
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Frequency synthesizer for the transceiver. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
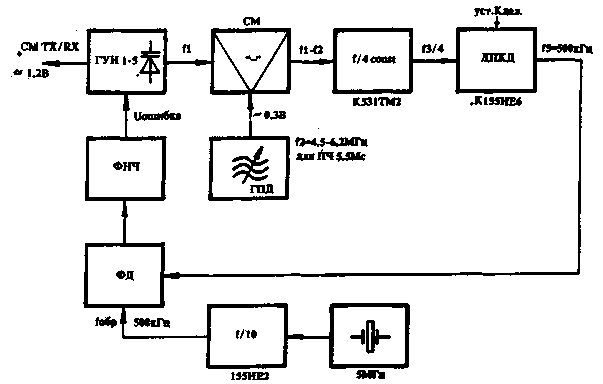
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Frequency synthesizers The synthesizer is used in a 5,5 MHz IF transceiver. A similar structure of the synthesizer is successfully used in the factory-made transceiver "Kontur-111" (Kharkov). The design of the synthesizer is shown in Fig.2. It is used for half a year in a transceiver with two conversions. Distinctive features of this synthesizer are good noise characteristics, which are not much worse than those of a conventional GPA, small size, smooth tuning, as well as the availability of the element base - only 1,7 microcircuits. The disadvantages include the fact that there is no stretching over the ranges and the overlap on all ranges is 28 MHz, which determines the XNUMX MHz range. There are no commutations in the GPA, which contributes to stability, the same tuning density and detuning on all ranges. The block diagram of the MF is shown in fig. one.
The GPA signal, which completely determines the stability of the midrange, is fed into the mixer, in which it is subtracted from the frequency of the VCO and selected by the circuits L7 - L11 - this is the so-called synthesizer IF. After that, the signal goes to the pulse shaper on the transistor VT11, and from the output of the transistor - to the D3 chip, which divides it by 4. This is done in order not to go beyond the passport value of the cutoff frequency D4. It is equal to 12 MHz. From the output of the divider to 4, the signal is fed to the DPKD, the division ratio of which is set by supplying a log. 1 (log.1 = 3-4,5 V) to the preset inputs of the D4 chip. Chip D5 and transistor VT14 are needed for counter D4 to work. From the D4 output, the signal is fed to a phase detector (PD), and a reference frequency voltage of 500 kHz is also supplied there from a quartz oscillator. The error signal from the FD through a simple low-pass filter, assembled on C9, C10, R2, is fed to the varicap in the VCO. When used in a 5,5 MHz IF transceiver, the VCO frequencies coincide on the ranges 3,5-14; 7-18; 10-21 MHz, which allows you to use the common circuits of both VCOs and synthesizer mixers. The VCO is assembled according to the capacitive three-point scheme and has 2 emitter followers for the transceiver mixer and 2 emitter followers for the synthesizer mixer, with VT4 acting as a voltage coupler. The voltage at the output of VT4 should be in the range of 0,3 - 0,4 V and is selected by capacitor C18. The midrange mixer has no features and operates from -0,2 V. The mixer circuit does not differ from that previously published in [1]. DPKD on the D4 chip has 4 preset inputs. In the absence of a log. 1 at the inputs, the division factor D4 is equal to 1. In the future, when applying a log. 1 to the inputs D4 through the voltage dividers R38 - R41 and R42 - R45 and the diode matrix VD9 - VD 13, the required Kdel is set. for this range. Kdel. D4 chips for each range is indicated in Table. one. Table 1
The crystal oscillator is assembled on a VT12 transistor, it operates at a frequency of 5 MHz. A pulse shaper is assembled on the VT13 transistor, which the D10 chip divides by 6. At its output, a voltage of a reference frequency of 500 kHz is obtained. Actually, it is not necessary to use quartz at 5 MHz, you can use quartz at 1 MHz, 2 MHz, while instead of the K155IE2 chip, you can turn on the divider by 2 or 4, respectively, on the K155TM2 chip. However, we do not have to compare exactly at 500 kHz, only in this case it is necessary to recalculate Kdel. DPKD and the frequency of the GPA. The FD is assembled on D 1, D2 microcircuits and VT5, VT6, VT7 transistors. Many different FD schemes have been tested in the MF, but the one shown in Fig. 2 turned out to be the best of all in terms of capturing and holding the frequency. The PD scheme is completely taken from [2]. The stability of the midrange is completely determined by the stability of the GPA, the scheme of which is traditional and has no features. All methods of GPA frequency stabilization are described quite well in the literature [1 - 3]. The only thing that is required is to set the tuning limit with capacitors C34, C36, C37 4,5-6,2 MHz. Capacitor C32 select the required detuning value. The synthesizer was mounted on a printed circuit board made of double-sided fiberglass with dimensions of 120 x 80 mm. Installation requirements are the same as for any digital equipment. Coils L1 - L5 and L7 - L11 are wound on frames from IF transistor receivers equipped with screens and cores. The frequency data for tuning the contours are given in Table 2. Table 2
The data for the number of turns and capacitance values are not given, because depend on the specifically chosen frameworks and cores. The GPA is made as a separate block on a board measuring 50 x 40 mm and is connected to the synthesizer mixer with a thin coaxial cable with a wave impedance of 75 ohms. Chips D1 and D2 in the FD to reduce the size of the board and the lengths of the conductors are installed one above the other (D1 over D2), after connecting the necessary conclusions according to the scheme. Chokes Dr1, Dr2 can be 50 - 150 mH, relay type RES-49. T1, T2 are wound on rings K12x6x5, having a permeability of 200 - 1000 NN (non-critical). In place of the diodes of the KD503A mixer, KD521, KD522, KD514A, KD512 and others like them also work well. KP302V is replaced by any of this series. Chip D3 K531TM2 can be replaced by K555TM2, K1533TM2 or K131TM2. The midrange tuning consists in setting the frequency of the VCO, it should be lower by about 10% of the frequency given in table. 2. A fragment of VCO tuning is given in [1]. The mixer circuits MF L7 - L11 are tuned to frequencies, which are also shown in Table 2. To do this, turn off the power from the GPA and VCO (so that their signals do not interfere) and a signal of the required frequency with a level of about 10 V is fed into the VT0,2 emitter with the GSS, then, using a voltmeter connected to the VT11 base, they achieve the maximum voltage amplitude by setting circuits L7 - L11 in resonance. For stable operation, the voltage at the base of the VT11 transistor should be - 0,5V. The midrange is powered by three voltages - +5 V; +12V;+15V. The synthesizer can be configured for a different transceiver IF value, such as 5; 9; 8,814 MHz, etc. To do this, you will have to change Kdel. D4. This can be done in accordance with Table 3. Table 3
Combining preset inputs D4, you can get Kdel from 1 to 16. GPA MF can also be stabilized using a digital scale, as done in [3]. Literature 1. Zhemkov S. Transceiver frequency synthesizer. Radio amateur. 1992, No. 9, P. 35 - 36.
Author: M. Serbenko (UB2MF), Kirovsk, Luhansk region; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
Artificial leather for touch emulation
15.04.2024 Petgugu Global cat litter
15.04.2024 The attractiveness of caring men
14.04.2024
▪ 800V MOSFET P7 CoolMOS by Infineon ▪ Electric clipper for hair in the nose and ears ▪ A new way to control the speed of light ▪ Artificial wood from the laboratory
▪ section of the site RF power amplifiers. Article selection ▪ article Where the table was food, there is a coffin. Popular expression ▪ article What part of hereditary information reflects the individuality of a person? Detailed answer ▪ article Packing equipment. Travel Tips ▪ article Fast Temperature Meter. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering ▪ article Libra from a stick. physical experiment
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: