Test station power supply. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Power Supplies
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
For adjustment, control and testing of electronic circuits and, if necessary, recharging the batteries, a test station power supply is offered, consisting of two stabilized and one regulated channel.
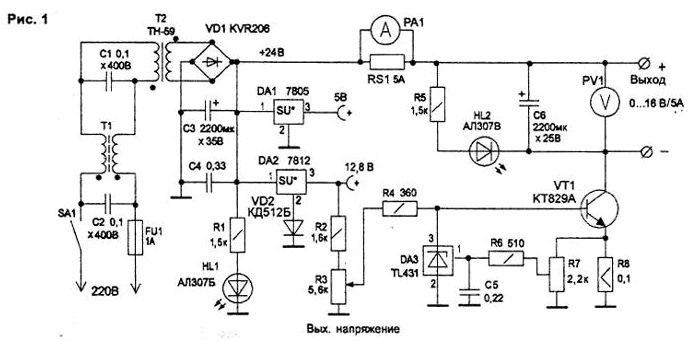
The power supply is made using radio components from decommissioned monitors and computer power supplies. The power supply circuit (Fig. 1) consists of:
- input noise filter on transformer T1 and capacitors C1 ... C2;
- step-down transformer T2;
- rectifier VD1 with smoothing capacitor C3;
- two analog voltage stabilizers on DA1 and DA2 microcircuits (DA2 output voltage for recharging batteries with a voltage of 12 V is increased using the VD2 diode);
- electronic voltage regulator on a composite transistor VT1;
- circuits for protecting the power transistor from overloads and short circuits on the parallel stabilizer DA3.
(click to enlarge)

The stabilized voltage from the output of the DA2 chip is also used to power the voltage regulator circuits on the composite transistor VT1. The regulator transistor has a gain of at least 400 and an output current of more than 5 A, which eliminates the need for additional amplifying stages.
To protect VT1 from failure in the event of a short circuit in the load, the circuit has a feedback circuit from the load current sensor R8 to the VT1 base through a parallel stabilizer on the DA3 chip. Increasing the voltage on the sensor R8 leads to the opening of the parallel regulator DA3, which shunts the base of the transistor VT1 and limits its current. The setting of the current limit can be done with a resistor R7 Instead of a parallel stabilizer, you can install any low-power reverse conduction transistor. The output voltage indication is made on the green LED HL2. To reduce fluctuations in the output voltage, a large capacitor C6 is installed.
The device is assembled on a printed circuit board with dimensions of 72x51 mm (Fig. 2), which is placed in a case from a computer power supply.
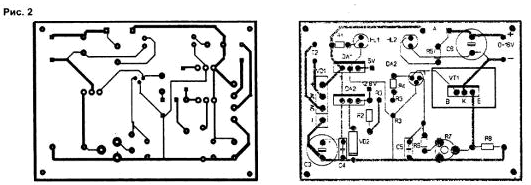
Switch SA1 and fuse FU1, together with an ammeter and voltage regulator R3, are installed on the front wall of the case, the ammeter is mounted in the window after removing the fan. The voltmeter in the circuit is shown conditionally; any tester in the voltage measurement mode is suitable as it.
The RA1 ammeter is made on a measuring head of the M2003 type with a total deflection current of 100 μA. The RS1 shunt is made of 10 turns of 0,8 mm copper wire wound on a 0,8 mm mandrel. The shunt is calibrated by connecting the tester in series with the ammeter in the high current measurement mode.
A step-down transformer with a power of 120 ... 150 W is used industrial, such as TN-58 (59) or TPP-292 (293,294,303), with a total voltage of the secondary windings of 18 ... 24 V and an allowable current of 3 ... 5 A. In the diagram the pinout is not indicated, it can be performed based on the voltages of the secondary windings and their connections. The surge protector is taken ready - from a computer power supply.
Instead of a bridge rectifier VD1, you can use 4 diodes D213B or D304, D246. It is not necessary to install radiators on diodes. The electrolytic capacitor C3 in the circuit is taken for a voltage of 35 V to reduce leakage and possible overheating when the power supply is operating at high load currents.
Integral stabilizers DA1 and DA2 are fixed on a metal case through mica gaskets. Indication of the on state of the power supply is made on the LED HL1. Transistor VT1 is mounted on the case through a gasket with fastening on the outside of the radiator. Resistor R8 can be made of nichrome wire 01 mm and 50 mm long, wound on a resistor type MLT-2.
The power supply circuit does not require special adjustment. It is enough to connect a load in the form of a car light bulb (0 candles) to the output (16 ... 50 V) and set the desired output voltage with the R3 regulator. Resistor R7 is set to a position at which the voltage at the load stops rising when the slider of resistor R3 is turned.
Authors: V.Konovalov, A.Vanteev, Laboratory "Automation and Telemechanics", Irkutsk Center "Energy Saving Technologies", Irkutsk.
 See other articles Section Power Supplies.
See other articles Section Power Supplies.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Radiometer on fire
28.02.2011
A device has been created that can distinguish the source of a fire even underground. To easily overcome a forest fire, you need to notice its source in time. Alas, as a rule, it is hidden by vegetation, and sometimes it can even be located under the soil surface. Devices installed on fire planes that study signals in the infrared range cannot recognize such foci.
Scientists from the Fraunhofer Institute for High Frequency Physics and Radar Technology, led by Dr. Nora von Wahl, decided to create a new device. They noticed that particles of dust, smoke, and plant branches are practically transparent to microwave radiation at a frequency of 22 GHz.
Having made a receiver operating at this frequency, they hung it in the air on a balloon robot. As measurements have shown, such a device at a height of one hundred meters sees a fire seat five by five meters in size, with an accuracy of 2,5 meters. The infrared sensor is more accurate, but the microwave one sees much better - even the layer of soil above the fire does not matter to him, and this is especially true when fighting peat fires.
Scientists hope to make the device smaller and more accurate, after which it can be used to protect forests. At least the German ones.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ sea turtle chemical cocktail
▪ Samsung to launch 3GB mobile memory
▪ Magnetic diode
▪ Transcranial magnetic stimulation improved short-term verbal memory
▪ Tile Mate keychain to control things
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site for the Builder, home craftsman. Selection of articles
▪ article Construction of a glider. Tips for a modeler
▪ article Which philosopher died voluntarily eating like a concentration camp prisoner? Detailed answer
▪ Martin's article. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
▪ article Audio Frequency Generator. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Selection of wire diameter when it is necessary to replace one wire with two or three. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese



 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: