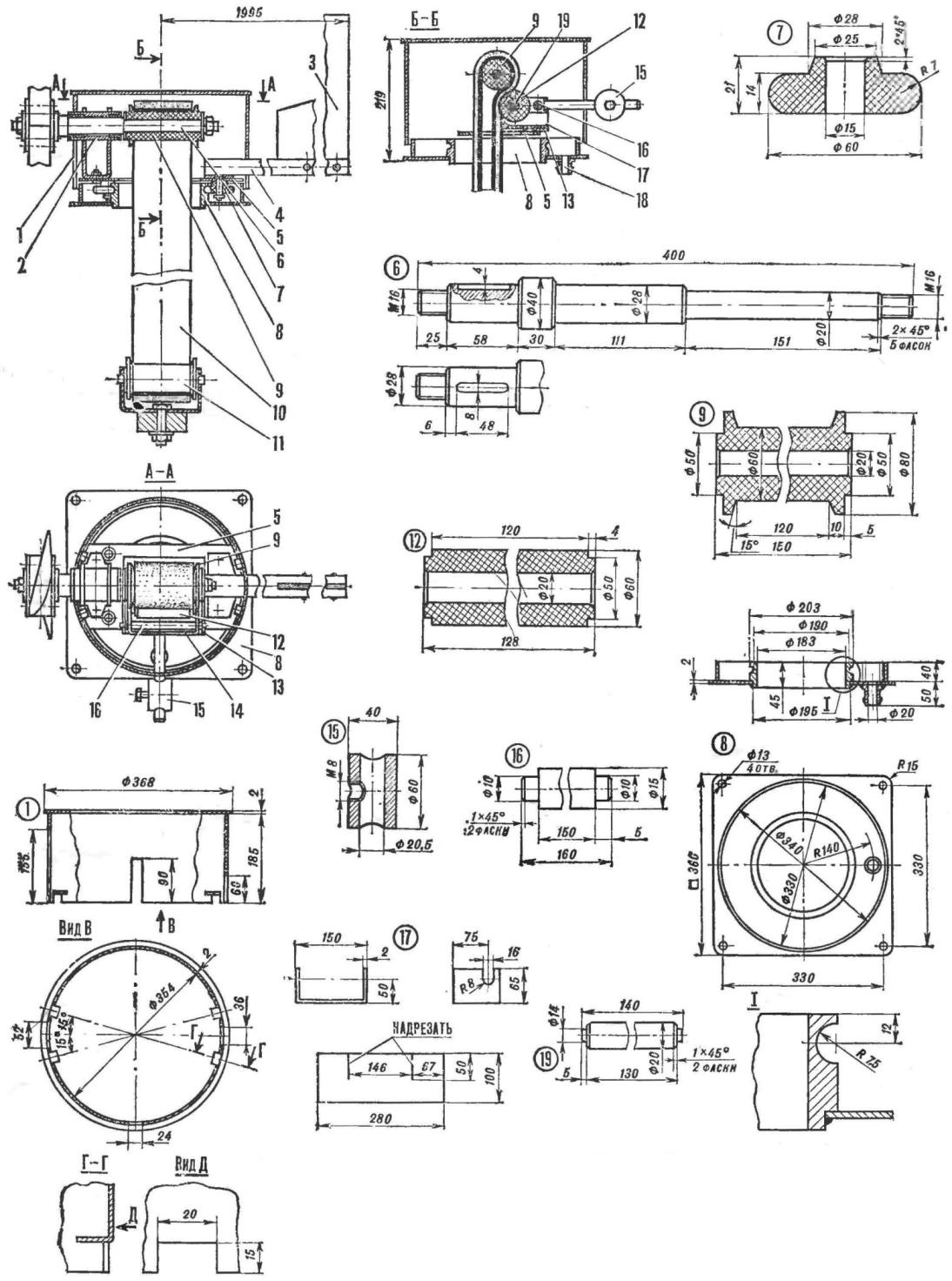
Rice. 2 (click to enlarge). Structural scheme of the water lift: 1 - casing of the drive mechanism, 2 - bushing of the shaft stand, 3 - stabilizer "shovel", 4 - stabilizer pipe, 5 - base, 6 - shaft, 7 - support roller, 8 - drive mechanism housing, 9 - drive roller, 10 - "conveyor" belt, 11 - tension mechanism, 12 - tie roller, 13 - base frame, 14 - wringer holder, 15 - counterweight, 16 - wringer holder axis, 17 - water inlet, 18 - drain fitting , 19 - pinch roller axis

Rice. 3 (click to enlarge). Propeller: 1 - sleeve, 2 - M8 coupling bolt, 3 - mounting cheek, 4 - propeller blade
The two-bladed propeller has a length of 2000 mm. Wooden blades are mounted on a metal sleeve with fastening cheeks and fastened with "" - bolts. The connection of the sleeve on the shaft is keyed with a tightening nut M16.
The stabilizer automatically sets the propeller against the wind. The guide "shovel" of the stabilizer is cut from a steel sheet 1 mm thick. For it, a longitudinal groove is sawn in the carrier pipe Ø21 mm, where it is inserted and fastened at the ends with two through rivets Ø5 im. To the pipe - at its very beginning, the heel is steamed. It has two holes for M8 bolts for connection with the base of the drive mechanism and another hole Ø25 mm, into which the upper flared part of the support roller pin enters during assembly.
The screw shaft is installed in the sleeve of the drive mechanism rack in nylon bearings, a leading rubber roller is put on from the end of the shaft, a conveyor belt is thrown over it. The base of the mechanism rotates relative to the body on the supporting rods. An annular groove is made in the body for this. The base board is cut from a 2 mm thick metal sheet. Holes Ø15 mm are drilled in it for the pins of the support rollers; during assembly, the pins are inserted into these holes and flared. The rollers are fixed with pressure washers. In addition, a rectangle with sides of 110x130 mm was sawn out in the center of the base for passing the tape. Next to it, a frame is welded under the axis of the holder of the wringer. On the one hand, there is an squeezing rubber roller in the holder, on the other hand, on the rolled axis, there is a counterweight, with which the roller is pressed against the tape, "extracting" water. A rubber visor is placed under it - a water intake. The drive mechanism is covered from above by a casing, which can be made of sheet metal.
The tension mechanism pulls the tape down: for this, it is weighted with a metal washer weighing about 2 kg, which is attached to the tension roller holder with an M10 bolt.

Rice. 4 (click to enlarge). Stabilizer: 1 - stem heel, 2 - stem, 3 - "shovel", 4 - rivet
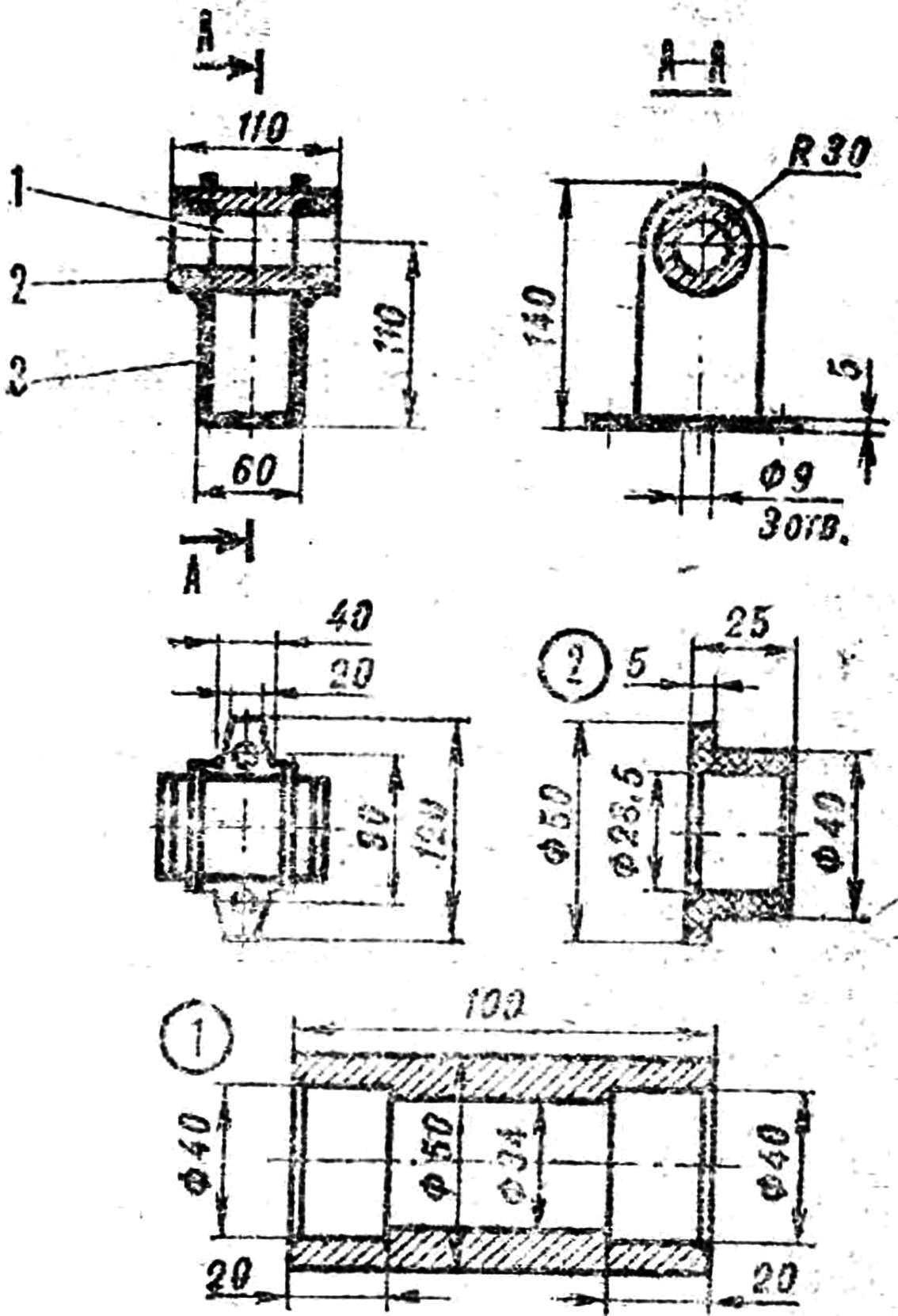
Rice. 5 (click to enlarge). Shaft stand: 1 - shaft sleeve, 2 - canron bearing, 3 - support

Rice. 6 (click to enlarge). Drive mechanism base: 1 - board, 2 - base frame, 3 - support roller pin

Rice. 7 (click to enlarge). Holder of the squeezing device: 1 - frame of the squeezing roller axis, 2 - counterweight axis

Rice. 8 (click to enlarge). Tension mechanism: 1 - tension roller, 2 - axle, 3 - clip, 4 - load, 5 - M10 bolt
The tape is a rubber strip 3-4 mm thick, foam rubber 15-20 mm thick is pasted on it. Both layers are connected at an oblique joint. Sponge rubber can also be used for the tape. The lift frame and supply tank (tank) are made from improvised materials, and the installation height must be chosen such that the tensioning mechanism is always in the water.
It is possible to perform a number of tasks, for example, to water the garden, directly while the windmill is running, but it is more convenient to store water for the future, filling the tank, where, by the way, it will warm up in the sun. The installation can be safely inserted without supervision. Even if the water begins to overflow the tank, it will flow back into the well through the control pipe.
The wind lift is able to provide "production" of 100 m3 of water per day.
If only there was wind!
Author: E.Makarova
 We recommend interesting articles Section Builder, home master:
We recommend interesting articles Section Builder, home master:
▪ Garden set
▪ Hallway wall
▪ Bulldozer shovel
 See other articles Section Builder, home master.
See other articles Section Builder, home master.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Volumetric microscope eye
23.04.2009
A microcamera made by American scientists allows you to see the cell from all sides at once. To create a three-dimensional image of a micro-object, scientists from Vanderbilt University, led by Associate Professor Chris Yanetopoulos, etched a depression in a single crystal of silicon.
Since, when such a material is etched, different planes of the crystal lattice dissolve at different rates, this recess took the form of a tetrahedral pyramid. The walls of the pyramid were covered with layers of gold or silver, giving them the properties of a mirror. A micro-object placed in a recess is reflected from the mirror walls, and the researcher sees it from all sides.
In fairness, it should be noted that such devices have already been used to study nanoparticles. And the Yanetopoulos group was the first to use a plate with pyramids of different sizes to study living microorganisms.
"This device is great for studying dynamic processes in living cells, because it allows you to follow them in three-dimensional space. For example, we were able to trace the path of centrioles during division," says Chris Yanetopoulos.
His colleague Dmitry Markov plans to study the deformation of a cell under pressure, which creates a microscopic trickle of water. Dimples in silicon are inexpensive to make, and their size can be varied over a wide range, which makes it possible to study a variety of objects.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ The music department was found in the brain
▪ Universal power controller for mobile applications
▪ The SportsArt G260 rowing machine generates electricity
▪ The sad fate of robots
▪ Anger Pill
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Metal detectors. Article selection
▪ article His example to others is science. Popular expression
▪ article Who are vertebrates? Detailed answer
▪ article Parker. Job description
▪ article SWR meter direct reading. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Crystals of metallic copper. Chemical experience
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese









 See other articles Section
See other articles Section 