
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Charger on the PIC12F675 microcontroller. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells This charger (charger) automates the process of charging batteries. If the battery is not discharged to a voltage of 1 V, it will discharge it to this voltage and only then will charging begin. At the end of it, the charger will check the battery's performance and, if it is faulty, will give an appropriate signal. The proposed charger is designed for simultaneous independent charging of three Ni-Cd or Ni-Mh batteries of size AA or AAA with a current of 0,23 A. It was developed on the basis of a similar design described in [1]. For the purpose of simplification, it uses a microcontroller with a built-in analog-to-digital converter. The schematic diagram of the memory itself is shown in fig. 1. It consists of a control unit and three identical discharge-charging cells A1-A3. To power it, a network switching power supply (PSU) was used, the circuit of which is shown in fig. 2. It is based on the construction described in [2].
The control unit is assembled on a microcontroller (MK) DD1 and register DD2. The choice of MK PIC12F675 is due to the presence of a built-in analog-to-digital converter and low cost. The codes of the program on which it works are presented in the table. Power microcircuits DD1, DD2 stabilized integrated stabilizer DA1. LED HL1 acts as a power indicator.
Each discharge-charging cell consists of a current stabilizer on a 1DA1 microcircuit (hereinafter, the positional designations of the elements of cell A1 are indicated) with a current-setting resistor 1R2, electronic switches on transistors 1VT1-1VT3, a discharge indicator on the 1HL2 LED of yellow glow and a charging indicator on the 1HL1 LED red glow. In the PSU, resistor R1 limits the inrush current. The diode bridge VD1 rectifies the mains voltage, and the C1C2L1 filter smooths out the ripple of the rectified voltage. The voltage converter is assembled on a TNY264P chip and operates at a frequency of about 132 kHz. Elements VD2, R5, C3 form a damping circuit that suppresses voltage surges on the primary winding of transformer T1. The voltage of the secondary winding of the transformer T1 rectifies the VD3 diode, and the C6L2C7 filter smoothes the rectified voltage. To control the output voltage, an optocoupler U1, a zener diode VD4 and a resistor R6 are used. After applying the supply voltage, MK DD1 sequentially checks for the presence of batteries connected to the cells. If there is no voltage at socket XS1, MK DD1 "concludes" that the battery is not installed and proceeds to analyze the state of the next cell.
When the battery is connected, MK DD1 measures its voltage, and if it is more than 1 V, the cell switches to the discharge mode. A high voltage level appears at pin 5 of the DD2 register, the 1VT3 transistor opens, and a discharge current of about 1 mA flows through it and the 8R100 resistor, and the 1HL2 LED starts to glow, indicating this mode. As soon as the battery voltage becomes less than 1 V, MK DD1 will turn off the discharge mode and the 1HL2 LED will turn off. A high level will appear at pin 6 of the DD2 register, transistors 1VT1 and 1VT2 will open, the battery will start charging and the 1HL1 LED will light up. In this mode, MK DD1 periodically measures the voltage on the battery, and when it reaches a value of 1,45 V, it starts to check whether the voltage is increasing or not. When the voltage stops increasing, the charging mode stops and the discharge mode briefly turns on (the 1HL2 LED lights up) and the voltage on the battery is measured. If it is 1,1 V or less, which indicates an unsatisfactory battery condition, the 1HL2 LED will flash. When connected to the battery charger, the voltage on which is less than 1 V, the charging mode is activated immediately. To cool the memory elements, an M1 fan is used, which starts working when the charging mode of any of the batteries is turned on. Since the supply voltage is less than the nominal voltage (about 8,5 V), it rotates slowly, but the performance is sufficient to cool the device. After all the batteries are charged, the fan stops working, and the HL1 green LED starts flashing, indicating that the charger can be disconnected from the mains.
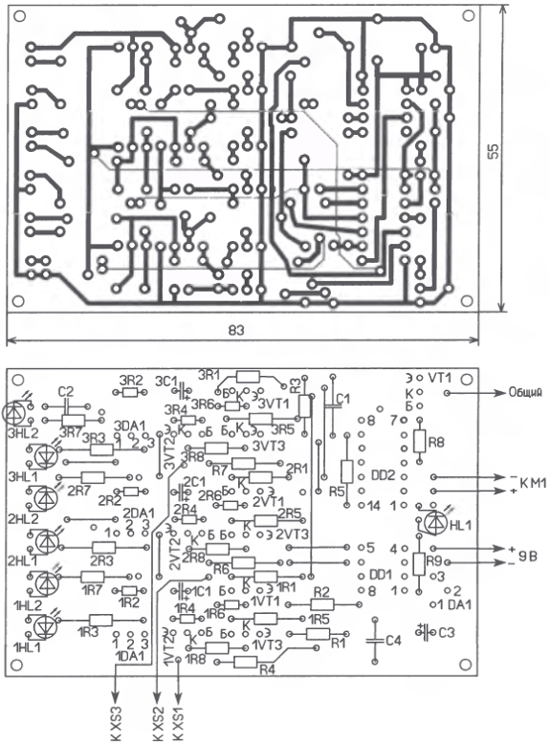
The details of the memory are mounted on a printed circuit board made of one-sided foil-coated fiberglass, the drawing of which is shown in fig. 3. It is designed for the installation of fixed resistors MLT, C2-33, oxide capacitors - K50-35 or imported capacitors C1, C2, C4 - K73-17. LEDs can be of any type with a housing diameter of 3 ... 5 mm, preferably with increased brightness. Panels are used to install microcircuits DD1, DD2, resistors 1R2, 1R4, 1R6, 1R8 are installed perpendicular to the board. All LEDs are installed on the side of the printed conductors, there are also four jumpers from the MGTF-0,12 wire. M1 fan with a supply voltage of 12 V and dimensions of 8x40x40 mm - from computer technology.
A drawing of the printed circuit board of the PSU is shown in fig. 4. For the transformer, an EFD25 magnetic circuit with a frame was used. The total gap between the halves of the magnetic circuit is 0,2 mm. The primary winding contains 171 turns of wire PEV-2 0,13, the secondary - 15 turns of wire PEV-2 0,75, inductor L1 - SBCP-47HY102B from TOKIN, inductor L2 - DM-3. To obtain an output voltage of 9 V, a BZX79-B8V2 zener diode with a stabilization voltage of 8,2 V was used. More details about the design and details of the PSU are described in [2].
The boards are interconnected by screws and plastic stands about 32 mm long (Fig. 5). After assembling the boards, they are placed in a case of a suitable size with seats for batteries on one side and a plug for connecting to the mains on the other. The fan is located in the lower part of the housing (Fig. 6) in the same place, and several ventilation holes are made in the upper part.
The device does not require adjustment. Before installing the chips in the panel, you need to check the voltage at the output of the power supply and at the output of the DA1 stabilizer. The finished program can be downloaded hence. Literature
Author: V. Kiba, Kamensk-Shakhtinsky, Rostov Region; Publication: radioradar.net
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ The Metaverse may be worse than social networks ▪ Radeon RX 7900M graphics card
▪ section of the website Audiotechnics. Article selection ▪ article by Richard Bach. Famous aphorisms ▪ article What stars are called red giants and how high is their average density? Detailed answer ▪ article Thermopsis lanceolate. Legends, cultivation, methods of application ▪ article Drawing with iodine. Chemical experience
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese






 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: