Power supply for a sick battery. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Power Supplies
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
Desktop computer motherboards often use nickel-cadmium batteries, which consist of three disk cells. When the computer is turned off, the battery powers the system clock and the SHOP chip, which contains the computer's internal settings. Over time, the nickel-cadmium battery becomes unusable. When the computer is turned off for more than a few hours, the battery is discharged so much that the system clock starts to lag far behind, the settings in the SHOP chip are lost.
Unfortunately, it can be very difficult to get a new battery - computer companies don't usually sell them. It is possible to adapt a cordless phone battery for the motherboard, but such a battery can cost more than a similar motherboard! It is not advisable to use domestic disk batteries D-0,06 and others to assemble a new battery, since their electrodes quickly oxidize and the contacts between the elements in the battery are broken.
The oldest battery can be "revived" with a simple mains power supply (see figure). Its assembly will take much less time than finding a new battery.
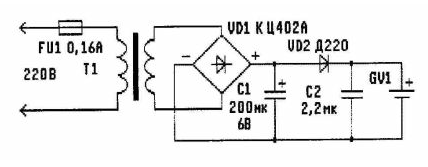
The power supply works as follows. The mains voltage through the fuse FU1 is supplied to the primary winding of the transformer T1. The transformer lowers the voltage to 3,5 V. Then it is rectified by the diode bridge VD1 and fed to the simplest stabilizer, consisting of capacitors C1, C2 and diode VD2. The stabilizer output is connected to the GV1 motherboard battery. There is no overcharging of the battery, since the voltage at the output of the stabilizer (about 3,5 V) is slightly lower than the nominal voltage of a fully charged battery. Thus, the power supply, constantly connected to the network, does not allow the voltage on the battery to drop below 3,5 V. When the mains voltage fails, the VD2 diode prevents the battery from discharging through the leaking capacitor C1. The power supply "gets along" very well with the internal charger of the computer.
Details. Diode bridge VD1 - any of the series KTs402, KTs405, etc., capacitor C1 - any electrolytic, for example K50-16. Diode VD2 - D220, D226,
KD105 and others. Capacitor C2 - paper or metal film, for example K73-17, etc. Any small-sized transformer with a mains winding of 220 V and a secondary winding of 3,5 V is suitable for the circuit. With a slight alteration, you can use "personnel" transformers from old lamp TVs, for example TVK-110-LM-K or TVK-110-L1. In such a transformer, the resistance of all windings is measured. The winding with the highest resistance is carefully connected to the network. If the transformer does not hum and does not heat up, it is suitable for work.
Measure the voltage on all secondary windings. If there is no winding with the required voltage, then a test winding containing 30 ... 40 turns is wound on the transformer frame with any insulated wire. Often this can be done even without disassembling the magnetic circuit. The voltage on the test winding is measured and the number of turns of the new secondary winding is calculated based on the fact that the voltage is proportional to the number of turns. The magnetic circuit is disassembled, unnecessary windings are removed and a new secondary winding is wound with a PEL wire with a diameter of about 0,2 mm. After assembling the power supply, measure the output voltage. If necessary, it can be slightly reduced by connecting another diode in series with the VD2 diode.
The details of the device are mounted inside the computer power supply (if space permits) or in a separate metal casing located inside the system unit. A metal casing is preferable to a plastic one from the point of view of fire safety, since the power supply is constantly connected to the network, without supervision.
Author: S.L.Dubovoy, St. Petersburg
 See other articles Section Power Supplies.
See other articles Section Power Supplies.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
The threat of space debris to the Earth's magnetic field
01.05.2024
More and more often we hear about an increase in the amount of space debris surrounding our planet. However, it is not only active satellites and spacecraft that contribute to this problem, but also debris from old missions. The growing number of satellites launched by companies like SpaceX creates not only opportunities for the development of the Internet, but also serious threats to space security. Experts are now turning their attention to the potential implications for the Earth's magnetic field. Dr. Jonathan McDowell of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics emphasizes that companies are rapidly deploying satellite constellations, and the number of satellites could grow to 100 in the next decade. The rapid development of these cosmic armadas of satellites can lead to contamination of the Earth's plasma environment with dangerous debris and a threat to the stability of the magnetosphere. Metal debris from used rockets can disrupt the ionosphere and magnetosphere. Both of these systems play a key role in protecting the atmosphere and maintaining ... >>
Solidification of bulk substances
30.04.2024
There are quite a few mysteries in the world of science, and one of them is the strange behavior of bulk materials. They may behave like a solid but suddenly turn into a flowing liquid. This phenomenon has attracted the attention of many researchers, and we may finally be getting closer to solving this mystery. Imagine sand in an hourglass. It usually flows freely, but in some cases its particles begin to get stuck, turning from a liquid to a solid. This transition has important implications for many areas, from drug production to construction. Researchers from the USA have attempted to describe this phenomenon and come closer to understanding it. In the study, the scientists conducted simulations in the laboratory using data from bags of polystyrene beads. They found that the vibrations within these sets had specific frequencies, meaning that only certain types of vibrations could travel through the material. Received ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive invisible material
13.12.2020
South Korean scientists have developed a new kind of camouflage "skin" that will allow the military to blend in with the environment. This material hides a person not only from conventional cameras, but also from infrared night cameras.
The new material is made up of "pixels" that contain thermochromic liquid crystals that can change color. The material also reacts to the ambient temperature - it is able to cool or heat up in order to "hide" from thermal imaging cameras.
In the experiment, the research team demonstrated the work of the "skin" using a patch glued to the hand. The hand was placed on different backgrounds and exposed to different temperatures. For example, on a blue background, the material also took on a blue color.
Despite this impressive achievement, the research team still has a lot of work to do. The researchers want the technology to independently react to the surrounding color and change accordingly. Currently, the data to change the color is entered manually using a program, but the team is already close to a decision.
In the near future, the researchers plan to demonstrate the operation of larger patches of "skin". Scientists are also developing more efficient power supplies that will allow the military to use cloaking technology in extreme environments such as the Arctic or the desert.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ The thinnest thin-film photocell
▪ rogue galaxy
▪ Found stars of the second generation
▪ XNUMXD graphene transistors
▪ copper display
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ site section Electrician's tool. Article selection
▪ article The concept of the Big Bang. History and essence of scientific discovery
▪ article Economics and Finance. Big encyclopedia for children and adults
▪ article Tatar honeysuckle. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
▪ article Radio frequency eavesdropper finder. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Two for the price of one. Focus Secret
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: