
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Converter for powering radios
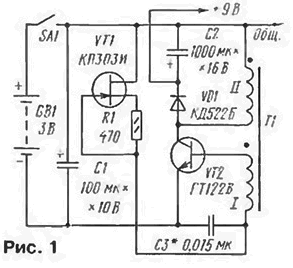
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Voltage converters, rectifiers, inverters Many small-sized transistor radios of the past years, both industrial production (Almaz-401, Sokol-403, Selga-404, Quartz-408, etc.), and home-made ones, were powered by a Krona- VTS" ("Korund") with a voltage of 9 V. There are still many such receivers in operation. This article talks about how to adapt them to power from two galvanic cells. Older "nine-volt" radios can use a three-volt supply if an additional voltage converter is used. Such a converter usually operates in a pulsed mode, which can interfere with radio reception at certain frequencies. Good results were achieved with the device, the scheme of which is shown in Fig. 1. Its basis, as well as devices [1], is the simplest for implementation single-cycle self-oscillator with transformer coupling and diode reverse connection [2]. The generator itself is made on the transistor VT2. The germanium transistor has a low saturation resistance, and this ensures easy start-up and normal operation of the converter at low supply voltage.
On the field-effect transistor VT1, the base current stabilizer of the transistor VT2 is assembled, designed to reduce the dependence of the output voltage on the voltage of the power source. Diode VD1 and capacitor C2 form a half-wave rectifier for output voltage pulses. When the power is turned on by the SA1 switch (radio switch), the current flowing through the source on the transistor VT1 and the I winding of the transformer T1 opens the transistor \ / T2. Through it, the current rises in the winding II of the transformer T1, in which energy is stored. After some time, the collector current of the transistor \/T2 reaches a maximum (for a given base current) and the current growth in the winding II stops. This occurs before the saturation of the transformer core. Transistor VT2 closes, and a burst of self-induction winding II through the diode VD1 charges the storage capacitor C2. Then the cycles are repeated. With a decrease in the EMF of the power supply by 50% (from 3 to 1,5V), the output voltage decreases by no more than 20%. The radio receiver remains operational even when the battery is deeply discharged, up to 1.2 V. The generation frequency depends on the supply voltage. At a nominal voltage of 3 V, the generation frequency is close to 60 kHz, as the power source is discharged, it gradually decreases, which is explained by the long energy accumulation time in the transformer T1, and at a voltage of 2 V it is about 30 kHz. Power from an unstabilized source, of course, somewhat reduces the output power of the receiver, but the primary current drawn from the battery is constant and relatively small. It depends on the quiescent current of radio receivers, which in most cases is equal to 6...10 mA [3], and the efficiency of the converter is about 60%. Its value - 30...45 mA - is close to the recommended modes of discharge of galvanic cells 316[3]. For comparison, the current surges in the transducer [1] reached 200 mA at loudness peaks. In order to simplify the design and reduce the dimensions, the converter is assembled not on a printed circuit board, but by the volumetric mounting method - in the form of a cube with dimensions of 20x20x22 mm. All parts are mounted on one side of the T1 transformer. The largest part - capacitor C2 - is installed inside the toroidal transformer T1. The transformer itself is made on a K20x10x5 magnetic circuit from two glued ferrite rings of the 2000NM1 brand. The windings are made with PEV-2 0,57 wire and are evenly distributed around the circumference, winding I has eight turns, and winding II has 11 turns. Instead of a toroidal one, an armored magnetic core of the B22 type with the same winding data can also be used. However, in this case, the capacitor C2 will have to be placed (glued) outside the transformer T1. which will increase the size of the device. Transistor VT2 GT122V must have a gain of at least 100. It can be replaced by MP37A, MP38A, silicon transistors cannot be used. The field effect transistor of the KP303 series can also be used with indexes V, G, D, E with a cut-off voltage of not more than 1 V. Capacitors C1 and C2 are oxide imported, with possibly smaller dimensions. The finished transducer is placed in a screen housing soldered from copper or brass foil with a separate cover, external dimensions are 22x22x24 mm. Setting up the converter is easy. Turning on the receiver and completely removing the sound with the volume control, select the resistor R1 so. so that the voltage at the output of the converter is 9 V. In this case, the primary current consumed from the battery must be within 30 ... 45 mA. After that, the operation of the receiver is checked at all frequencies and ranges. Unfortunately, in such a simple design, it is often not possible to completely get rid of interference. If interference whistles occur at some frequencies, then you can try to eliminate them by selecting (within a small range) the capacitance of the capacitor C3. In order for the receiver to work stably at high volume, it is also desirable to increase the capacitance of its decoupling oxide capacitors by a factor of 2...4. The described converter is used in a dual-band (SV-DV) receiver of the third complexity group - "Quartz-302". Block 1 is installed in the available free space next to the power supply compartment (Fig. 2).
Two 316 (AA) batteries are close in size to the Krona battery and are placed in the receiver's power compartment. Current. consumed from the battery was 36 mA. Literature
Author: A.Pakhomov, Zernograd, Rostov region
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ The harm of music before bed ▪ Smallest 128Gb Flash Memory Chip
▪ site section Chargers, accumulators, batteries. Article selection ▪ article Banking law. Lecture notes ▪ article Who and when was the first to propose the use of fighting seals? Detailed answer ▪ article Fractures and dislocations. Health care
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: