 Free technical library
Free technical library
Appendix 5. Characteristics of explosion-proof connections of explosion-proof equipment
Parameters of explosion-proof connections of electrical equipment of the 1st, 2nd, 3rd categories according to PIVRE (PIVE)

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Rules for the technical operation of consumer electrical installations (PTE)
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
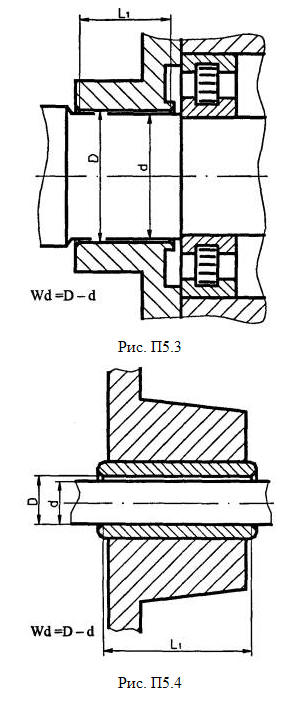
Table A5.1
| Type of flameproof connection |
Free volume of the shell, cm3 |
Category 1 |
Category 2 |
Category 3 |
| Slit length L1, mm |
Slot length to bolt hole L2, mm |
Gap width* W1 and Wd, mm |
Slit length L1, mm |
Slot length to bolt hole L2, mm |
Gap width* W1 and Wd, mm |
Slit length L1, mm |
Slot length to bolt hole L2, mm |
Gap width* W1 and Wd, mm |
| Fixed flameproof joints (Fig. A5.1 and A5.2) |
Until 200 |
5 |
5 |
0,5 |
5 |
5 |
0,3 |
5 |
5 |
0,2 |
| From 200 500 up |
8 |
5 |
0,5 |
8 |
5 |
0,3 |
8 |
5 |
0,2 |
| From 500 2000 up |
15 |
8 |
0,5 |
15 |
8 |
0,3 |
15 |
8 |
0,2 |
| over 2000 |
25 |
10 |
0,5 |
25 |
10 |
0,3 |
25 |
10 |
0,2 |
| Connections of movable mates (Fig. A5.3) |
From 500 2000 up |
15 |
- |
0,5 |
15 |
- |
0,4 |
15 |
- |
0,3 |
| over 2000 |
25 |
- |
0,6 |
25 |
- |
0,4 |
25 |
- |
0,3 |
| 40 |
- |
0,75 |
40 |
- |
0,5 |
40 |
- |
0,4 |
| Connections of control rods and rollers (Fig. A5.4) |
Until 200 |
10 |
- |
0,25 |
10 |
- |
0,25 |
10 |
- |
0,15 |
| From 200 500 up |
15 |
- |
0,25 |
15 |
- |
0,25 |
15 |
- |
0,15 |
| From 500 2000 up |
15 |
- |
0,25 |
15 |
- |
0,25 |
15 |
- |
0,15 |
| over 2000 |
25 |
- |
0,15 |
25 |
- |
0,25 |
25 |
- |
0,15 |
*In PIVRE, the slot width is denoted by S1 and Sd.

 See other articles Section Rules for the technical operation of consumer electrical installations (PTE).
See other articles Section Rules for the technical operation of consumer electrical installations (PTE).
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Buildings of the future
03.05.2007
British scientists have come up with two types of materials for the houses of the future.
“The butyblocks we developed, from the word bitumen, serve as an excellent replacement for concrete. And most importantly, they are 100% waste,” says Dr. John Fort from the University of Leeds. According to his idea, first you need to mix broken glass, smelter slag, sewage sludge, incinerator ash, and pulverized ash from thermal power plants. Then add melted bitumen obtained from the processing of old tires, and pour into molds. Next, the blanks are placed in an oven, heated, the bitumen oxidizes and becomes six times stronger than concrete.
True, the author of the work does not mention whether any harmful substances are emitted in a building built from such blocks, which are found in excess in both slag and ash. But among the future plans is the creation of vegeblocks, where vegetable oil waste will be used.
Other material for the home does not cause any complaints in terms of home security, moreover, it is specifically designed to increase such security. British scientists, together with colleagues from Germany, are developing this material for Greek builders who need to build housing in earthquake-prone areas.
To protect the inhabitants of such housing from natural disasters, scientists propose adding polymer nanoparticles to a high-strength gypsum composition from which walls are erected. A characteristic property of these nanoparticles is the ability to turn into a liquid with increasing pressure. As a result, the particles literally flow out from the top of the developing crack and, having found themselves in an area with less pressure, become solid again, healing the crack.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Photoshop for smartphones
▪ Will chickens save Canada?
▪ head grows
▪ Orbital lunar probe LADEE crashed as planned
▪ AMOLED with a large diagonal
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Calls and audio simulators. Article selection
▪ article Go under the window, wander under the window. Popular expression
▪ What criteria were used to periodize the history of modern times? Detailed answer
▪ article Hungry Rice. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
▪ article Solar collectors. Accumulation tank. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Always only two. Focus secret
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese



 See other articles Section
See other articles Section 