
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Power outage buzzer
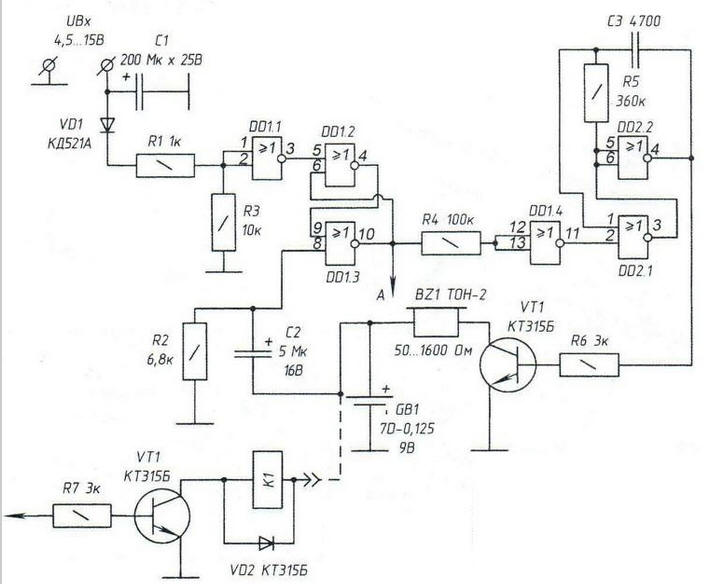
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Protection of equipment from emergency operation of the network, uninterruptible power supplies Many houses in villages and dachas are left without owners in the winter, empty, although things (sometimes even valuable ones) and household appliances remain in them. This is where the danger of theft awaits the owners, so they prudently put an alarm in the house, usually powered by a 220 V household electrical network. But in rural areas it often happens, especially during bad weather, gusts of wind, that the voltage in the lighting network "disappears". In this case, the proposed device will be useful in security systems for various purposes. When using it, even turning off the power of the security system will not help thieves, and here's why. In the event of a mains power failure, the device will turn on an audible signal, which will be active until the reset button is pressed. The button is built into the break in the power supply circuit from the battery (battery) so that the owner of the home, without switching wires and "pulling out" the plug from the outlet, can easily put the device into standby mode. A key cascade with an executive relay K1 is needed to turn on emergency power, for example, from additional batteries (the executive contacts of the relay are not shown in the diagram). In this case, when the audio node is not needed, the elements DD1.4, DD2.1, DD2.2, C3, R5, R6 are removed. Principle of operation of the device A constant voltage in the range of 4,5 - 15 V (Uin), taken from the network adapter, enters the input of the device and, smoothed by the oxide capacitor C1 (K50-24), passes through the VDV1 diode (KD521, KD522, D220 with any letter index) , limiting resistor R1 and is fed to the input of the logic element FF1.1. This element can be turned on as an inverter. Then the normal state at its output is a low voltage level (logical "0"). The normal state assumes the presence of an alternating voltage of 220 V in the lighting network. On the elements DD1.2, DD1.3, a memory cell with two stable states is implemented - a logical trigger. When the reference voltage Uin disappears, a high level will be set at pin 5 DD1.2. The same level will be present at pin 10 of the DD1.3 element and will remain here until the supply voltage is removed from the entire electronic assembly with the reset button (not shown in the diagram), or by removing the connector from the battery (see below). Through the limiting resistor R4, the high-level voltage is fed to the input of the pulse generator implemented on the logic elements DD1.4, DD2.1, DD2.2. The C2R2 chain allows you to set the trigger to a state that excludes false positives. The pulse generator (audio frequency) is started by a logical "1" coming to the input DD1.4 (output 12 chips). The pulse frequency is determined by the values of the elements C3 and R5. With the values indicated in the diagram, the generator frequency is approximately 800 Hz. Transistor VD1 works as a current amplifier. Due to this, a wide range of devices can be used as a sound emitter BZ1: from piezoelectric capsules of the ZP-Z type with high DC resistance (impedance) to dynamic telephone capsules with a resistance above 50 ohms.
Thus, while voltage is supplied to the input of the first element DD1.1 (controlled devices are in good condition), there will be a logical "4" at the output 2.2 of the DD0 element - and silence in the sound capsule BZ1. As soon as the controlled voltage disappears, the generator starts. The trigger on the elements DD1.2, DD1.3 retains its state even when the controlled power supply Ubx is resumed, so the generator, even after the mains voltage is restored, works constantly. To bring the circuit back to the ready state (reset the trigger), you need to briefly disconnect the GB1 battery, then remove and reapply power to Ubx. The battery is connected after applying voltage to the Ubx contacts. The battery and the controlled voltage are connected to the device through a RP10-11 connector or similar. You can adjust the tone of the oscillator by changing the capacitance of the capacitor C3. As the capacitance decreases, the pulse frequency increases. The common power wire of the microcircuits and the controlled circuit should be connected. If it is necessary to automatically turn on the backup voltage source or additional signaling, a node on a transistor key with an executive relay K1 is connected to point "A". Diode VD2 prevents reverse current surges through the relay winding at the on-off moments of K1, thereby protecting the transistor and eliminating relay contact bounce. The circuit is implemented on two CMOS K561LE5 microcircuits, does not require tuning, works stably in 24-hour mode and is easy to repeat. As an autonomous battery, a DT12-012 battery with a capacity of 1,2 Ah or a similar one for a voltage of 12 V is used. Batteries can be used as GB1.
The current consumed by the circuit elements in standby mode (at a high voltage level at the input of the DD1.1 microcircuit) is only 8 mA. Practice has established that a charged battery is enough for 3-4 months of constant operation of the device in standby mode. Therefore, in this circuit, there is no need to connect GB1 through the diode in the forward direction (for constant recharging from the mains power supply) - you can damage the battery. Installation of device elements and options for replacing parts The network adapter (Ubx power supply) can be of any brand. The elements of the device are installed on the circuit board. Transistor VT1 type KT312, KT315 with any letter index. All fixed resistors type MLT-0,25. Oxide capacitors K50-6, K50-12 or similar. Capacitor C3 - type KM6 or similar. Relay K1 (if necessary) - low-power, for a response voltage of 7 - 9 V, for example, RES-15 (version RS4.591.003). For reference: the switching current of the executive contacts of the RES-15 relay in the 220 V circuit is only 150 mA. Author: A.Kashkarov
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Ultra-recycled foods shorten life ▪ Workaholics have fatter kids ▪ Nokia Slimming Electronic Gadgets
▪ section of the site Grounding and grounding. Selection of articles ▪ article Mendeleev Dmitry. Biography of a scientist ▪ article Who and when attacked ground targets from aircraft with darts? Detailed answer ▪ article Sowing rice. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: