Microphones. Reference data. Part 2

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Reference materials
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
Microphones are classified on the basis of the conversion of acoustic vibrations into electrical ones and are divided into electrodynamic, electromagnetic, electrostatic (condenser and electret), carbon and piezoelectric.
Microphones are characterized by the following parameters:
- Microphone sensitivity is the ratio of the voltage at the output of a microphone to the sound pressure acting on it at a given frequency (typically 1000 Hz), expressed in millivolts per pascal (mV/Pa). The larger this value, the higher the sensitivity of the microphone.
- Rated operating frequency range - the frequency range in which the microphone perceives acoustic vibrations and in which its parameters are normalized.
- Frequency response flatness - the difference between the maximum and minimum sensitivity level of the microphone in the nominal frequency range.
- Electrical impedance modulus - normalized value of the output or internal electrical resistance at a frequency of 1 kHz.
- Directivity - dependence of the microphone sensitivity (in the free field at a certain frequency) on the angle between the microphone axis and the direction to the sound source.
- Microphone noise floor - expressed in decibels, the ratio of the effective voltage value due to pressure fluctuations in the environment and thermal noise of various resistances in the electrical part of the microphone, to the voltage developed by the microphone on the load at a pressure of 1 Pa when the microphone is exposed to a useful signal with an effective pressure of 0,1 Pa.
In telephone sets, electrodynamic, electret and carbon microphones are mainly used. But, as a rule, in 95% of push-button TAs, electret microphones are used, which have increased electro-acoustic and technical characteristics:
- wide frequency range;
- small uneven frequency response;
- low non-linear and transient distortions;
- high sensitivity;
- low self-noise level.

Fig 1. Scheme for switching on a condenser microphone
On fig. Figure 1 is a diagram explaining how a condenser microphone works. The membrane (1) and electrode (2) made of electrically conductive material are separated by an insulating ring (3) and represent a capacitor. A rigidly stretched membrane, under the influence of sound pressure, oscillates relative to a fixed electrode. The capacitor is connected in an electrical circuit in series with a DC voltage source GB and an active load resistance R. When the membrane vibrates, the capacitance of the capacitor changes with the frequency of the sound pressure acting on the membrane. An alternating current of the same frequency appears in the electrical circuit and an alternating voltage appears on the load resistance, which is the output signal of the microphone.
Electret microphones, according to the principle of operation, are the same condenser ones, but the constant voltage in them is provided by an electret charge deposited on the membrane with a thin layer and retaining this charge for a long time (over 30 years).
Since electrostatic microphones have a high output impedance, to reduce it, as a rule, a source follower on an n-channel field-effect transistor with a pn junction is built into the microphone housing. This allows you to reduce the output impedance to a value of no more than 3 + 4 kOhm and reduce signal loss when connected to the input of a microphone signal amplifier. On fig. 2 shows the internal circuit of an electret microphone with three leads MKE-3.

Rice. 2. Internal circuit of the MKE-3 electret microphone
For electret microphones with two leads, the microphone output is made according to the open-drain amplifier circuit.

Rice. 3. Internal circuit of the electret microphone MKE-389-1

Rice. 4. Wiring diagram for electret microphones with two leads
On fig. 3 shows the internal circuit of an electret microphone with two leads. FEM-389-1. The connection diagram of such a microphone is shown in fig. 4. According to this scheme, you can connect almost all electret microphones with two leads, both domestic and imported.
The table shows their technical characteristics
Microphone options
Name
brand |
Feelings
tions the
mVPa |
Range
frequencies
Hz |
Level of
noise
db |
For example
Pete.
В |
Cons.
current
mA |
Coeff.
harm.
% |
Not equal-
dimension
FH
db |
| M1-A2 "PINE" |
515 |
1507000 |
28 |
-1,2 |
0,007 |
- |
2 |
| M1-B2 "PINE" |
1020 |
| M4-V "SOSNA" |
> 20 |
| M7 "PINE" |
>5 |
26 |
| IEC-1A |
620 |
3004000 |
30 |
2,34,7 |
0,2 |
2 |
| IEC-1B |
| FEM-3 |
420 |
5015000 |
30 |
-4,5 |
- |
12 |
| FEM-84 |
620 |
3003400 |
30 |
1,34,5 |
- |
| MKE-377-1A |
612 |
15015000 |
33 |
2,36 |
0,35 |
4 |
| MKE-377-1B |
1020 |
| MKE-377-1B |
1836 |
| MKE-378A |
612 |
3018000 |
2,36 |
0,35 |
1 |
| MKE-378B |
1020 |
| FEM-389-1 |
612 |
3004000 |
26 |
- |
4 |
2 |
| MKE-332A |
35 |
5012500 |
30 |
29 |
- |
- |
| MKE-332B |
612 |
| MKE-332V |
1224 |
| MKE-332G |
2448 |
| MKE-333A |
35 |
5012500 |
30 |
29 |
| MKE-333B |
612 |
| MKE-333V |
1224 |
| MKE-333G |
2448 |
| PANASONIC |
SIZE |
| WM-034 CY |
60 |
2016000 |
- |
4,510 |
0,8 |
9,7x6,7 |
| WM-034 |
60 |
2016000 |
| WM-034 CY 195 |
| WM-52BM |
1,510 |
0,3 |
9,7x4,5 |
| WM-54BT |
2012000 |
2,510 |
0,6 |
| WM-60AY |
58 |
2016000 |
210 |
0,5 |
6x5 |
| WM-60AT |
| WM-60 A 103 |
55 |
10012000 |
| WM-62A |
58 |
2016000 |
6x2,5 |
| WM-66 D 103 |
50 |
1010000 |
6x2,7 |
| WM 55 A 103 |
60 |
2016000 |
1,510 |
0,5 |
9,7x5 |
| WM 56 A 103 |
58 |
| WM 55 D 103 |
10010000 |
| china, standing in all consumer phones and caller IDs |
| SZN-15E |
58 |
8015000 |
- |
310 |
- |
9,7x9 |
The current consumption of the IEC-1 microphone is not more than 0,2 mA, MKE-377-1 and MKE-378 is not more than 0,35 mA. The current consumption of the M1-A2, M1-B2 and M-7 microphones is not more than 70 μA.
The difference between the MKE-332 microphone and the MKE-333 is that the MKE-332 is unidirectional, and the MKE-333 is non-directional.
Harmonic coefficient at a frequency of 1000 Hz at a sound pressure of 3 Pa for MKE-377-1 and MKE-389-1 microphones is not more than 4%, MKE-378 is not more than 1%.
The unevenness of the frequency response of sensitivity in the nominal frequency range for the MKE-3 microphone is not more than 12 dB, and for M1-A2, M1-B2, IEC-1 and MKE-389-1 is not more than ±2 dB.
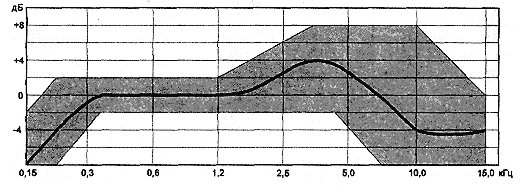
Rice. 5. Tolerance region of the frequency response of the MKE-377-1 microphone

Rice. 6. Tolerance region of the frequency response of the MKE-378 microphone
Publication: cxem.net
 See other articles Section Reference materials.
See other articles Section Reference materials.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Boots with spring studs
27.06.2003
Generics Group engineers have created a fundamentally new boots - with spring spikes. In them, plastic spikes are attached to a compressed steel springy plate.
Any force acting on the cleat causes the spring plate to collapse, absorbing the energy and reducing the pressure on the foot at that point. At the same time, the ends of this plate are bent down, bringing the secondary spikes into contact with the ground. This gives extra grip and distributes the load. The whole mechanism is enclosed in a durable plastic that prevents the accumulation of dirt inside.
Since spring boots significantly reduce the risk of injury to athletes compared to conventional sports shoes, the creators of the novelty are confident that their offspring will be in great demand.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Microsoft is blocking the installation of Linux on its tablets
▪ Creative people enjoy wasting time.
▪ Volkswagen Golf new generation
▪ Capturing methane from the air with zeolites
▪ Flies are more dangerous than thought
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ site section Regulators of current, voltage, power. Article selection
▪ article yellow press. Popular expression
▪ article What are the dimensions of the largest bear? Detailed answer
▪ Article Device for adjusting the angles of alignment. Personal transport
▪ article Drilling glass. Simple recipes and tips
▪ article Weakened knee. Focus Secret
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024








 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese





 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: