
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Fluorescent lamps and their characteristics. Reference data. Part 2
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Reference materials Ballasts for fluorescent lamps, ballast circuits (ballasts), starters, lamp ignition using a starter, glow discharge starters, thermal (thermobimetallic) starters, semiconductor starters, a two-lamp switching circuit, the main parameters of some types of ballasts. Ballasts for fluorescent lamps
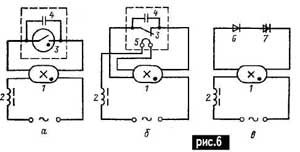
Most modern LLs are designed to operate in AC electrical networks. They are connected to the network only together with a ballast (ballast), which ensures the ignition of the lamps and their normal operation. Control gear circuits are classified according to the type of ballast and the way the lamp is ignited. Most often, inductive ballast is used, less often - inductive-capacitive. Ballasts in the form of active resistance or pure capacity are used only in special cases. According to the method of ignition of the lamps, circuits and control gear are divided into starter and non-starter. The latter, in turn, are divided into fast and instant ignition schemes. To facilitate the ignition of lamps operating in a network without an additional transformer, electrodes are widely preheated to a temperature that provides thermal emission sufficient to ignite a discharge at lower voltages. Heating is produced by their short-term inclusion in the current circuit, which is achieved by closing the contact of the corresponding device (starter, dinistor, etc.). When the contact is subsequently opened, a voltage pulse occurs that exceeds the mains voltage. This impulse, applied to the lamp with the electrodes not yet cooled down, should ignite a discharge in it. To do this, it is necessary that the pulse has a certain minimum amplitude and energy. The most common starter circuits for connecting lamps to the network through a choke are shown in fig. 6 (a - circuit with a key or a glow discharge starter; b - with a thermobimetallic starter; c - with a simple electronic starter). Designations in fig. 6: 1 - fluorescent lamp; 2 - throttle; 3 - key or starter contacts; 4 - capacitor; 5 - heater; 6 - diode; 7 - dinistor. The magnitude of the voltage pulse depends on the inductance of the inductor, the resistance of the electrodes, the instantaneous value of the current at the moment of breaking the circuit, and also on the current-voltage characteristic of transients in the starter. Since the moment of breaking is random, the voltage peak can also have random values from zero to the largest value. Starters Short-term closing and subsequent opening of the circuit can be done manually using a key or automatically using a special device called a starter. There are the following types of starters: glow discharge, thermal, electromagnetic, thermomagnetic, semiconductor, etc. The process of igniting a lamp with a starter can be divided into four stages in the general case: preparatory - from the moment the voltage is applied to the starter closing; heating of the lamp electrodes - from the moment of closing to the moment of opening; ignition attempt - at the moment of opening; preparing the starter for the next inclusion. Certain types of starters may not have the first stage. From the point of view of optimal lamp ignition conditions, it is desirable to reduce or eliminate the first stage, since it delays the moment of lamp ignition, to provide a contact time sufficient to heat the electrodes to a temperature at which a significant decrease in the discharge ignition voltage occurs, and to ensure that, when the starter circuit is opened, a voltage pulse of sufficient magnitude and duration is generated to ignite the discharge. In addition, the requirements for maximum simplicity, high reliability, etc. are imposed on the starter. These requirements are contradictory to a certain extent, therefore, when designing a starter, compromise solutions must be sought. The most widespread are glow starters (Fig. 7, where a is the internal structure; b - evacuated starter mounted with a capacitor on the contact panel; c - appearance of the assembled starter in the case). The starter is a miniature lamp in which one or both electrodes are made of a bimetallic plate. In the normal state, the electrodes are at a small distance from each other. When the voltage is turned on, a glow discharge occurs between them, heating the bimetallic plates, which bend from heating and close the circuit (1st stage of the glow discharge). From this moment, a short-circuit current flows through the electrodes of the lamp, heating them to a high temperature (stage 2). As soon as the contact closes, the discharge in the starter goes out; the bimetallic plates cool down and, returning to their normal state, open the circuit. At the moment of opening, an increased voltage pulse occurs, which ignites a discharge in the lamp (3rd stage). When an arc discharge is established in the lamp, the voltage across it drops to the burning voltage. The starter is made in such a way that the voltage at which a glow discharge occurs in it is higher than the operating voltage on the lamp and lower than the minimum voltage in the network. Therefore, when the lamp is on, the discharge in the starter does not occur, the bimetallic plates remain cold and the starter circuit is open. If the lamp does not ignite after the first opening, then the starter starts repeating the process again until the lamp lights up. The duration of the glow discharge and contacting stages are determined by the distance between the bimetallic electrodes and the heating and cooling rates, which in turn depend on their design, as well as on the composition and pressure of the filling gas.
For starters of industrial types, the duration of the glow discharge stage is on average 0,3 ... 1 s. The duration of a separate contact is 0,2 ... 0,6 s, which is not enough to warm up the electrodes. Therefore, ignition usually occurs after two to five attempts. Starters of asymmetric design (with one electrode in the form of a bimetallic plate and the other in the form of a wire) have a slightly longer contact time than starters of a symmetrical design. However, the magnitude of the voltage pulse in them depends on the polarity of the electrodes at the moment of breaking the contacts. In addition, when working in circuits with a capacitive ballast device, the glow discharge period in asymmetric starters is longer. The starter is mounted on an insulating socket with two pins and covered with a metal or plastic case. Starters have standard dimensions (Fig. 7). A miniature small capacitor is mounted in the case, which serves to reduce radio interference. In addition, it affects the nature of the transients in the starter so that it contributes to the ignition of the lamp. Without a capacitor, the voltage peak in the starter reaches a very large value - on the order of several kilovolts, but has a very short duration (1-2 μs), as a result of which the pulse energy is very small. Turning on the capacitor leads to a decrease in the peak to 400...900 V, an increase in its duration from 1 to 100 µs, and a significant increase in the pulse energy. This is explained by the fact that in the absence of a capacitor during the opening of the starter electrodes at the last points of contact, the metal is heated by current to a very high temperature, and short-term local arc discharges occur, maintaining which consumes most of the energy accumulated in the inductance of the circuit, so very little energy remains on the voltage pulse that occurs after the last arc is extinguished. On fig. 8 shows oscillograms of voltage at the starter (upper oscillogram) and current in the lamp circuit during the ignition process. Thermal (thermobimetallic) starters The advantage of these starters is the absence of the first preliminary stage, since the contacts are closed in the absence of current; higher ignition peak and longer contact time, typically on the order of 2-3 s. But they also have their drawbacks: they consume additional power to maintain the heating element in working condition, they are more complex in design, the circuit for switching them on is more complicated, they are not immediately ready for operation after the lamp is turned off. For these reasons, they are used only in special cases, for example, for lighting lamps at low temperatures. Solid state starters There are a number of schemes for such starters. All of them work on the principle of a key. The most complete requirements for starters are met by semiconductor starters waiting for ignition (Fig. 6, c, REZ / 01). They provide sufficient heating of the electrodes in time and opening in a certain phase of the voltage, which guarantees the magnitude and duration of the pulse. Other types of starters are used very rarely due to the complexity of the design.
Two-lamp switching circuit On fig. Figure 9 shows a diagram of a two-lamp ballast with a split phase, which provides a high power factor of the installation and a decrease in the ripples of the total luminous flux of the lamps (Fig. 9, a - diagram; Fig. 9, b - vector diagram of currents and mains voltage; c - oscillogram of changes in the light fluxes of lamps (1) and (2) and the total flux (1 + 2)). In order for the total current to be in phase with the mains voltage, it is necessary to provide a shift in the leading branch equal to the shift in the lagging one, i.e. about 60°, while cos f installation reaches a value of 0,9...0,95, and the depth of pulsations of the total flow is reduced to 25%. Typically, the phase shift lies in the range from 90 to 120°. In table. 4 shows the main parameters of some types of control gear for a rated voltage of 220 V with a power factor of about 0,5. Table 4
Author: S.I. Palamarenko, Kyiv; Publication: electrik.org
Traffic noise delays the growth of chicks
06.05.2024 Wireless speaker Samsung Music Frame HW-LS60D
06.05.2024 A New Way to Control and Manipulate Optical Signals
05.05.2024
▪ Cool Bitts ICEbox kit for immersion cooling experiments ▪ Low noise precision amplifier ▪ Fabric to keep you cool in the heat
▪ section of the site Fundamentals of safe life (OBZhD). Article selection ▪ article General characteristics of emergencies of natural origin. Basics of safe life ▪ article What fruits of civilization are the most dangerous? Detailed answer ▪ article Head of telephone and telegraph communications. Job description ▪ article Refrigerators and freezers. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering ▪ article Knife can be at the top. physical experiment
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: