
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Automatic charger powered not only by 220 volts. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
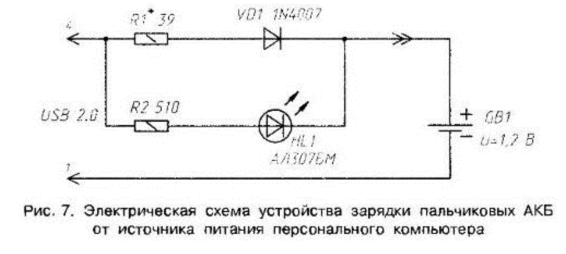
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells Among publications in amateur radio literature, one can often find descriptions of electronic devices and components designed to charge batteries for various purposes from a 220 V AC network. Indeed, this flow of schemes is unlimited and varied. Recently, however, the interest of radio amateurs has been increasingly attracted by chargers for various batteries operating from other voltage sources - car batteries, various batteries (batteries) and a personal computer. With the advent of Ni-Mn and Ni-Cd portable batteries on the public market, having an appearance consistent with AA and AAA batteries (finger batteries of various diameters and lengths) with an operating voltage of 1,2 ... 1,4 V, the need for devices charging of these batteries only increases. Electronic charging devices offered by the industry can already be purchased everywhere, but their price is unlikely to satisfy a novice radio amateur or someone who is able to make a charger with their own hands. Moreover, such a device does not require expensive parts, it is simple to repeat, assemble, reliable in operation (fire and electrical safety) and will take only one evening. The simplest device for recharging batteries with a voltage of 1,2 ... 1,4 V is the electrical circuit shown in fig. 7. This device is designed to connect to the USB bus of any modern personal computer (hereinafter referred to as PC). As you know, 4 contacts of the multifunctional USB port have the following purpose: two - respectively, power "+" and "-" (5 V), the other two serve as an information bus for data exchange with peripheral devices. According to the diagram (in Fig. 7), in this case, only two ±5 V power contacts are used.
Using this device, you can charge portable batteries with a current of approximately 100 mA (in accordance with the resistance of the resistor R7 indicated in the diagram in Fig. 1). Since different AA batteries have different power capacities, it will take different time to charge these batteries accordingly. Thus, batteries with a capacity of 1400 mAh with a nominal voltage of 1,2 V will need to be charged using this circuit for about 14 consecutive hours, and, for example, other batteries with the same nominal voltage of 1,2 V, but with an energy capacity of 700 mAh, will need charge with a continuously running PC for only 7 hours, i.e. half the time. Here it is appropriate to remember that the return of useful energy for different types of batteries (batteries) will be different, mainly comparable to the energy intensity of each specific battery. The charging current in this circuit flows through the circuit R1 - VD1. Moreover, the battery is connected through a connector or removable contacts. The indicator circuit R2, HL1 is introduced into the circuit for a visual representation of the mode of operation of the charger. While the battery is not connected, the HL1 LED does not light up, as soon as the charging current in the circuit takes place (and this happens when the load is connected, i.e. GB1), the indicator LED HL1 starts to glow. It can be of any type and color, with a current of up to 10 mA. If there is no need to indicate the status of the device, which is not uncommon, since the current consumption within 100 mA is safe for the USB port. PC, to which even ultra bright LEDs and local illumination lamps can be connected) - the R2, HL1 circuit is excluded from the circuit. The charging current can be adjusted by changing the resistance of the resistor R1. So, with the values \u100b\u1bof the elements indicated in the diagram, the charging current will be XNUMX mA, and with a decrease in the resistance of the resistor RXNUMX, the charging current will increase proportionally. Not only radio amateurs, but also many manufacturers of industrial chargers, including foreign ones, follow the path considered. On fig. 8. Shown is an AAA battery charger powered by a PC USB port.
The electrical circuit of this device is comparable in simplicity and efficiency with the presented charger circuit in fig. 7. Another equally important issue is charging portable batteries for various purposes with direct current from car batteries with a voltage of 12 and 24 V (the latter are relevant for some types of domestic and foreign trucks, for example, Volvo FL7). For this purpose, various chargers are used. Information for radio amateurs It is possible to charge portable batteries from car batteries (when the nominal voltage of portable batteries is less than car batteries) directly, but this method is fraught with rapid deterioration of the portable battery, is unsafe, and can only be applied in the short term in emergency circumstances, in field (and similar) conditions, as an exception, when it is impossible to charge a portable battery in other ways. It is best to use a special charger with adjustable output current in such a situation, the electrical circuit of which is shown in fig. 9. This scheme is widely used for recharging cell phone batteries with a nominal voltage of 3,6 ... 3,8 V from a car battery, for example, for cell phones of the Motorola or Sony Ericsson family. Here you should take into account the different connectors for connecting cell phones to the charger. As can be seen from the diagram, it uses a two-color indicator LED with a common cathode, which accordingly indicates in red if the cell phone battery is discharged (the charging current exceeds 15 mA) and in green, if the cell phone battery is fully charged (charging current is less than 10 mA) or that the load (cell phone) is not connected at all. At the same time, if there is no load at the output of the charger, then the output voltage will be slightly higher than the nominal, that is, about 4,2 ... 4,4 V. Oxide capacitors C1, C3 smooth out voltage ripples when the car engine is turned on . The basis of the electrical circuit of this device is taken from an industrial car charger for Motorola family phones, and the device itself is shown in the photo fig. 10.
Chargers for other types of cell phones are built on a similar principle. For self-manufacturing of the charger, you can go the other way by assembling a simple circuit shown in Fig. eleven. This device charges Ni-Cd (nickel-cadmium) and Ni-Mn (nickel-manganese) batteries. The device is able to work both autonomously (independently) and as part of a whole system of radio equipment, when an uninterruptible power supply is required (a spare battery is always ready for use). In this case, the battery can be permanently connected to the charger, regardless of whether the battery is used to power the load devices at the moment or not. The DA1 chip is a popular K1006VI1 timer, included as a comparator with two load switching thresholds. A feature of this microcircuit is its powerful output stage, which allows you to deliver a maximum current of up to 300 mA to the load. The reference low voltage for both comparators (comparison circuits of the K1006VI1 timer) is supplied from a reference voltage source implemented on the VD1 zener diode. In this case, the output of the DA1 microcircuit (pin 3) may have a voltage in the range of 0 ... 8,4 V - depending on the voltage at the two threshold inputs (pins 2 and 6 of the DA1 microcircuit, respectively). The voltage at these inputs is set by variable resistors so that there is a delay between the appearance of the output voltage at pin 3 and its disappearance (so that there is hysteresis). Establishment For adjustment, an adjustable constant voltage source is connected to the output of the device. The device can charge portable batteries, both in the form of individual finger cells, and consisting of batteries of the same type of cells connected in series. The variable resistor R6 plays the role of adjusting the charger shutdown threshold (when the battery reaches full capacity). With it, you should set the shutdown threshold of 1,4 V (for one cell of AA or AAA type batteries - for other batteries, a different voltage is used in accordance with the passport data). Similarly, the resistance of the variable resistor R4 is adjusted, depending on which the charging mode is switched on. The threshold for charging should be approximately 1,1 V (if one AAA type cell is used). The maximum current of the charger is determined by the parameters of the DA1 chip and cannot exceed 250 mA (since there is a limiting resistor R3). The device can be supplemented with a current amplifier and a powerful output stage, then the useful charging current will increase, but this is the subject of another article and a proposal for innovative radio amateurs. In this case, to charge portable low-capacity batteries, the resistance of resistor R3 is chosen so that the charging current is no more than 0,1 of the nominal battery capacity (indicated in the battery data sheet or on its case in Ah). In practice, the resistance of this resistor can be in a wide range of 15-510 ohms. Diode VD2 prevents the battery from discharging through the output stage of the DA1 chip when there is no charging current, and there is a low voltage level at pin 3 of DA1. About details All fixed resistors type MLT-0,25. Zener diode VD1 type KS456A, KS147A. Indicator LED - any with current up to 12mA. The glow of this LED indicates that there is no charging current (there is no contact with the load - the battery or the battery is fully charged). Rectifier diode VD2 type D247, D213 with any letter index or similar. Variable resistors R4, R6 are multi-turn, for example SP 1-49V. Oxide capacitor C1 type K50-29 or similar prevents interference (smooths power ripples), for example, when a car engine is running. Non-polar capacitors C2-C4 type. KM6 or similar. Their role is to prevent the influence of interference on the operation of the microcircuit. With the help of this device, due to the wide range of output voltage adjustment at a current of up to 300 mA, it is possible to charge different types of batteries, that is, this device can be used universally. Author: Kashkarov A.P.
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Puma BeatBot helps runners train
▪ section of the site Security and safety. Article selection ▪ article Greenhouse dugout. Tips for the home master ▪ article Which animal has fingerprints like a human? Detailed answer ▪ article Deputy director for teaching and educational work. Job description
Comments on the article: mira please provide a price list for Lamps nickel-manganese (Ni/Mn) -2 pcs, cadmium (Cd) -2 pcs
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese




 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: