
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Features of the circuitry of 16-bit set-top boxes. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Телевидение More recently, the eight-bit "Dendy" video game consoles and their counterparts have sparked a "computer revolution" in the minds and hearts of children and teenagers. However, progress does not stand still. 16-bit, 32-bit and even 64-bit TV game consoles are already showing great graphical and musical capabilities. It is clear that the more bit depth, the better. But on the other hand, the more expensive the prefix and the programs for it. Today, many people prefer 16-bit video set-top boxes, which provide good quality at a relatively low price. Appearing in the late 80s, they are still steadily occupying their niche in the market today. Of the many models of 16-bit video game consoles sold under various brands, the family developed by the Japanese company Sega Enterprises Ltd. has won universal recognition. More than a thousand game programs have been created for the Sega consoles, books and booklets with their colorful descriptions are being published. Due to the popularity of such consoles, many games originally developed, for example, for IBM PC or Amiga computers, are successfully converted for them. The careful study of the issues of unification of set-top boxes, copyright protection for their appearance and technical solutions is striking. Although manufacturers are scattered all over the world from Canada to Singapore, all Sega consoles look the same, the design of cartridges and joysticks, the types and purpose of connector pins, and power supply parameters are carefully maintained. Depending on the television standards adopted in different countries, several modifications of the set-top boxes "Sega" are produced [1]. The most famous American ("Sega Genesis"), Asian (or Japanese) and European versions. The compatibility of their game cartridges is ensured by special adapters, the so-called "Mega Key" expanders. In addition to branded ones, there are many "Sega"-compatible set-top boxes sold under various names, for example, "StarDrive-2", "SuperAlpha". Due to certain circumstances, Asian rather than European models are most common in our country. There are three generations of video consoles "Sega". The first was "Sega Mega Drive" (we'll call it "Sega-1" for short), then in 1990 - "Sega Mega Drive-2" (hereinafter - "Sega-2"), and a little later - "Sega Mega CD". The first two are designed to work with cartridges, the last - with laser discs. An analysis of the game software market for 16-bit consoles shows that cartridges as software carriers are unlikely to give way to laser discs in the foreseeable future. A massive transition to them, obviously, will occur after the wide distribution of 32-bit set-top boxes. For these reasons, we will limit the range of issues considered in the article to the circuitry of Asian models of the first and second generations. From the point of view of repair features, the differences between Sega-2 and the previous model are not obvious: the system connector has an input that allows you to control the correct connection of additional devices (for example, a specialized CD-ROM), and the joystick has an increased number of function buttons. Program compatibility is only guaranteed from the bottom up. This means that games released for "Sega-1" (there are more than 200 of them known) will also work for "Sega-2", but not necessarily vice versa. A few words about the design and technological features of the "Sega" consoles. Recently, surface mounting of electroradioelements on a printed circuit board is increasingly used in them. This progressive technology can significantly increase labor productivity in assembly and installation work, improve the quality of solder joints, reduce the dimensions, weight and, ultimately, the cost of the product. But not every manufacturer can afford to make printed circuit boards on complex and very expensive robotic surface-mount systems. So the use of such technology with a high degree of probability indicates a large company and good product quality. For surface mounting, special miniature components are produced: the so-called chip resistors and chip capacitors with dimensions of approximately 3,2x1,6x1 mm, microcircuits, transistors and diodes in a small package with gull-wing profile leads. In English literature, they are often referred to as SMD (Surface Mounting Devices - surface-mounted devices). The nominal resistance of the chip resistor can be determined by the inscription on its case, consisting of three, and for precision resistors - four digits. The last one shows how many zeros need to be added to the right of the previous numbers to get the resistance in ohms. For example, the inscription "150" means 15 ohms, "561" - 560 ohms, "112" - 1100 ohms (1,1 kOhm), "106" - 10 MΩ, and "2741" - 2,74 kOhm. For low-resistance resistors, the integer part of the resistance value in ohms is separated from the fractional letter R. For example, "4R7" means 4,7 ohms, "54R9" - 54,9 ohms. Unfortunately, it is difficult to determine the values of chip capacitors by their appearance, since, as a rule, there is no corresponding marking on them. The rating is only indicated on the packaging in which such capacitors arrive at the assembly line. Failed chip resistors can be replaced with conventional power of 0,063 or 0,125 W, and chip capacitors can be replaced with small-sized ceramic ones (KM - 56, K10 - 17), shortening and molding their conclusions. "SEGA" SET-TO-BOARD DEVICE Set-top boxes "Sega" of Asian models generate a TV signal of the PAL standard. A 512 color image consists of 320 dots horizontally and 224 dots vertically. The soundtrack of the games is stereophonic. The power consumed from a network - 8... 14 W. The connection diagram of the main components of the attachment is shown in fig. 1. Its basis is a processor board, which occupies almost the entire base unit. It has connectors to which all other nodes are connected: a 64-pin socket for a game cartridge ("CARTRIDGE"), a 60-pin system plug ("SYSTEM"), two nine-pin plugs for joysticks ("CONTROL 1" and "CONTROL 2 "), power jacks ("ADAPTOR") and stereo headphones ("PHONES"), a socket for connecting to a TV ("A / V") at low or, through a modulator, at high frequency.
"POWER", the LED indicator lights up. The "RESET" button is used to bring the device to its original state, and in some cases - to select one of several game programs recorded in one cartridge. There is a volume control for the soundtrack "VOLUME". In practice, there are prefixes, the composition of which differs from that described. Sometimes there is no LED indicator, volume control, headphone jack. The high-frequency television modulator is located outside or inside the set-top box, the modulator can be connected to the antenna input of the TV through a mechanical switch. AC ADAPTER The "Sega" prefix is powered from the AC network through a transformer power supply with a rectifier made according to the usual bridge circuit (Fig. 2, a). Compared to a similar block for "Dendy", it can deliver almost twice as much power and develops a voltage of 1,2 V at a load current of 10 A. A typical load characteristic of the block at a mains voltage of 220 V is shown in Fig. 2, b.
The adapter is usually equipped with a transformer with a magnetic core with a cross section of about 4 cm2, for example, of size Ш16x24. The primary (network) winding contains 2100 ... 2300 turns of wire with a diameter of 0,15 mm, the secondary (lowering) - 120 ... 130 turns of wire with a diameter of 0,51 mm. The capacitance of the filter capacitor is 1000 ... 3300 uF. Its operating voltage must be at least 16 V, but for reliability it is recommended to use capacitors rated for 25 V. Diodes 1N5391, if necessary, can be replaced by a KTs410 block with any letter index or small-sized rectifier diodes rated for a current of at least 1 A, for example, KD208A, KD212A. As a precautionary measure, it is desirable to include a 0,25 A fuse in the transformer primary winding circuit. You can also use a VP1-2-0,25A-250 fuse in a ceramic case with flexible leads. One of the simple protective devices described in [2] will also be useful. It is unacceptable to use a network adapter from Dendy to power "Sega". Due to overload, at best, it will not develop a voltage sufficient for the normal operation of the video set-top box, and at worst, it will fail. MODULATOR This device transfers the spectrum of low-frequency image (VIDEO) and sound (AUDIO) signals generated by the set-top box to the frequency band of one of the meter-range television channels. The completeness of the design, the same overall and mounting dimensions of the modulators in different Sega models allow us to speak of their unification and sufficient sophistication. A typical modulator (the circuit diagram is shown in Fig. 3) contains three stages: a high-frequency image carrier signal generator, an audio intermediate frequency (IF) signal generator, and a mixer.
The IF sound generator is assembled on a transistor VT2. For various variants of the PAL standard for which Asian Sega models are designed, this frequency is 4,5 (PAL - M), 5,5 (PAL - B), 6 (PAL - I) or 6,5 MHz (PAL -D). If necessary, the generator can be easily tuned to the frequency of 6,5 MHz adopted by us by changing the position of the trimmer of the transformer T1 and selecting the capacitance of capacitors C7 and C11. The generator frequency is modulated by changing the capacitance of the collector junction of the transistor VT2 under the action of the AUDIO signal. The range of this signal is in the range of 0,5 ... 2 V. If the TV reproduces the sound of games with wheezing and distortion, you should try to change the operation mode of the transistor with a selection of resistors R2 and R3 or reduce the modulating signal, for example, by connecting a resistor with resistance C2 in parallel several kilohms. On the transistor VT1, an image carrier frequency generator is assembled. The frequency of its oscillations determines the circuit L1C3. The signal from the output of the generator is fed to the base of the transistor VT3, which acts as a mixer. The emitter of this transistor from the secondary winding of the transformer T1 receives an IF sound signal, and through the resistor R10 - a video signal (VIDEO) with a swing of 1 - 1,5 V. Capacitor C13 shunts the emitter circuit of the transistor VT3 at high frequency, only slightly attenuating relatively low-frequency modulating signals. The output of the modulator through the XW1 connector is connected by a coaxial cable to the antenna input of the TV. In practice, there are modulators whose circuits have some differences from that shown in Fig. 3:
Not only S9018 transistors, but also 2SC3194, 2SC458 transistors can be installed in the modulator. They can be replaced by almost any low-power transistors of the np-n structure with a cut-off frequency of at least 600 MHz, for example, KT355AM or KT325, KT368 with any letter indices. The modulator board is closed with a metal screen measuring approximately 45X35X15 mm with holes for adjusting the inductance of the transformer T1 and coil L1. If this node is located inside the base unit of the set-top box, contact pads XT1-XT4 are connected by short conductors directly to the processor board. The modulator, made as a separate module, is placed in a plastic case with dimensions of approximately 80X40x20 mm. It has openings for access to the XW1 socket and for the passage of a four-core shielded cable, ending with a plug that connects to the "A / V" socket of the video set-top box. The purpose of the plug contacts is shown in fig. 4. Unused contacts are usually absent in it. In the figure, they are conventionally shown with crosses.
The current consumed from the power supply through the VCC circuit does not exceed 6...9 mA. Modulators from "Sega" and "Dendy" [3] are interchangeable. CARTRIDGE The cartridge is a removable ROM in which the game program is recorded. It is customary to measure its information capacity in megabits. The simplest games require at least 1 Mbps, while the most dynamic and colorful games require much more. For example, the BOO game cartridgeGERMAN has an information capacity of 24 Mbit and stores more than 1800 color image frames. If you try to copy data from it into conventional PROMs with ultraviolet erasure, you will need 48 27512 or 384 K573RF6 microcircuits. Since in the set-top boxes "Sega" 23 bits of the address are output to the "CARTRIDGE" connector, and the data bus is 16-bit, cartridges with a capacity of up to 128 Mbit can be connected to them. They recognize the information capacity of a particular cartridge by marking the ROM installed in it. For example, the inscription "42LG8M16B" means that the chip has a capacity of 8 Mbit with a 16-bit data bus organization. If it is not possible to determine the capacity of the microcircuit by marking, you can try to do this by counting the number of bits of the address and data buses connected to it. Most often, unpackaged ROM microcircuits filled with a drop of compound are used in cartridges, sometimes microcircuits in plastic cases with 42 or 44 pins are used. The appearance of the cartridge from the side of the connector and the purpose of the most commonly used contacts are shown in fig. 5. The plug of the cartridge connector is printed on the end of its board. The numbering of contacts can be either purely numeric (top row - odd, bottom - even numbers), or alphanumeric (bottom row - A1 - A32, top - B1 - B32). The top side is the side of the board where the microcircuits are located. Regardless of the numbering method, the mutual position of the contacts corresponding to the same signals is always the same. The numbers of electrical communication lines on the diagrams of the cartridges below correspond to the digital designations of the pins of their connectors.
The simplest of the cartridges (the diagram in Fig. 6, the game "TOY STORY') contains only one microcircuit. This is a conventional mask ROM with an information capacity of 32 Mbps, the data in which is entered during the manufacturing process. The outputs DO - D15 become active only with simultaneous low-level signals to the CS and OE inputs. If at least one of these signals is high, the ROM outputs remain in a high-impedance state. The CHECK cartridge connection control circuit is connected to a common wire inside it. If the cartridge is missing or loosely installed in the video set-top box connector, the signal level CHECK is taken high by its main processor and it goes into the state of waiting for this signal to be low.
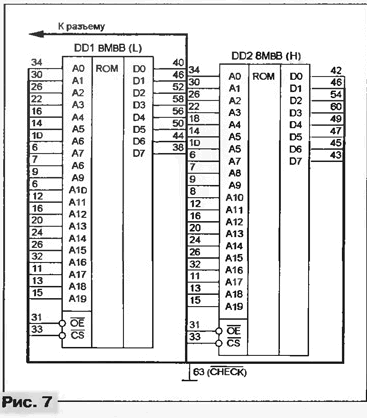
In cartridges with two eight-bit ROMs (scheme in Fig. 7, the game "MORTAL KOMBAT - 1"), most often in one of the microcircuits (usually marked with the letter L) the lower ones (DO - D7) are recorded, and in the other (H) - the older ones ( D8 - D15) bits of each 16-bit data word. But there are cartridges in which the discharges are distributed between the microcircuits differently.
A more complex option (the diagram in Fig. 8, the game "BOOGERMAN") contains two 16-bit ROMs, and the OE signal passes to the corresponding input of only one of them, depending on the level of the A20 signal. The selection logic is implemented on the elements of the DD3 chip (similar to K555LAZ). The information capacity of the ROM DD1 and DD2 is sometimes not the same.
On fig. 9 shows a diagram of a cartridge with two game programs recorded in one ROM. They are changed each time the "RESET" button is pressed. The RES pulse generated at this moment by the base unit of the set-top box changes the state of the counting trigger DD2.1, including the first (A18 = 0) or second (A18 = 1) game.
Recently, games have been spread that can be interrupted at any time, saving the game situation, and resumed at the next launch of this situation. It also provides the ability to remember the names of players, store and update a list of records. Cartridges of such games contain not only permanent, but also random access memory, data in which can be written during the game and saved when the power is turned off. This is usually achieved by using so-called FLASH memory instead of conventional ROMs. Another option is to install an additional cell-backed CMOS RAM chip into the cartridge. Since the current drawn by such RAM in storage mode is negligible, a miniature cell (or battery) of very small capacity can be used. One of the possible schemes for additional RAM is shown in Fig. 10. It can be used in conjunction with a ROM assembled according to any of the above schemes. To switch ROM / RAM, the signal A19 was used, but it could be some other bit of the address bus. The crystal select signal (CS) is supplied to the ROM chips not from pin 33 of the connector, but via circuit 33.1 from the output of logic element DD2.2.
Diodes VD1 and VD2 switch the power circuit of the DD1 chip (analogue K537RU2) to the GB1 battery when the cartridge is disconnected from the base unit. In this case, the transistor VT1 is closed, since its base and emitter are connected to a common wire through resistors R2, R3 and the internal resistance of the cartridge microcircuits disconnected from the power supply. Through the resistor R1, a high logic level voltage is supplied to the CS input of the DD1 microcircuit, maintaining it in an unselected state. This ensures the safety of the data recorded in the RAM. In the cartridge connected to a working set-top box, the transistor VT1 serves as a non-inverting amplifier with a common Zaza and transmits the crystal selection signal generated by the DD2.4 element to the CS input of the DD1 microcircuit. The average current consumed by the cartridge is 20...80 mA. Its printed circuit board usually has room for several bypass capacitors in the power circuit, which manufacturers usually do not install for reasons of economy. If the game crashes, you should still install ceramic capacitors here, choosing their capacity at the rate of at least 0,068 microfarads per cartridge chip. Cartridge repair should begin with an external inspection, removing dirt from the connector contacts with alcohol or a hard eraser and carefully soldering all vias on both sides. If the cartridge, in addition to the ROM, has a microcircuit of a small or medium degree of integration, then if a malfunction is suspected, it should be replaced. When it was not possible to establish a defect with such an inspection, you can try to warm up the case of the ROM chip well with a soldering iron - sometimes this helps to restore contact. JOYSTICK The prefix "Sega" is usually equipped with two identical joysticks (game manipulators). One of them, the main one, is connected to the "CONTROL 1" connector on the left, and the second, additional, to the "CONTROL 2" connector on the right side of the set-top box. On the top panel of the manipulator there can be three, four or six round buttons. "Four-button" joysticks, outwardly similar to a similar device from "Dendy", are very rare. "Three-button" consoles are usually supplied with "Sega-1", and "six-button" - "Sega-2". Buttons "A", "B", "C" control the main game actions (shooting, jumping), and "X", "Y", "Z" (if any) cause auxiliary actions, they usually enter various passwords and codes. Any joystick must have a cross, by pressing the corners of which (they are indicated by arrows or the inscriptions "UP", "DOWN", "LEFT", "RIGHT") set the corresponding direction of movement of the game object. The d-pad for standard joysticks is located on the left, but especially for left-handers, those in which it is on the right are also produced. In addition to those listed, the manipulator usually has several more buttons and switches. With the help of one of them - "START" - they start the game, as well as pause and resume it. The pace of the game can be slowed down with the "SLOW" switch (simulates pressing this button repeatedly). The "MODE" button changes the operating mode of the console in some games. It is especially necessary to say about the buttons "TURBO A", "TURBO B", "TURBO C" provided in many joysticks for "Sega-1". They do not perform independent actions, but only imitate repeated pressing of the "non-TURBO" buttons of the same name. The joystick from "Sega-2" is fully compatible with the prefix "Sega-1". The reverse replacement is also possible, but will not be complete, since the games released recently are usually designed to use the entire Sega-2 set of buttons. Schematic diagrams of joysticks are shown in fig. 11 and 12 respectively for "Sega-1" and "Sega-2". Each of them has only one specialized frameless microcircuit. The current it consumes does not exceed 300 μA.
Timing diagrams of the input and output signals of the joystick are shown in fig. 13 ("Sega-1") and 14 ("Sega-2").
The button status polling cycle is triggered by the SYN signal generated by the set-top box. Usually these are single pulses of negative polarity or bursts of four such pulses with a duration of 5...50 µs, repeating with a period of 20...80 ms. The output signals can be conditionally divided according to the formation logic into three groups: A / B and START / C, LEFT / X and RIGHT / MODE, UP / Z and DOWN / Y The differences between the groups are fundamental, for example, pressing the "LEFT" button leads to an immediate a change in the logic level at the corresponding output, and when you press the "A" or "B" buttons, the SYN pulses go to the "A / B" output directly or with inversion. On fig. 13 and 14 show one signal from each group when different buttons are pressed.
Each of the three "TURBO" buttons of the "Sega-1" joystick, when pressed, connects the corresponding input ("A", "B" or "C") of the DD1 chip with its F / 2 output. The pulses at this output are in the form of a "meander" with a period of 80 ms. The ABC circuit (the common wire of these buttons) is connected inside the microcircuit to the F / 2 output protection device against overload that occurs when the "TURBO A" and "A", "TURBO B" and "B" or "TURBO C" and "buttons are pressed simultaneously. WITH". A general view of the printed circuit board of the "six-button" joystick is shown in fig. fifteen.
The contact pads ХТ1 - ХТ9 are connected by a cable to the socket XS1, the appearance and purpose of the sockets of which are shown in Fig. 16. When repairing a joystick, you should first of all make sure that there are no wire breaks in this cable. Please note that the contact pads of the same name ХТ1-ХТ9 on the joystick boards for "Sega-1" and "Sega-2" have different purposes and are connected to different sockets.
A diagram of a simple device that replaces a failed frameless microcircuit in the Sega-1 joystick is shown in fig. 17. All parts are placed in the body of the manipulator: the DD1 chip is glued to the back of its printed circuit board, the connections are made with pieces of a thin mounting wire. If the SB1-SB8 buttons remain connected to the faulty microcircuit, the resistors R1-R8 can be omitted - their functions will be performed by the resistance of the channels of its MIS transistors.
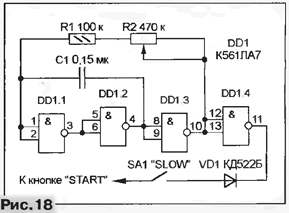
It is much more difficult to replace a faulty microcircuit in the Sega-2 joystick, since the shape of its output signals depends on the number of pulses in the SYN pack. A possible way out is to make a replacement, as described for "Sega-1", but with such a joystick it will be possible to play only those games that do not require additional buttons. The "SLOW" mode will help restore the assembly assembled according to the diagram in fig. 18. This is a pulse generator, the repetition period of which, within the range of approximately 20 ... 120 ms, is regulated by a variable resistor R2 (its type does not matter, any small-sized one will do). If there is no need for on-line adjustment, instead of R1 and R2, you can install one constant resistor, choosing it when setting up the device.
PROCESSOR BOARD The block diagram of the processor board of the "Sega" set-top box is shown in Fig. 19. This is a fairly complex computing system, consisting of a central, video and music processors.
The microprocessor MC68000 is used as the central one. It has a 23-bit address bus (AO-A22), a 16-bit data bus (DO-D15), a control bus, and works according to a program read from a ROM located in the cartridge, or from a laser disc whose drive is "MEGA-CD " can be connected to the "SYSTEM" jack. The central processor controls the operation of all other nodes of the set-top box. The joysticks are connected to it through the "CONTROL 1", "CONTROL 2" connectors and an interface chip, which is part of the so-called KSB - a set of specialized LSIs that perform many important functions in the set-top box. The RAM of the central processor with a capacity of 32K 16-bit words is made on static memory chips. The video processor (one of the KSB microcircuits) processes the graphic data. It generates R, G, B primary colors video signals and SYNC sync mixture. The output of the set-top box ("A / V" socket) receives a full color television signal of the PAL standard, formed from the signals of the video processor by the PAL encoder. A three-bus information highway connects the video processor with video RAM, which consists of two dynamic memory chips with a total capacity of 64 KB. The regeneration of this RAM is also a function of the video processor. The music processor consists of an eight-bit Z80A microprocessor, a sound synthesizer on one of the KSB microcircuits, and an 8 KB static RAM. They are connected by a 16-bit address bus (MAO-MA15), an eight-bit data bus (MDO-MD7) and a control bus. The stereophonic signal of the sound accompaniment of the game generated by the music processor is fed to the audio frequency amplifier (UHF). Sound signals can also be sent here directly from the cartridge or system connector. The PHONES headphone jack and the A/V socket are connected to the UZCH output. The operation of all processor board nodes is synchronized by a crystal oscillator signal, the nominal oscillation frequency of which is 53,203424 MHz (exactly 12 times higher than the color subcarrier frequency in the PAL television standard). The MC68000 is clocked at a frequency of seven, and the Z80A is clocked at a frequency of 15 times less. Let's consider the device of the processor board in more detail. For convenience, all the schematic diagrams below use the same signal names and continuous numbering of elements. VOLTAGE REGULATOR The scheme of this node is shown in fig. 20. The input unstabilized voltage comes from the network adapter through socket X1. Chokes L1, L2 suppress high-frequency interference. If you suspect a malfunction, you can measure the resistance of the DC chokes with an ohmmeter, which should not exceed 0,6 ohms. In some models of set-top boxes, jumpers are installed instead. The voltage from socket X1 is also supplied to the "SYSTEM" socket (via the VCC-IN circuit), which can be used for diagnostic purposes. Diodes VD1, VD2 (analogues KD208A, KD212A, KD212B) protect the video set-top box from accidental reverse polarity voltage supply. In some models, one of the diodes is missing.
On the DA1 and DA2 microcircuits, two identical 5 V voltage regulators are assembled. The first of them, through the VC1 circuit, usually powers the central and video processors, video RAM, cartridge and devices connected to the "SYSTEM" socket. The second, along the VC2 chain, is the rest of the nodes. Load sharing facilitates the thermal regime of the DA1, DA2 microcircuits and reduces the power connection between the analog and digital parts of the device. The processor board together with the cartridge consumes a current of 0,5 ... 0,8 A. The total power dissipated on the stabilizer microcircuits reaches 5 W; both of them are usually mounted on a common metal heat sink. It is desirable to increase its area to 80 ... 120 cm2, which will increase the reliability of the video set-top box. There are processor boards on which the VC1 and VC2 circuits are interconnected, as shown in fig. 20 dashed line. In this case, both stabilizer microcircuits must be of the same type and have the closest possible parameters, which should be taken into account when replacing them. In addition to those indicated in the diagram, you can use, for example, LM7805CK or domestic KR142EN5A, KR142EN5V. Oxide and ceramic capacitors C1-C24 are designed to ensure stable operation of stabilizers and noise filtering. They are distributed over the entire area of the processor board and are installed in close proximity to the microcircuit power pins. The total number of capacitors on boards manufactured by different companies may be different. In those consoles where there is no LED indicator for the supply voltage HL1, it is recommended to install it by drilling a hole in the housing cover for this and fixing an LED in it with glue, for example, AL307BM. QUARTZ GENERATOR The set-top boxes "Sega" use a hybrid HO-12C crystal oscillator from HOSONIC, the appearance and pin assignment of which are shown in fig. 21.
In a sealed case with dimensions of 20,8x13,2x5,8 mm, in addition to a quartz resonator, there are packageless and film resistors, capacitors and transistors that form an oscillator. The supply voltage of this node is 5 V, the current consumption is not more than 25 mA. The signal at the OUT output (connected to the FCLK circuit of the set-top box) has TTL levels, its nominal frequency is 53,203424 MHz. A faulty node can be replaced with a crystal oscillator on ordinary elements, assembling it, for example, according to one of the schemes given in [4]. The difference in its frequency by several hundred kilohertz from the specified one will not affect the stability of the set-top box and the quality of the generated image. MICROPROCESSOR MC68000 Back in the early 80s, the American company Motorola Semiconductor Ipc. developed a family of 16-bit microprocessors [5], the basic model of which MC68000 was used in computers Apple MACINTOSH, Commodore AMIGA-500, Commodore AMIGA-600. He still appears in the catalogs of electronic devices. Using it, the authors of the "Sega" set-top box were able to apply proven circuit solutions and a large set of software development tools. With a 16-bit ALU, the internal address and data registers of the MC68000 microprocessor are 32 bits each, so it is often considered that its capabilities are close to 32-bit processors. Details about its architecture, command system and operating modes can be found in [5 - 7]. The scheme of inclusion of the microprocessor in the prefix "Sega" is shown in fig. 22. The MC68000P10 chip is usually used (in parentheses are the pin numbers of the MC68000FN8 installed in some models). The last digits of the name indicate the maximum clock frequency of the processor in megahertz, the letters in front of them indicate the type of package: P - 64-pin DIP, FN - 68-pin QFP (for surface mounting). The information below on the purpose of the microprocessor pins will be useful when analyzing waveforms of signals during the repair of a video set-top box.
A1 - A23 (outputs) - 23 - bit address bus. The internal program counter has 24 bits, but the AO does not have an external output. AS (output) - address strobe. A low level means that the address output to A1 - A23 can be decoded. BERR (input) - backbone error. The peripheral reports that it has detected an error on the processor buses. ВG (exit) - tires provided. The processor reports that it has freed up buses for the peripheral. BGACK (input) - confirmation of the provision of tires. The peripheral reports that it has hijacked the processor buses. BR (input) - tire request. The peripheral asks the processor to provide buses. CLK (input) - clock pulses. Depending on the processor modification, their maximum repetition rate can be 8, 10, 12,5 or 16 MHz. DO - D15 (inputs-outputs) - 16-bit data bus. DTACK (input) - confirmation of data transfer. The addressed device indicates that it is ready to communicate with the processor. E (output) - pulses with a period equal to 10 periods of the CLK signal. FCO - FC2 (outputs) - function code. Allows you to use four memory segments of 16 MB each. GND is a common wire. HALT (input - output) - stop. When this input is low, the processor is suspended until the high level is applied again. Most of its outputs go into a high-impedance state for the duration of the shutdown. If a double system error is detected, the processor itself stops working, signaling this with a low level on the HALT pin. IPL0 - IPL2 (inputs) - interrupt request. The numerical value of the code on these pins corresponds to the interrupt priority. LDS (output) - low byte data strobe. RES (input - output) - the initial setting of the processor. Initialized by a high to low transition. When a RESET instruction is encountered in an executable program, the processor itself sets and maintains a low level on this pin for 24 periods of the CLK signal. R/W (output) - direction of data transfer. High level - reading, low - writing. UDS (output) - high data byte strobe. VCC is the supply voltage (+5V). VMA (output), VPA (input) - signals for joint work with microcircuits of the MC68xx series. A failed microprocessor can be replaced with almost any of its modifications, for example, MC68000P8, MC68NS000P10 (with reduced power consumption), SCN68000, etc. Clock pulses CLK with a frequency of 7,6 MHz and a reset signal RES with a duration of approximately 10 μs come from the KSB. Resistors R2 - R11, R28 and capacitors C25 - C3O are not installed in some variants of processor boards. MICROPROCESSOR Z80A "Old age" (developed by the American company Zilog in the second half of the 70s) does not prevent it from taking a leading position in the class of eight-bit processors. It gained wide popularity due to its use in the first mass home and office computers "ZX-SPECTRUM", "YAMAHA-MSX", "SHARP MZ80B". The architecture, pin assignment, timing diagrams of the Z80A signals are discussed in detail, for example, in [8]. The scheme of inclusion of this microprocessor in the prefix "Sega" is shown in fig. 23. The 3,547 MHz MCLK clock and MRES reset signals of about 100 ms are from the KSB. All circuits of the data bus, the least significant bit of the address bus and some control signals are connected to a + 5 V power supply (VC2) through resistors R29 - R42.
In many models of set-top boxes on the processor board, there is a place for installing pick-up elements. For example, when replacing the Z80A chip with its counterparts Z8400A (Gold Star), Z80B, KR1858VM1, it may be necessary to select the capacitance of the capacitor C31. RAM The total amount of RAM "Sega" - 136 KB. This includes: 32KX16 central processor static RAM on DD3, DD4 chips (Fig. 24), 8Kx8 additional static RAM on the DD5 chip (Fig. 25), 64Kx8 dynamic video RAM on DD6 and DD7 microcircuits (Fig. .26). Control signals for additional RAM come from the Z80A microprocessor and KSB, the rest of the memory - only from KSB.
As DD3 and DD4, chips are usually installed MB84256 - 12LL (Japan), H61256 - 70, D43256A - 15, HM62256LFP - 12T (Malaysia), KM62256BLG - 10L (Korea). DD5 can be types ТММ2064АР - 70, UM6264M - 12, MCM6264CJ - 15 (Japan). Their access time is 70 ... 150 ns, which allows, if necessary, to use the KR537RU17, KR537RU17E, KR537RU17ZH microcircuits as a replacement. Sometimes an SRM20256 - LM12 is installed here, the capacity of which is four times the required 8 KB. The design of the printed circuit board allows this to be done without any modifications. Moreover, the normally unused pin 1 pad is connected to the KSB, which theoretically allows the development of game programs that require up to 16 KB of additional memory. Chips DD6, DD7 can be types HM53461ZP - 12, D41264V - 15, MB81461 - 12, M5M4C264L - 12 (Malaysia, Japan). The HM53461ZP - 12 pinout is shown in fig. 27. Its reference data can be found in [9]. All of these microcircuits are dual-port video RAM. Each has a dynamic RAM port with 64KX4 organization and a serial SAM port containing four 256-bit registers. The dual-port architecture minimizes conflicts between the processor and video generator, thereby speeding up the processing of graphic information.
RAM - video port - RAM is similar to conventional dynamic random access and is controlled by RAS, CAS, WE signals. Data is written and read on bus 1/01 - 1/04. Sampling time - 100...150 ns, regeneration cycle - no more than 4 ms. In the set-top boxes "Sega" (diagram in Fig. 26), the data bus of the RAM ports is combined with the address bus AO - A7. This is done to reduce the total number of trunks. SAM - the port is controlled by DT/OE, SOE, SC signals. Its data bus is SI/01 - SI/04. This is a "fast" access port with a 40...60 ns access time. Between the RAM - and SAM - ports there is a 256 - bit data exchange path. Exchange operations are performed in the RAS - CAS cycle with certain values of control signals. Port calls can be asynchronous. The processor has the right to change through the RAM - port information in any cell of the video - RAM, even during the formation of video signals from the data output to the SAM - port. A special masked write mode is provided that allows you to change the state of several bits of a memory cell without affecting the rest (for example, quickly draw a line against the background of an existing image). When choosing a replacement for memory chips, one should take into account not only their information capacity, but also their design. For example, many processor boards have chips in SOP packages for surface mounting. They can be easily replaced with analogues in DIP packages, if the printed circuit board has pads for both types of packages. Otherwise, you will need to make an adapter board. KSB. This is the most important node of the processor board. All microcircuits included in it are multifunctional. Almost all signals from the MC68000 and Z80A microprocessors, RAM and connectors are connected to them. As an example, we give the composition of the KSB of the TA series:
The SE series is also often used, consisting of three microcircuits (SE - 93, SE - 94 and SE - 95) that perform similar functions. The most successful is the use of the MD2 chip in the latest models of the Sega-270 set-top boxes, which replaces the entire KSB. For small dimensions and increased reliability, I had to pay with a case that has 208 pins with a pitch of 0,5 mm. FORKS XP1 ("CONTROL 1") AND XP2 ("CONTROL 2"). On fig. 28 and 29 are diagrams of their connection with the KSB, respectively, in "Sega - 1" and "Sega - 2". The appearance of the plugs and the purpose of their conclusions are shown in fig. 30. Chain names in brackets refer to "Sega - 2". The power circuit (VC2) is protected from short circuits in the joysticks by resistor R43, common to XP1 and XP2. Sometimes it is replaced by a jumper. Resistors R44 - R47 are shown as an example. In different models of set-top boxes, they can be included in different circuits, their number may be more or less.
SOCKETS XS2 ("SYSTEM") and XS3 ("CARTRIDGE"). Their contacts (the purpose is indicated in Tables 1 and 2, respectively) can have alphanumeric or numeric numbering. Many signals are output in parallel to both sockets, and this can be used for diagnostic purposes. For example, with a cartridge inserted into the XS3, check for address and data signals on the XS2 contacts. Malfunctions of contacts B1 - VZ, B10 - B15, B18 - B21, B26, B28 - B31 of the "CARTRIDGE" socket usually do not affect the performance of the set-top box, since they are not involved in the cartridges of most games. If necessary, the set-top box can be powered from any source of constant voltage 9...10 V, rated for a current of at least 0,8 A, by connecting it to the VCC-IN circuit of the "SYSTEM" socket. EXTERNAL SIGNALS KSB Chains whose names in Table. 1 and 2 begin with the letters X or Y connected to the KSB (except for XB2 and XB15). Apparently, they are designed to control the "Sega-32X" expander, which turns a 16-bit prefix into a 32-bit one. Special cartridges that are incompatible with conventional ones work with the expander. The functional purpose of some of the signals: ХВ2 (input) - signal from electrical or mechanical contactor; XB13 (output) - negative horizontal scanning pulses (H) with a duration of 4 and a repetition period of 64 μs; XB14 (output) - similar vertical scanning pulses (V) with a duration of 0,2 and a repetition period of 20 ms; ХВЗО, ХВ31 (inputs) - signals for selecting external devices, for example, FLASH memory in a cartridge.
Schemes of nodes transmitting external signals to the CSF are shown in Fig. 31. When you press the SB1 "RESET" button, the low logic level at the corresponding input of the KSB is replaced by a high one. In some models of processor boards, the initial installation requires an opposite (low) level signal and a button (it is designated SB1') is connected as shown by a dashed line, and elements R51, R56, C3 are missing. Unlike the prefix "Dendy", the operation of which is suspended when the "RESET" button is held for a long time, "Sega" switches to its initial state at the moment it is pressed, since the CSB from the signal edge generates short single reset pulses RES and MRES, respectively, for the MC68000 and Z80A. The Schmitt trigger on the operational amplifier (op-amp) DA4.1 is designed to receive the XB32 signal mentioned above from the cartridge or expander "Sega-2X". In the XB15 circuit, a jumper is sometimes installed instead of the capacitor C36. The SA2 slide switch is located next to the XS2 socket. They can be controlled without disassembling the console. It is used when working with the "Sega-CD" CD drive. Depending on the position of SA2, the KSB receives a high or low signal. The transistor VT1 shown by the dashed line is installed only in those consoles to which the "Sega-CD" drive is permanently connected. It summarizes the docking control signals with the system board of the cartridge (CHECK) and drive (CTRL). The CHECK signal has priority - the processor primarily services the cartridge. Transistor VT2 at the time of switching on the supply voltage generates a high-level pulse with a duration of 1,5 ... 2 s. The operation of most game programs does not depend on the considered signals (with the exception of RESET). Cascades on transistors VT1, VT2 (their counterparts are KT3102A), as well as the SA2 switch, may be absent. AF AMPLIFIER On fig. 32 shows a diagram of that part of the processor board where the audio frequency signals from the music processor (SOUND1 - SOUND3), the cartridge (SOUND4, SOUND5) and the system connector (SOUND6, SOUND7) are summed and amplified. The signals of the last two sources in game programs are used very rarely. But, for example, by connecting a sound generator to contacts B1 (SOUND4) and VZ (SOUND5) of the "CARTRIDGE" socket, you can check the sound path of the video set-top box without opening it. The music processor generates a high-quality stereo sound (SOUND1, SOUND2) and an additional mono SOUND3, which is reminiscent of the sound quality of the Dendy set-top box in sound quality. They are summed channel by channel in the circuits R60 - R73, C38 - C43. The SOUND3 signal, passing through the active low-pass filter on the op amp DA5.1, goes through resistors R79 and R80 to both stereo channels. Similar filters are often included in the SOUND1, SOUND2 circuits to suppress "steps" in digitally generated signals. The two-channel preliminary UZCH was assembled on the DA6.1 and DA6.2 op-amps. The signals from their outputs through resistors R88 and R89 are fed to a power amplifier for stereo phones (op-amp DA6.3 and DA6.4). The double variable resistor R92 included in the feedback circuits of these op-amps controls the volume. In set-top boxes that do not have an output for stereo phones and a volume control, instead of R91 - R93, resistors with a nominal resistance of 8 kOhm are installed between pins 9, 6.3 of the DA13,14 and 6.4 DA10 OU. The signals S - LEFT, S - RIGHT and MONO are output, and the last of them (mono) is obtained by summing the stereo components and, after amplification in a cascade on the DA6.2 op amp, is fed to the full color television signal generator (PAL encoder). You can hear the surround sound of the game by connecting headphones or an external stereo amplifier with speakers to the console. Some models do not have stereo audio signals. The non-inverting inputs of all op-amps (except DA5.1) are supplied from a voltage divider made of resistors R74, R75 with blocking capacitors C50, C52, a constant bias equal to half the supply voltage. Sometimes there is no divider, and the necessary voltage is supplied to the UZCH from the PAL encoder chip In different models of video set-top boxes, the values \uXNUMXb\uXNUMXbof the passive elements of the UZCH may differ from those indicated in the diagram. Other types of op amps are often used as well. Sometimes the amplifier is partially performed on transistors. There are even models of set-top boxes in which the UZCH is single-channel (apparently, the company saved on radio elements). Almost any general-purpose op-amp capable of operating at a supply voltage of 5 V is suitable as a replacement for UZCH microcircuits, for example, K1423UD2, K1401UD2A, K1401UD2B, foreign op-amps of the 324 series. In case of complete failure, the entire node can be replaced by any home-made mono or stereo ultrasonic frequency converter with a nominal input voltage of about 20 ... 50 mV with an output voltage amplitude of 1,5 ... 2 V. Its inputs are connected to capacitors C46, C47 (up to or after them), which are easy to find on the board, focusing on symmetrical RC circuits R60 - R73, C38 - C43. PAL ENCODER The conversion of video signals R, G and B into a full color television signal of the PAL standard is performed by a specialized microcircuit, most often MC13077 from Motorola (encoder circuit - in Fig. 33) or СХА1145 from Sony (Fig. 34). Both of them are universal and can work in PAL and NTSC standards. The letter at the end of the name of the microcircuit indicates the type of its package: P - DIP, M - for surface mounting.
The KSB receives video signals of red (R), green (G) and blue (B) colors, as well as a mixture of horizontal and vertical synchronization pulses (SYNC). Resistor voltage dividers reduce the range of these signals at the inputs of the encoder microcircuit from 4 ... 5 to 1 ... 1,5 V. The clock frequency of 17,73 MHz (quadruple the color subcarrier frequency in the PAL system) is set by a quartz resonator. Sometimes the internal clock generator of the microcircuit is not used, and the signal of the required frequency is supplied from the outside. In the device assembled according to the scheme in Fig. 34, to switch from an external to an internal generator, the jumper X1 - X2 is transferred to the X4 - X2 position (naturally, the ZQ80 resonator with capacitor CXNUMX should also be installed, if they were absent). The elements connected to the outputs Y1 - Y7 of the MC13077 and Y1 - Y6 CXA1145 microcircuits form the frequency response of the brightness of the converter's th channel. If you suspect a break in the inductors, you can check their DC resistance with an ohmmeter (L3, L4 - 1,6 ... 1,8; L5 - 0,6 Ohm). As in UZCH, the values of resistors and capacitors may differ from those indicated in the diagrams. The main output signal of the VIDEO converter through the "A / V" socket (XS5 in Fig. 33, XS6 in Fig. 34) goes to a high-frequency modulator or directly to the video input of the TV. The appearance and purpose of the contacts of these sockets are shown in fig. 35 and 36.
The CXA1145 chip performs additional functions: it amplifies the MONO audio signal, generates high-power video signals at the RO, GO and VO outputs, which can be fed to a color monitor or TV with the appropriate inputs. At the same time, the image quality is higher, since there is no double conversion RGB - PAL - RGB. A voltage of 2,5 V from pin 14 of the SHA1145R chip is sometimes supplied to the UZCH to the non-inverting inputs of the op-amp. The MC13Q77 chip can be replaced by the MC1377 - B by turning it on according to the scheme given in [10]. It needs +12V to power it. The prefix "Sega" with a faulty and unrepairable PAL encoder can still be used if there are R, G, B, SYNC signals at the KSB outputs. They need to be submitted to the interface module with a home computer TV (for example, "Orion - 128", "ZX - SPECTRUM"). You may need additional emitter followers and trimmers to adjust the balance. TROUBLESHOOTING FOR VIDEOS The most common causes of failures of any game consoles are wire breaks in the connecting cords and cables, contact failures in the connectors. So you should always start troubleshooting with checking the quality of the connections. Many units of the set-top box perform the functions common to any microprocessor system and are quite easy to diagnose and repair. The exception is the KSB, whose microcircuits have a complex non-standard structure and numerous internal and external connections. Troubleshooting in them is difficult, besides, microcircuits of one series cannot be replaced by analogues from another. In practice, a technique is often used that makes it possible to dispense with the complete electrical circuit of a particular set-top box. It is enough to have a good idea of the structure of the main nodes and the organization of connections between them. First of all, you should make sure that the voltages in the VC1 and VC2 circuits are within 4,85 ... 5,15 V, and the double amplitude of their ripples does not exceed 80 mV. Then, after analyzing the external manifestations of the malfunction and assuming that the KSB is operational, it is necessary to determine the nodes to be checked. It is necessary to carefully inspect the installation, take waveforms of signals at characteristic points and replace parts whose serviceability is questionable. If the work done has not yielded results, it can be concluded with a high degree of probability that the malfunction is in the KSB. After that, it remains to decide which is easier: without a guarantee of results and with the risk of damaging the printed circuit board, replace multi-output microcircuits or buy a new video set-top box. To facilitate troubleshooting in digital nodes, you can use the so-called MFD tables (Manual Fault Diagnostics - manual failure diagnosis) [11]. To compile such a table, you need a logic probe [12, 13], which allows you to determine the nature of the signal in the circuit under test: H - constant high level; L - constant low level; Z - high impedance state; P - pulses without the predominance of one of the levels; HP (LP) - impulses with a predominance of a high (low) level; Р1 (НР1, LP1) - similar single impulses; RT (NT, LT) - bursts of pulses lasting a short time; HLZ - pulses of complex shape (with more than two levels). In table. Figures 3 and 4 show the MFD tables for the outputs of two microprocessors available in the "Sega" prefix. The probe readings were taken in the following states of the console: 1 - a few seconds after switching on (without cartridge); 2 - after pressing the "RESET" button (without cartridge); 3 - during the game (cartridge installed). By repeating the measurements in the device to be repaired and comparing the results, you can quickly find the faulty node. Of course, MFD-tables, giving a qualitative assessment of signals, serve only as a kind of hint. You need to be creative in how you design and use them. Depending on the model of the attachment and the probe used, the results may vary slightly. It is important to note the characteristic features of each signal, reflecting them in the legend and notes to the tables. For example, the letters RT in Table. 3 indicates pulses close in shape to a "meander" and lasting approximately 2,5 s. For a more detailed study of a multiprocessor system, which is the prefix "Sega", it is necessary to apply signature analysis and other complex methods. Literature
Author: S.Ryumik, Chernihiv, Ukraine
Energy from space for Starship
08.05.2024 New method for creating powerful batteries
08.05.2024 Alcohol content of warm beer
07.05.2024
▪ Live cell weight change control in real time ▪ Genetic pacemaker powered by light ▪ Created a device to simulate odors in computer games ▪ Quantum innovations from IBM
▪ section of the site Audio Art. Article selection ▪ article Organization of the Commission's work at emergency facilities. Basics of safe life ▪ article Indian indigo. Legends, cultivation, methods of application ▪ article Digital VHF radio tuning scale. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Comments on the article: Oleg My sega produces a green image. Games start, everything works, but everything is like through green glass ... From your article, I realized the problem may be in the SHA microcircuit. Will replacing it fix the issue? RoboDron Great, helpful article! On the shelves, without water and with schemes! Thanks!!!
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese
































 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: