Dual band VHF antenna. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / VHF antennas
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
Interest in operating on the 144 and 430 MHz bands in local networks has caused a corresponding interest in multi-band VHF antennas. Installed on one mast and powered by one coaxial cable, they can significantly reduce the cost of their manufacture.
On fig. 1 shows the structure of a simple dual-band VHF antenna proposed by DJ2AZ. It consists of a quarter-wave emitter (GP) for the 144 MHz band, on the lower part of which a quarter-wave "glass" for the 430 MHz band is installed ("bottom" down, electrically connected to the emitter at the bottom).
(click to enlarge)
On the 144 MHz band, this "glass" is equivalent to a small inductance included in a quarter-wave radiator at the level of the upper cut of the "glass". Its influence is small and in the process of tuning is compensated by a change in the length of the emitter. On the 430 MHz band, the length of the upper (above the "glass") part of the radiator will be 5/8L. "Glass" works on this range as a matching transformer, providing normal power to the upper part of the emitter.
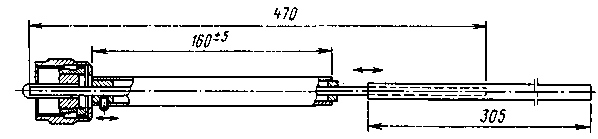
A possible variant of the design of such an antenna is shown in Fig. 2. It is designed for direct connection to the radio station through the PL-259 connector (standard for many foreign-made radio stations). For other installation options, its lower part (relating to the connector) is modified accordingly.
The main emitter is composite. Its lower part is made of aluminum (preferably brass or copper) rod with a diameter of 4 mm. A tube with an outer diameter of 6 mm and a wall thickness of 1 mm is pulled over its upper part, by moving which the antenna is tuned. The "glass" is made of a tube with a diameter of 8 mm and a wall thickness of 0,5 mm. In its lower part there is a metal insert through which the position of the "glass" on the emitter is fixed with a locking screw. In the upper part of the "glass" there is an insert made of Teflon or any other high-frequency dielectric, which fixes its position in relation to the main radiator and prevents atmospheric precipitation from entering the "glass".

The radiator diameter of 4 mm in this embodiment of the antenna was chosen for purely design reasons - it corresponds to the diameter of the central contact of the PL-259 connector (the lower end of the radiator performs the functions of this contact). With other versions of the antenna, the diameter of the radiator, of course, may be different, but then it is necessary to proportionally change the diameter of the tube forming the "glass", as well as the upper regulating nozzle on the radiator.
The "ground" of this antenna is ordinary: counterweights for each range (at least three), a metal surface (car roof), etc. By the way, this antenna can also be made as a conventional dipole, consisting of two such emitters.
The antenna is tuned to a minimum SWR on both bands by selecting the length of the radiator and, within small limits, the position of the "glass" on the radiator. You need to start from the lowest position of the "glass". First, by selecting the length of the radiator, the antenna is tuned to the 144 MHz band. Then, by changing the position of the "glass", a minimum SWR is achieved in the 430 MHz band. After that, if necessary, adjust the antenna on the 144 MHz band.
Author: Victor Menzlewski. Mehrbandantennen fur den VHF/UHF Bereich; Publication: cxem.net
 See other articles Section VHF antennas.
See other articles Section VHF antennas.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
The world's tallest astronomical observatory opened
04.05.2024
Exploring space and its mysteries is a task that attracts the attention of astronomers from all over the world. In the fresh air of the high mountains, far from city light pollution, the stars and planets reveal their secrets with greater clarity. A new page is opening in the history of astronomy with the opening of the world's highest astronomical observatory - the Atacama Observatory of the University of Tokyo. The Atacama Observatory, located at an altitude of 5640 meters above sea level, opens up new opportunities for astronomers in the study of space. This site has become the highest location for a ground-based telescope, providing researchers with a unique tool for studying infrared waves in the Universe. Although the high altitude location provides clearer skies and less interference from the atmosphere, building an observatory on a high mountain poses enormous difficulties and challenges. However, despite the difficulties, the new observatory opens up broad research prospects for astronomers. ... >>
Controlling objects using air currents
04.05.2024
The development of robotics continues to open up new prospects for us in the field of automation and control of various objects. Recently, Finnish scientists presented an innovative approach to controlling humanoid robots using air currents. This method promises to revolutionize the way objects are manipulated and open new horizons in the field of robotics. The idea of controlling objects using air currents is not new, but until recently, implementing such concepts remained a challenge. Finnish researchers have developed an innovative method that allows robots to manipulate objects using special air jets as "air fingers". The air flow control algorithm, developed by a team of specialists, is based on a thorough study of the movement of objects in the air flow. The air jet control system, carried out using special motors, allows you to direct objects without resorting to physical ... >>
Purebred dogs get sick no more often than purebred dogs
03.05.2024
Caring for the health of our pets is an important aspect of the life of every dog owner. However, there is a common assumption that purebred dogs are more susceptible to diseases compared to mixed dogs. New research led by researchers at the Texas School of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences brings new perspective to this question. A study conducted by the Dog Aging Project (DAP) of more than 27 companion dogs found that purebred and mixed dogs were generally equally likely to experience various diseases. Although some breeds may be more susceptible to certain diseases, the overall diagnosis rate is virtually the same between both groups. The Dog Aging Project's chief veterinarian, Dr. Keith Creevy, notes that there are several well-known diseases that are more common in certain breeds of dogs, which supports the notion that purebred dogs are more susceptible to disease. ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Generation of stable femtosecond pulses
28.12.2013
The development of electronics and communications requires a hardware base that is highly accurate, economical and productive. For communications and GPS navigation satellites, it is especially important to reduce payload mass and improve signal stability.
Scientists from Moscow State University (MSU), together with their colleagues from Switzerland, are actively conducting research that will bring us closer to solving this problem, and will also prove useful in many other areas.
Recently, a publication appeared in the journal Nature Photonics, which describes the new achievements of this group of scientists. In particular, one of the authors of the article, Mikhail Gorodetsky, noted that the work includes at least three important results: scientists have discovered a technique for generating stable femtosecond pulses, the so-called "optical ridges" and microwave signals.
The physicists used a microresonator (in this particular case, a millimeter-scale magnesium-fluorite disk) to convert continuous laser radiation into periodic ultrashort pulses. The scope of these lasers ranges from the study of chemical reactions at ultrashort time intervals, and to eye surgery.
As Mr. Gorodetsky noted, traditional femtosecond mode-locked lasers use the most complex optical devices, a special transmission medium and micromirrors. The new invention makes it possible to obtain stable pulses (solitons) using only one passive optical resonator, or rather, its own non-linearity. In the future, this will make it possible to reduce the overall dimensions of devices of this type by an order of magnitude.
Pulses with a duration of 100–200 femtoseconds have been obtained in the laboratory, but the authors are confident that much shorter solitons can also be generated. The researchers suggest that their discovery will allow designing a new generation of compact, stable and cheap optical pulse generators that can operate in modes that are unattainable for devices using other technologies. At the same time, scientists have shown the possibility of generating signals with a very low noise level. Such microwave generators are especially important for metrological applications, radar, telecommunications equipment, including satellite communications, as well as broadband spectroscopy, telecommunications, and astronomy.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Laser against dust
▪ Microscopic robots out of thin air
▪ Jupiter doesn't revolve around the sun
▪ Tracking the reaction of museum visitors to exhibits
▪ Relativistic contraction of the electric field
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Household electrical appliances. Selection of articles
▪ article The roof of your house. Tips for the home master
▪ article Which postal service delivers valentines with lip prints instead of stamps? Detailed answer
▪ article operator. Job description
▪ article Forest air in the room. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Increasing the output power of stabilized power supplies. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: