Bipolar power supply from a unipolar source. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Power Supplies
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
This circuit is very easy to assemble and practically does not require special adjustment.
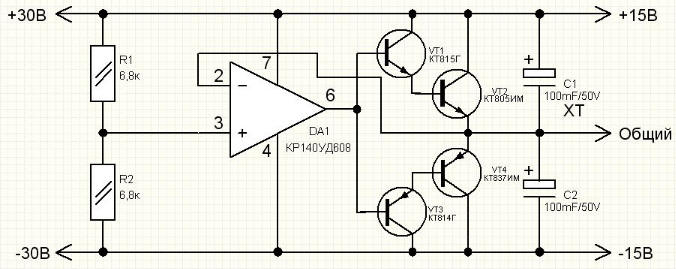
(click to enlarge)
Features:
- operating voltage range - 6-30V;
- load current - 1A;
- voltage deviations at an input voltage of 30V and a load of 1A - +/- 1%.
The whole circuit is based on the principle of operation of a comparator assembled on a KR140UD608 microcircuit. A reference voltage equal to half the supply voltage is applied to the non-inverting input of the microcircuit (pin3). The reference voltage is set by voltage dividers (R1, R2).
The inverting input of the microcircuit (pin 2) is supplied with a feedback voltage taken from the output of the emitter follower, consisting of transistors (VT1-VT4). From the output of the microcircuit (pin 6), the signal is fed to the input of the emitter follower. Pins 7 and 4 of the DA1 chip are connected respectively to the input supply voltage (pin 7 - "+", pin 4 - "-").
The beauty of this circuit is that it is able to operate from 6V with a maximum allowable 30V and balance the voltage arms regardless of input voltage surges.
 See other articles Section Power Supplies.
See other articles Section Power Supplies.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Smart sweat control patch
24.08.2019
Scientists from the University of California at Berkeley (UC Berkley, USA) have developed new sensors that can measure the rate of sweating in real time and determine the amount of electrolytes and metabolites in sweat. The sensor looks like a patch and is easily glued to the skin. In the future, such a sweat test could replace a blood test, and a patch - a needle prick.
The new sensors contain a spiral microscopic tube - a microfluidic device - that collects sweat from the skin. By tracking the rate at which sweat passes through the microfluidic system, the sensors can report how much a person is sweating. The microfluidic tube is also equipped with chemical sensors that can detect the amount of electrolytes (mineral compounds capable of conducting electrical charge) in sweat, such as potassium and sodium, and metabolites, such as glucose.
The developers came up with a new sensor design: they applied a sensor tube to a sheet of plastic patch using roll printing technology, similar to how newspapers are printed in a printing house. This method allows the production of large quantities of disposable patches at a low cost and in a short time.
To test what sweat can reveal about a person's health in real time, the researchers conducted an experiment with several volunteers who had a band-aid applied to their forehead, forearm, armpits and upper back. While the study participants rode the exercise bike, the sensors measured the level of sweating and determined the amount of sodium and potassium in the sweat. The data showed that the intensity of sweating is indicative of the overall fluid loss in the body during exercise.
The scientists also tried to use a "sweat sensor" to measure glucose levels in healthy people and diabetic patients. They then compared the data with the results of a blood test. In this case, the readings didn't match, which is why a sweat test can't replace a blood test right now - at least not in glucose tests. The researchers plan to study the correlations in the two types of analysis in more detail.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Samsung Bespoke 4-Door Flex Refrigerator with Meal Plan and Digital Cooking
▪ PNY CS900 960 GB Solid State Drive
▪ Ill - stay at home
▪ Year of the computer virus
▪ STMicroelectronics smart sensor based on L6364W IO-Link transceiver
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ site section Infrared technology. Article selection
▪ article Requirements for lighting of premises and workplaces. Basics of safe life
▪ article What is the Rh factor? Detailed answer
▪ article Black alder. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
▪ article LCD-thermometer on a microcontroller. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Overhead transmission lines with voltage up to 1 kV. Climatic conditions. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: