
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Radio amateur communication technologies based on VoIP. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Civil radio communications The rapid development of telecommunication systems using the Internet in the late 90s of the last century and the beginning of this century created a precedent for the emergence of new areas of amateur radio communications. The birth of IP telephony and the further improvement of digital encoding protocols and speech transmission over any distance became the starting point of the idea of combining the advantages of radio communications and the capabilities of modern network technologies Voice Over Internet Protocol (VoIP). At the Seventh Conference of Siberian Radio Amateurs, held in September last year in Berdsk (Novosibirsk region), a new type of amateur radio communication was presented - Echolink, experiments with which are being conducted on VHF through a special VHF-Internet gateway installed on the collective radio station UA90XC in Akademgorodok. Novosibirsk. VoIP in amateur radio practice The alternative direction of amateur radio communications began to actively develop in the West since 1997 and has now reached a global scale [1]. A large number of HF and VHF repeaters and simplex repeaters in different countries of the world were connected to the Internet. Radio amateurs have the opportunity to communicate with each other regardless of transmission, both through a computer and without its direct use - working on portable or mobile VHF/UHF transceivers. For a number of objective reasons, Russia, until 2002, was practically not represented in any of the amateur radio communication systems using VoIP technologies. This is primarily due to the still low availability of Internet services outside large cities and the high cost of provider services. However, there are also purely psychological reasons for the low motivation of Russian shortwave athletes to master and implement VoIP technologies in communication practice. Unfortunately, the captivity of psychological stereotypes that have developed over the years is sometimes an insurmountable obstacle to the perception of new ideas. Of course, Internet QSOs are not taken into account for DXCC and when working in contests, but the amateur radio movement is multifaceted and cannot be reduced only to sports aspects. On the other hand, today no one questions the feasibility and convenience of using VHF repeaters as auxiliary means of amateur communications. If the repeater is connected to the Internet and registered in one of the existing international VoIP systems, it becomes a means of not only local, but long-distance and international high-quality communications. Moreover, each user can, at his own request, connect or disconnect the desired correspondents, work through repeaters in other cities and countries, simply by sending the appropriate DTMF codes from his portable station. This is especially useful for young radio amateurs of categories 3 - 4, who, without violating the instructions, can acquire the language skills of conducting QSOs with foreign correspondents. The practical implementation of amateur radio VoIP communication systems is very simple and accessible even to novice radio amateurs. It is enough to have a computer with a sound card, a headset and the ability to connect to the Internet. If you want to create a local simplex radio frequency link, just connect your computer to an amateur VHF radio station according to the following scheme: the output of the low-frequency receiver (headphone jack) is connected to the “Line In” jack of the sound card , the microphone input of the transmitter is connected to the “Line Out” socket of the sound card, the PTT connector of the radio station is connected through the interface to the COM port of the computer. A simple circuit with an optocoupler can be used as a receive/transmit control interface (see Fig. 1). This interface can also be used for digital communications (RTTX PSK31, SSTV) without modification.
Currently, several communication systems operate based on VoIP technology. The most famous of them are IRLP, i-Link, e-QSO and Echolink. The IRLP (Internet Radio Link Project) system [2] was created in 1997 in Canada by David Cameron (VE7LTD) and became widespread in 2000-2001. It is implemented in software on the Linux platform and is a united network of repeater nodes in different cities around the world. Unlike other systems, access to which is possible both through a networked personal computer and via a radio channel, IRLP is functionally oriented to work only from the air. Its users (usually members of local IRLP clubs) have a special DTMF login ID, without which it is impossible to log into the system. For this reason, IRLP has not been widely adopted. One of the pioneers in the development of amateur VoIP technologies was the l-Link[3] system created by Grim Barnes (MOCSH). Structurally, it was a simplified prototype of the modern Echolink system, but unlike the latter, it required a circuitry-technically more complex specialized ASCII interface based on a P1C controller. This circumstance significantly limited the ability of radio amateurs to organize radio frequency gateways based on l-Link. However, thanks to the possibility of computer login via the Internet, l-Link, until 2002, was very popular among Western radio amateurs. With the advent of Echolink, the system practically ceased to exist. The e-QSO system [4] was created in the UK by Paul Davis (M0ZPD). It ranks second in popularity after Echolink. It is distinguished by its simplicity of software (600 KB), minimal requirements for a computer and operating system, and does not require special network protection settings (firewall). The program monitor displays a list of individual e-QSO servers and conferences currently connected to the system. They are called rooms. The user can optionally connect to any room and conduct QSOs with the correspondents available there. It is also possible to organize your own room with a local radio frequency gateway. From September 2002 to May 2003, such a simplex e-QSO radio gateway operated in Novosibirsk on a frequency of 145.525 MHz around the clock under the call sign UA90XC-L. Since May 2003, this gateway has been connected on a permanent basis to the Echolink system, where until now it almost exclusively represents the Russian Federation. Echolink is the most advanced amateur radio VoIP communication system today [5]. Suffice it to say that since 2002, the total number of radio amateurs registered in it has already exceeded 120 thousand. Every day, from 1500 to 3000 thousand call signs from all over the world are online, including repeaters, radio links and thematic conferences. System developer Jonathan Taylor (K1RFD). The software has many advantages over the above-mentioned systems. First of all, this is an improved voice transmission protocol and the availability of expanded capabilities for controlling program functions via a radio channel. If a radio amateur is in the range of reliable reception of a repeater, he does not need to make a general call on the frequency. Thanks to the built-in speech synthesizer, the program broadcasts the call signs of all connecting stations. It is possible to actively request information about the list of connected stations by sending the user DTMF code 08. You can also randomly establish a connection with the desired stations or repeaters. To do this, you need to know the node number of the station and enter it from the DTMF keyboard. After completing a QSO, all you need to do to disconnect from the station is to send the # symbol. The presence of a built-in digital tape recorder, activated by VOX, makes it possible to keep a voice log of ongoing QSOs, conferences or round tables with recording of time and call signs. You can view the connection log and manage the program status not only via a radio channel, but also via the Internet from a remote computer through the built-in active web page. More detailed information in Russian about the Echolink system and program settings can be obtained on the “Echolink in Novosibirsk” web page at echolink.amel.nsc.ru. There is also a forum where you can ask questions and get advice on issues of interest. A list of all stations connected to Echolink with their node numbers is also available, updated every 5 minutes. The five-month experience of online work of the Novosibirsk echolink showed very high activity of Russian-speaking correspondents from all countries of the world. Thematic round tables are held on an ongoing basis with American, Canadian and Finnish radio amateurs on the design and calculation of HF and VHF antennas, technical support for VHF field days (VE3XAX), modern aspects of digital communication on HF (W2/UR5LCM), design of 23 cm equipment ( 0H2NC), development of additional software functions of the Echolink system (VE3IVM). English- and Spanish-speaking radio amateurs are also active. In conclusion, I would like to express hope for the awakening of interest and more active development by Russian radio amateurs of new combined types of communication using IT technologies. Authors: Yuriy Cherednichenko (UA90FC), Ivan Buryi (RW90X), Novosibirsk; Radio #3 2004 How eQSO and Echolink programs work with links Working in the eQSO and Echolink systems, I made several interesting observations about how two popular amateur radio programs eQSO and Echolink work based on the MS Windows XP operating system, through what ports do they work, what remote resources do they connect to, and what happens? To analyze data flows, I used the TCPView v.2.31 program (sysinternals.com/). Using this program, you can very clearly see which addresses and ports are open and which connections are made between the local (your) and remote computers. 1. Operation of the eQSO v program. 1.20.10 eQSO is a program for amateur radio VoIP communication via the Internet (Fig. 2). The program is easy to use and does not require registration.
It gained its popularity because it uses the TCP protocol, which eliminates data loss during transmission. The information obtained from analyzing the operation of the eQSO program is given below.
When running, the eQSO program creates (opens) two processes (Fig. 3):
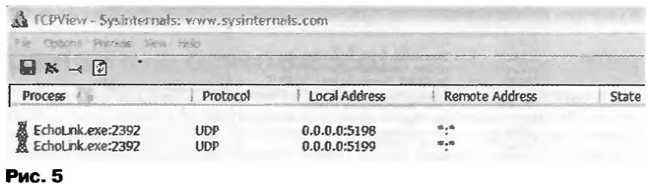
Both processes, after running them on the local machine, select any free port (starting from approximately 1024 and above). This port can only be the same for both processes. In our example, this is port 1046. During other launches, the program can select and open any other port. So, for example, the author’s number of the port that was opened, during different launches of the eQSO program, was as follows: 1044, 1051, 1054, or others. Both processes of this program operate using the TCP protocol. It follows from this that the eQSO program can be successfully used in local networks if your computer (workstation) is located behind the Firewall server. 2. Operation of EchoLink v. 1.7.863 The EchoLink program works much more interestingly and completely different from eQSO. Her work is divided into two phases; phase 1 (Fig. 4) is the establishment of a communication session by the EchoLink program; phase 2 (Fig. 5) is the state of the program’s work processes after the session is established.
At the moment the program starts and the session is established, the four processes created (opened) by it are running: the first two processes work using the TCP protocol and serve to establish a connection with the remote resource (server) 68.63.170.8:5200, with which you are currently connecting for your local address, for example: 195.239.0.82:1106; the second pair of processes runs over UDP protocol for local ports 5198,5199 on your computer. Once a connection to the server is established, the first two processes (TCP) are removed from your local computer's memory, leaving only the second pair of processes running over UDP on local ports 5198 and 5199 on your computer. But there is a pitfall here. UDP is an unreliable protocol: it sends data packets that do not include a header requiring the remote computer (server) to acknowledge receipt of the packet (as is done in the TCP protocol) and there is no complete guarantee that they will reach the final destination. And it follows from this that for normal operation of the Echolink program, if the latter is located behind the Firewall of the local network in the communication system, you need to ask your system administrator to give you full access to ports 5198, 5199 on the Firewall. Otherwise, you won’t hear anything and no one will hear you either! After reading the material in this article, I think there will be fewer questions on repeater, link and direct amateur radio channels regarding the reasons for the inoperability of these wonderful amateur radio programs, such as eQSO and Echolink. And more detailed information about EchoLink in Russia can be found on the website echolink.ru. Literature and Internet sites
Author: Sergey Chuchanov (UR3IRS), Druzhkovka, Donetsk region, Ukraine
A New Way to Control and Manipulate Optical Signals
05.05.2024 Primium Seneca keyboard
05.05.2024 The world's tallest astronomical observatory opened
04.05.2024
▪ The most massive neutron star discovered ▪ Reducing the altitude of aircraft will help the environment ▪ Tamron 16-300mm F/3.5-6.3 Di II VC PZD Macro Lens (Model B016) ▪ Monitor Acer Nitro EI322QURP
▪ section of the site Consumer Electronics. Selection of articles ▪ article by Honore de Balzac. Famous aphorisms ▪ article Where can one find burials in the form of coffins nailed to rocks? Detailed answer ▪ article Thyme. Legends, cultivation, methods of application ▪ article Ice alarm for a car. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese



 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: