Circuit breaker for electronic circuits. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Protection of equipment from emergency operation of the network, uninterruptible power supplies
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
Electronic devices based on microprocessors and less integrated microcircuits are sensitive to supply voltage parameters. To ensure the safe operation of such devices, voltage stabilizers with protection are used. In many power supplies, it comes down to cutting off power to the circuit in the event of a short circuit in it or a sharp increase in load current. Such, for example, are the popular voltage stabilizers KR142EN5.
The "minus" of such stabilizers is that they are too inert in the protection mode: operation (stopping the power supply to the circuit) occurs after 200 - 500 ms and strongly depends on the nature of the current change in the load - simple stabilizer nodes react to an abrupt increase in current, and smooth is often not perceived. The inertia of switching on protection in 200 ms can cost the owner very dearly. Protective circuits have been published in the literature that respond to changes in load current faster than 100 nanoseconds, this is a very good indicator. However, they contain many elements and are difficult for beginner radio amateurs. The author has developed a simpler protection that operates even with a smooth change in load.
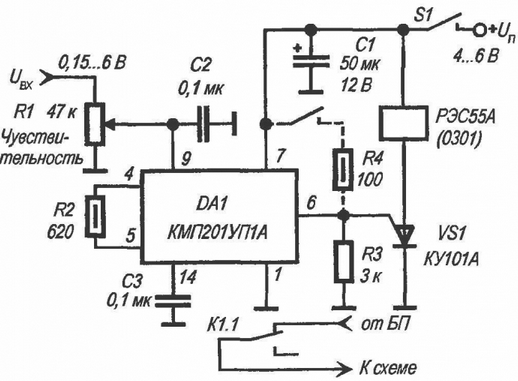
Schematic diagram of the protection unit
Any radio amateur can repeat the proposed scheme. The node contains only one microassembly KMP201UP1A, does not require configuration and adapts to any power source with a common negative wire. I recommend building a node into every home radio power supply, and especially into those power supplies that power expensive electronic instrument assemblies. The device is powered by a constant stabilized voltage of 4 ... 6 V, in the "normal" standby mode it consumes a current of 0,8 mA from the voltage source. Through the normally closed contacts of relay K1, the voltage from the power supply unit (PSU) is supplied to the protected electronic circuit.
As long as the voltage at the input of the circuit does not exceed the limit set by the divider on the resistor R1, the voltage at pin 6 of the microassembly is close to zero. As soon as the set limit is exceeded, a voltage of 6/1 Un is supplied from pin 2 to the control electrode of the thyristor VS3. The thyristor opens and remains open until the circuit is energized or its anode or cathode circuits are broken. The relay is on, therefore, the power supply to the protected circuit is stopped. This voltage drop is perceived by the protection node. The sensing node can also be used in other cases where an immediate response to a few mV increase in R1 is required. For example, using the node as a control circuit for ULF, we get an amplifier with acoustics, which automatically turns on when a signal appears at the input. For this application, a low power relay should be connected directly between pin 6 of DA1 and ground. To switch the load, use short-circuit contacts (the insert in the diagram is shown by a dotted line). The sensitivity of the input signal is adjusted by R1.
Thyristor VS1 can be replaced by KU101B. Relay K1 is any low-power relay that operates at a voltage of 3 ... 4 V. Reed relays are convenient for this purpose. If this is not available, you can make it yourself. For this, 200 turns of PEL transformer wire with a diameter of 0,1 mm are wound on a low-power reed switch with normally open contacts. This winding serves as a self-made relay coil, and the switching contacts are standard reed switch contacts. Such a relay operates at a low supply voltage of 2...4 V and consumes current up to 50 mA. Therefore, it is designed to operate in a pulsed mode and is quite suitable for replacing K1 in our circuit. Fixed resistors type MLT-0,5. Capacitors C2, C3 type KM or similar. Electrolytic capacitor C1 type K50-6. The chain, shown in the diagram by a dotted line, serves to check the node and force the protection to be turned on.
To disable the protection, it is necessary to briefly break the power circuit of this circuit by pressing the S1 button. Now the device tests the input voltage again and is ready to turn on the protection.
Author: A.Kashkarov
 See other articles Section Protection of equipment from emergency operation of the network, uninterruptible power supplies.
See other articles Section Protection of equipment from emergency operation of the network, uninterruptible power supplies.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Dual GPU Nvidia Tesla K80
26.11.2014
Nvidia has unveiled a new solution for the Nvidia Tesla Accelerated Computing Platform, the Tesla K80 dual-GPU graphics accelerator.
The accelerator is designed for a wide range of applications, including machine learning, data analysis, scientific and high performance computing (HPC). The Tesla K80 has nearly twice the performance and twice the memory bandwidth of its predecessor, the Tesla K40.
The Tesla K80 has been designed for the toughest computing challenges in areas such as astrophysics, genomics, quantum chemistry, data analysis and more. It is also optimized for advanced "deep learning" tasks, one of the fastest growing areas in the machine learning industry.
The Tesla K80 compute speed is up to 8,74 teraflops for single precision floating point and 2,91 teraflops for double precision. According to the company, the Tesla K80 is ten times faster than the fastest CPUs in scientific and engineering applications such as Amber, Gromacs, Quantum Espresso and LSMS.
Among the key features of the Tesla K80 dual-processor accelerator: two GPUs on board - twice the data transfer rate in applications that use the capabilities of multiple GPUs; 24 GB of ultra-fast GDDR5 memory - 12 GB of GPU memory (double that of the Tesla K40) can handle twice the datasets; 480GB/s bandwidth - increased bandwidth allows scientists to process petabytes of information twice as fast compared to the Tesla K10; 4992 parallel CUDA cores - accelerate applications up to 10 times compared to the CPU; dynamic Nvidia GPU Boost technology - dynamically changes GPU frequencies depending on the specific applications for maximum performance; dynamic parallelism - allows GPU threads to dynamically spawn new threads for fast and easy data processing in adaptive and dynamic structures.
Tesla K80 will be able to find application in scientific, engineering, commercial and enterprise HPC and data center applications.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ BLE 5.0 radio module RN4870
▪ Smart chair Sharp
▪ Drops of quantum mechanics
▪ Voyo A15 tablet with Exynos 5250 processor
▪ Data transmission over optical fiber at a speed of 22,9 million Gbit/s
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site for the Builder, home craftsman. Selection of articles
▪ article How the DVD Format Works. video art
▪ Why do salmon swim upstream when spawning? Detailed answer
▪ article physiologist. Job description
▪ article Calculation of electrical loads. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Voltage converter on the K155LA18 chip. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: