
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Voltage converter on the K155LA18 chip. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
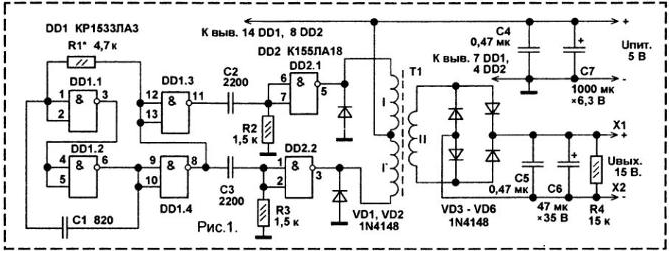
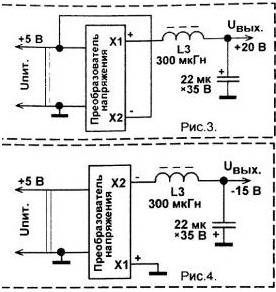
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Voltage converters, rectifiers, inverters The K155LA18 integrated circuit consists of two two-input 2I-NOT elements, the outputs of which are made according to an open collector circuit. The microcircuit allows an output current of up to 300 mA, while the maximum allowable voltage in the log state. 1 at the outputs is 30 V. Such parameters make it possible to use it not only for direct control of various actuators - stepper motors, electromagnetic relays, electric motors, incandescent lamps, LEDs, but also indicate the possibility of its use in voltage and current converters. On fig. 1. An example of the practical implementation of a step-up voltage converter is given. The converter includes a master oscillator made on the TTLSH chip KR1533LAZ, which is 4 elements 2I-NOT, two differentiating circuits C2R2, C3R3, a voltage converter made on the transformer T1 and TTL chip K155LA18 and an AC rectifier with a filter, made on four diodes VD3 - VD6 and capacitors C5, C6. The master oscillator is made on three inverters, operates at a frequency of about 120 kHz. Differentiating circuits R2C2, R3C3 reduce the duration of anti-phase pulses at the inputs DD2. This is necessary in order to prevent the simultaneous presence of the output transistors of logic elements DD2.1, DD2.2 in the open state. In addition, after the output transistor of the inverter DD2.1 is closed, the output transistor of the inverter DD2.2 opens with a slight delay, and vice versa. The amplitude of the voltage amplitude at the outputs DD2 is about 15 V. Capacitors C5, C6 smooth out the ripple of the rectified voltage. Diodes VD1, VD2 protect the output transistors DD2 from reverse voltage. The converter provides an unstabilized DC output voltage of 12...15 V at a load current of 80 mA. In this case, the current consumption will be about 250 mA, and the heating of the DD2 case will not exceed 50°C. Instead of the domestic KR1533LAZ microcircuit, you can install an imported SN74ALS00N. You can apply other inverters from these series. The use of microcircuits from the K1, K155 series in place of DD555 is not excluded. but, at the same time, the resistance of the resistor R1 will need to be reduced by about 5 times and the capacitance of the capacitor C1 should be increased by the same amount. Diodes 1N4148 can be replaced with any of the series KD212, KD247, KD510 or Schottky diodes MBR0540T1 (0,5 A, 40 V), MBRS140T3, MBRS1100T3, 1N5819, MBR150, MBR160. The efficiency of the device when using Schottky diodes will be higher. The transformer is made on the K16x8x6 ring from M2000NN, M2000NM ferrite. The primary winding is wound with PEV-2 wire with a diameter of 0,35 mm - 2x45 turns. The secondary winding contains 170 turns of the same wire. Two layers of adhesive tape are placed between the windings. The sharp edges of the ring are blunted before laying the windings, after which the ring is wrapped with two or three layers of varnished cloth or adhesive tape. After laying, each winding must be impregnated with transformer varnish or compound; zaponlak can also be used. Oxide capacitors - K50-29, K50-35 or analogues, non-polar - K10-17, K10-50, KM-5, KM-6. Resistors - small-sized any type for general use MLT, S1-14, S2-23, S1-4. The considered voltage converter on digital microcircuits was created for experimental purposes. In the course of experiments, it was found that in order to increase efficiency and increase output power, it is desirable to use a slightly larger low-frequency ferrite magnetic core. The use of this converter may be appropriate if the device already has a generator at a frequency of 80. 120 kHz, or it can be assembled on the remaining free logic elements. On fig. 3 shows the application of this device as a step-up voltage converter, while the supply voltage and the output voltage of the converter are added.
On fig. 4 shows a diagram of switching on the converter as a voltage inverter with an increase in output voltage.
If necessary, increase the power of the converter, you can turn on two or three K155LA18 microcircuits in parallel. If a higher output voltage of the converter is needed, for example, to power a vacuum electroluminescent indicator, then the number of turns of the secondary winding of the transformer must be proportionally increased, and in order for the winding to fit on the ring, the wire is selected with a smaller diameter. Author: Butov A.L.
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ New 14A voltage conversion modules in EXCALIBUR package ▪ A new value for the upper limit of the neutrino mass has been established ▪ Camera for filming color video in absolute darkness
▪ site section Power supply. Article selection ▪ Zirlich-Manirlich article. Popular expression ▪ article Which animals cannot walk backwards? Detailed answer ▪ article KARA YS circular saw operator. Standard instruction on labor protection
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: