Transformerless charger 20 volts 140 milliamps

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
I offer a low-power charger (charger) with a quenching capacitor (Fig. 1). It is designed to charge batteries with a maximum output current of 140 mA and a voltage of up to 20 V. The transistor threshold circuit allows you to set the charging voltage of 13,8 ... 14,4 V (for batteries - 12,6 V), at which the charging current is turned off , i.e. overcharging of the battery is prevented. This is facilitated by a gradual decrease in the charging current with increasing voltage on the battery.
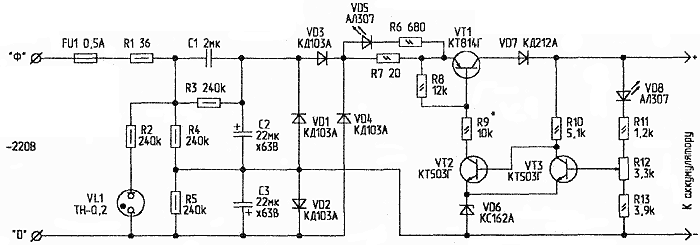
Rice. 1. Schematic diagram of the charger (click to enlarge)
In the memory circuit, special attention is paid to safety. The phase wire "Ф" of the 220 V network is connected through a fuse and an inrush current limiter R1 to a quenching capacitor C1, the other output of which and the neutral wire of the network "0" are connected to a capacitor voltage divider.
Through the diode bridge VD1 ... VD4, the voltage from the capacitors C2, C3 is connected to the key circuit on VT1 ... VT3. Resistor R7 - shunt charge current indicator VD5. The charging current in the form of wide pulses with a frequency of 100 Hz enters the battery through the VT1 key and the VD7 diode. In the pauses between charging pulses, the battery is discharged for desulfation through a threshold circuit on VT3 and VD6.
Resistor R12 sets the maximum battery charge voltage. When it is reached, the transistor VT3 opens, and VT2, VT1 close, the charge current stops, and the green LED VD5 goes out, indicating the charge. After some time, due to self-discharge, the voltage on the battery decreases, and the threshold trigger on VT2, VT3 turns on the charging current again, opening VT1. Flashing VD5 with a period of about 5 s indicates the charged state of the battery. In this mode, the battery can power the bell circuit or the emergency fluorescent lamp. With the current "fan" outages, this is an important property of the memory.
The most critical part of the memory is capacitor C1. Here you can use 2 capacitors of the K73-14 type (1 μF x 400 V) or 4 K73-17 (0,47 μF x 630 V) connected in parallel. Electrolytic capacitors C2, C3 - K50-35 (22 uF x 63 V). It is undesirable to use imported "electrolytes", because they have large losses during reloading.
Diodes VD1 ... VD4 can be used with any Uobp> 100 V and IMax> 200 mA. KD103A and 1N4007 work well. Transistors - with Uke> 80 V.
When you turn on the charger for the first time, you need to set the R12 regulator slider to the lower position according to the diagram. The green LED VD5 should be lit. During operation, it is worth checking the absence of heating VT1. Overheating can be eliminated by reducing the resistance R9 or replacing VT1, VT2 with transistors with a large β.
Upon reaching Uak = 13,8 V by rotating R12, you need to turn off the charging current.
Connect the charger to a 220 V network using an indicator screwdriver or a neon bulb TN-0,2 with a 240 kOhm (0,5 W) resistor to determine the phase wire in the outlet.
To charge 6-volt batteries, the VD6 zener diode must be replaced with KS133 or KS147.
When the battery is disconnected from the charger, the voltage at the output of the charger (cathode VD7) is zero. Relative to the neutral wire of the network, both output wires of the charger have a potential of about 30 V. Closing the output wires of the charger does not disable it, because. the maximum current is limited by C1 at 140 mA.
Literature
- O. Khovaiko. Power supplies with a capacitor voltage divider. - Radio, 1997, N11, p.56.
- A.Sorokin. Charging and desulfating machine. - Radio amateur, 1998, N10, p.30.
- A. Trifonov. Ballast capacitor selection. - Radio, 1999, N4, p.44.
- S. Biryukov. Calculation of a network power supply with a quenching capacitor. - Radio, 1997, N5, p.48.
- S. Biryukov. Digital devices on the IC, 1999.
- R. Levitsky. On the use of capacitors in AC circuits. - Radio, 1969, N8, p.49.
- Pulse charger. - Radio, 1995, N8, p.61.
Author: Yu.Semenov, Voronezh; Publication: cxem.net
 See other articles Section Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells.
See other articles Section Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Samsung Connect Tag Smart Keychain for Tracking People and Objects
26.10.2017
Samsung Electronics introduced the Connect Tag tracker, which allows you to know where your loved ones are, as well as track the location of any valuables. According to the company, it is the world's first mobile device to use NB-IoT (Cat.M1), a specially created low-power mobile communications standard for small data transfers. The tracker uses an electronic SIM card (eSIM).
Using a secure internet connection, Samsung Connect Tag detects your location and sends smart notifications. The device uses GPS, cellular networks, and a navigation system that allows you to determine the location using Wi-Fi hotspots to ensure the accuracy of the device's operation indoors and outdoors.
The Samsung Connect Tag can be attached to a child's backpack to always know where the child is, or attached to a dog's collar so as not to lose a pet. Samsung Connect Tag can also be hung on a keychain.
Like many other Samsung IoT devices, the new tracker will be linked to a special SmartThings platform to interact with the user's smart home appliances. So, thanks to the Geo-fence function, Samsung Connect Tag will inform the selected devices that the user is nearby. You can set the lights or TV to turn on automatically when you enter your home, set certain zones to receive notifications, for example, when a child enters the school grounds or a dog runs out into the backyard.
Finding a car in a large open parking lot is no longer difficult - the On-demand function will help you determine the location of the car. All you need to do is press a button on your smartphone.
Another feature allows the tracker holder to submit their current location themselves. Even a small child will be able to tell exactly where he is. In addition, thanks to notifications, you can get a record of all the movements of loved ones.
Dimensions Samsung Connect Tag only 42,1 x 11,9 mm, weight 25 g. The device is protected from dust and moisture thanks to a special protection system according to IP68 class. It holds charge up to 7 days. The kit includes a special ring that allows you to attach the tracker to bags, collars, key rings.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Enabling and disabling gluttony
▪ Neuromorphic chips for artificial intelligence
▪ Metal cracks can heal
▪ You can love a caring robot
▪ paper transistors
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Spy stuff. Article selection
▪ article Peshkov Alexei Maksimovich (Maxim Gorky). Famous aphorisms
▪ article Why do geese fly in formation? Detailed answer
▪ article Bayonet with a run-out. Tourist tips
▪ article Mobile phone charger repair. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article A burning candle from the pocket. Focus Secret
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: