
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Stereo decoder with pilot tone. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
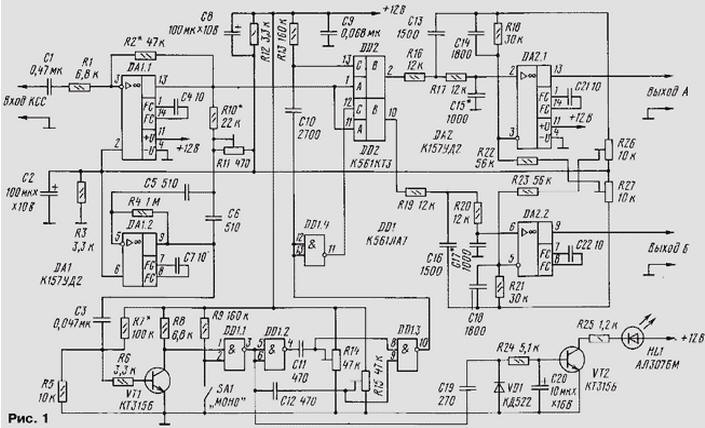
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Civil radio communications Every year the number of broadcasting stations operating in the VHF-2 band (88 ... 108 MHz) is growing everywhere. To encode a stereo signal in this range, a system with a pilot tone is used. To ensure the operability of domestic equipment in two broadcasting systems, the receiver must be supplemented not only with a high-frequency path for operation in VHF-2, but also with a stereo decoder for a system with a pilot tone. Currently, stereo decoders (SDs) are built on the basis of imported microcircuits TA7343AP, TA7342R, TDA7040T, etc. A domestic dual-system integrated SD - KR174XA51 - has also appeared. However, radio amateurs often go on to develop their own LEDs [1]. I want to offer one of the options for such a device, assembled entirely on non-deficient domestic radio elements. This design uses the principle of time division of channels, well known for the designs of LEDs with a system of polar signal modulation [2, 3]. This principle is also used in SDs assembled on TA7343AP and similar microcircuits. In contrast to them, the described design does not have a PLL system and a generator. To recover the 38 kHz subcarrier, a simple method of doubling the pilot tone frequency is used here. Despite this, the decoder allows for a fairly high-quality reception of stereo radio programs with good channel separation. Schematic diagram of the stereo decoder is shown in fig. 1. It consists of a buffer amplifier (DA1.1), a bandpass active filter (DA1.2) tuned to a frequency of 19 kHz, a frequency doubler on a VT1 transistor and a DD1 microcircuit, a switching unit on the keys of the DD2 microcircuit, low-pass filters with compensators crosstalk on the DA2 chip. The principle of operation of SD. The complex stereo signal (CSS) from the frequency detector of the radio receiver is fed to the DA1.1 buffer amplifier, which has a gain of about 6. This amplification is necessary to obtain the pilot tone signal level, which ensures the operation of the active filter on the DA1.2 chip connected to the amplifier output through resistors R10 , R11. The trimmer resistor R11 sets the maximum quality factor of the filter at a frequency of 19 kHz. From the output of the buffer amplifier, the signal goes to the switches assembled on the keys of the DD2 chip. The sinusoidal signal of the pilot tone, isolated and amplified by an active filter, is converted into a rectangular shaper in the transistor VT1 and the logic element DD1.1. On elements DD1.2 and DD1.3, capacitors C11 and C12 and resistors R14, R15, a frequency doubling device is assembled. Let us dwell on the principle of operation of the device in more detail, since the degree of separation of stereo channels and the level of noise at the output of the LED depend on the quality of the doubler. On fig. 2 shows waveforms of signals at the main points of the doubler.
When a rectangular signal is received at the input, positive and negative pulses appear on the right (according to the scheme) plates of capacitors C11 and C12 relative to the DC voltage levels Up1 and Up2, set respectively by trimming resistors R14 and R15. These pulses are fed to the inputs of the element DD1.3. Since the DC voltage levels Up1 and Up2 are above the threshold switching voltage of the element Upor, the output of this element is logical 0. Positive pulses at each input of DD1.3 do not affect the operation of the doubler. But each negative pulse on any of the capacitors C11 or C12 translates the element DD1.3 into the state of a logical unit at the output. The duration of the element in this state (tU1 or tU2) depends on the recharge time of the corresponding capacitor to the level of the threshold switching voltage of the element Uthr. The recharge time of the capacitors depends on their capacitance and on the levels Up1 and Up2, set by trimming resistors R14 and R15. By changing these levels, you can change the duration of the pulses tU1 and tU2 and thereby achieve the shape of rectangular pulses at the output of the element DD1.3, close to the meander and a frequency twice as high as the original. The pulses with a frequency of 38 kHz formed in this way from the pilot tone signal are fed to the control output of the upper (according to the scheme) key of the DD2 microcircuit, and inverted by the DD1.4 element - to the control output of the lower key. The isolation capacitor C10 together with the resistor R13 provide the opening of the upper key in the absence of pulses with a frequency of 38 kHz, i.e., when the LED is switched to the "Mono" mode. The lower key in this mode is open with a high level signal from the output DD1.4. High levels of pulses from the outputs of DD1.3 and DD1.4 coincide in phase with the positive and negative pulses of the suppressed subcarrier. Therefore, when the keys work in turn, the signal of the left channel is allocated at the output of the first (upper according to the scheme), and the signal of the right channel is allocated at the output of the second. Further, the signals of the two channels are processed and frequency corrected by two active low-pass filters on the DA2.1 and DA2.2 microcircuits. These filters are included according to the scheme of crosstalk cancellers. The principle of their operation is described in [2,4]. They effectively suppress the high-frequency components of the CSS, and the compensators further increase the degree of separation of the stereo channels. From the output of the LED, the signals of channels A and B are fed to the input of the pre-amplifiers of the audio frequency of the receiver. The LED is equipped with a stereo mode indicator. It consists of a diode VD1, a smoothing capacitor C20, a transistor VT2 and an LED HL1. The current of the LED glow is set by the resistance of the resistor R25 within 8 ... 10 mA. The indicator is connected through the capacitor C19 to the input of the frequency doubler. Switch SA1 decoder can be forced into the "Mono" mode. And by connecting pin 2 of the DD1 microcircuit through a decoupling diode (not shown in the diagram) to a tuning indicator (for example, LED), you can automatically switch to the "Mono" mode when the radio is tuned and if the radio station's signal strength is insufficient. The supply voltage of the LED can be in the range of 6 ... 15 V. The lower limit is determined by the minimum supply voltage of the DA1 and DA2 microcircuits. Therefore, as these microcircuits, it is desirable to use those that, in accordance with the technical characteristics, have a wide supply voltage limit, for example, K157UD2, K140UD20, K544UD2, K140UD17, etc. Digital microcircuits DD1 and DD2 are interchangeable with the same ones from the 564 series, and when the supply voltage is limited to 9 V - and the 176 series. Transistors VT1 and VT2 are any low-power silicon npn structures. Diode VD1 - series KD521, KD522, D220, D223 with any letter indices. Resistors and capacitors are also any. As capacitors C11 and C12, it is desirable to use specimens with similar capacitance and TKE values. The LED was assembled on a printed circuit board, the drawing of which is shown in Fig. 3.
To establish a decoder, a low-frequency generator and an oscilloscope are required. By applying a signal from the generator with a frequency of 19 kHz and an amplitude of 5 ... 10 mV to the input of the LED, the signal at the output of the buffer amplifier DA1.1 is controlled by an oscilloscope. Then, by connecting the oscilloscope to the output of the active filter DA1.2, by rotating the engine of the tuning resistor R11, the maximum amplitude of the sinusoidal signal of 19 kHz is achieved. Further, by connecting the oscilloscope to pin 3 of the DD1.1 element, by selecting the resistor R7, the shape of the rectangular oscillations is set, close to the meander (the duty cycle is 2). After that, the oscilloscope controls the signal at pin 10 of the DD1.3 element and by rotating the engines of the trimmer resistors R14 and R15 they also achieve a square wave shape of doubled frequency (38 kHz), close to the meander. This is usually obtained with the position of the sliders slightly above (according to the scheme) the average position. After the performed checks, connect the LED to the output of the frequency detector of the receiver and, listening to the stereo program, by slightly changing the position of the trimmer resistors R11, R14, R15, achieve the best separation of stereo channels with a minimum noise level. The final separation of stereo channels is regulated by trimmers R26 and R27. It will not be difficult to set up this LED even without devices - when receiving a stereo transmission by ear on headphones. It is first necessary to set the sliders of all tuning resistors to the middle position, and on the collector of transistor VT1, by selecting resistor R7, set a constant voltage equal to half the supply voltage. Then, by rotating the slider of the resistor R11, achieve the ignition of the HL1 LED. By controlling the reception of the transmission by ear, resistors R14 and R15 set the maximum separation with a minimum of noise, while it may be necessary to slightly adjust the resistor R11. The final setting is again carried out by resistors R26 and R27. Literature
Author: I.Potachin, Fokino, Bryansk region
The world's tallest astronomical observatory opened
04.05.2024 Controlling objects using air currents
04.05.2024 Purebred dogs get sick no more often than purebred dogs
03.05.2024
▪ The most distant object in the solar system ▪ Maxim RS-485/RS-422 transceivers MAX33072E/MAX33073E ▪ Excess weight harms memory and learning ability
▪ section of the site Power supply. Article selection ▪ article Tobacco smoking: impact on the human body, consequences. Basics of safe life ▪ article Where can you see and taste natural watermelon snow? Detailed answer ▪ Article Nasturtium is large. Legends, cultivation, methods of application ▪ article Electronic ignition system. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: