
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Mains voltage stabilizer with microcontroller control. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Surge Protectors A long-term deviation of the mains voltage by more than 10% from the nominal value of 220 V in many regions of our country, unfortunately, has become a common occurrence. With an increased (up to 240 ... 250 V) voltage in the network, the service life of lighting devices is significantly reduced, the heating of transformer power supplies and motors in refrigerator compressors increases. Reducing the mains voltage below 160 ... 170 V causes a significant increase in the load on key transistors in switching power supplies (this can lead to their overheating and subsequent thermal breakdown), as well as jamming of motors in refrigerator compressors, which also leads to their overheating and output out of service. Even greater voltage fluctuations for single-phase consumers powered by a three-phase network occur in the event of a break in the neutral wire in the area from the point of connection of the consumer to the four-wire network to the transformer substation. In this case, due to phase imbalance, the voltage in the outlet can vary from several tens of volts up to linear 380 V, which will inevitably lead to damage to almost all complex household appliances connected to the outlet. The proposed stabilizer will help to avoid the troubles associated with extreme voltage fluctuations in the network. To stabilize the mains voltage in domestic conditions, ferroresonance stabilizers are mainly used. Their disadvantages include distortion of the sinusoidal form of the output voltage (for example, it is forbidden to connect a refrigerator to such a stabilizer), the limited power of household stabilizers (300 ... 400 W) with significant weight and size indicators, the inability to work without load, a narrow stabilization range failure at high voltage in the network. The compensation voltage stabilizer is free from these shortcomings, the block diagram of which is shown in fig. one.
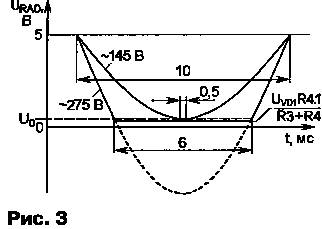
It works on the principle of stepwise voltage correction, carried out by switching the taps of the winding of the autotransformer T1 using triac switches Q2-Q6 under the control of a microcontroller (MK) that monitors the voltage level in the network. The method used in the stabilizer for estimating the amplitude of the mains voltage is extremely simple to implement and provides quite sufficient measurement accuracy for this application. However, it imposes a number of restrictions on the possible use of the device. First of all, the mains voltage frequency must remain constant (50 Hz). This condition may be violated, for example, if power is supplied from an autonomous diesel generator. In addition, the measurement accuracy decreases with an increase in the nonlinear distortion of the mains voltage waveform, which occurs during the operation of closely spaced powerful consumers with a pronounced inductive nature of the load. The schematic diagram of the device is shown in fig. 2. According to the program recorded in the memory, MK DD1 measures the mains voltage in each period (20 ms). From the divider R1R2, the negative half-waves of the mains voltage, passing through the zener diode VD1, form pulses on it with an amplitude determined by the stabilization voltage of the zener diode, in this case 10 V. From the divider R3R4, which reduces the amplitude of the received signal to the TTL level (Fig. 3), these pulses come to line 0 of port A, configured for input.
Using the trimmer resistor R4, the lower signal level at the MK input is set to 0,2. ..0,3 V below the log level. 0. At room temperature and a stabilized supply voltage, the voltage level of the transition of the digital input of the CMOS microcircuit from the state of the log. 1 to the state of the log. 0 (and back from 0 to 1 with some hysteresis, which in this case can be neglected due to its constant value) remains almost constant. As can be seen from fig. 3, when the mains voltage changes from 145 to 275 V, the duration of the pulses corresponding to the log. 0, varies from about 0,5 to 6 ms. By measuring the duration of these pulses, the MC program calculates the level of mains voltage in the current period. (R4.1 is the resistance of a part of the resistor R4 from the bottom - according to the diagram - output to the engine). After turning on the stabilizer, the mains voltage is controlled for 5 s. If it is in the range of 145 ... 275 V, the green LED HL2 "Normal" flashes, otherwise the LED HL3 "Low" or HL1 "High" lights up (depending on the value of the mains voltage). In this state, the stabilizer is until the voltage in the network enters the specified limits. If after 5 s the mains voltage remains within acceptable limits, the MK issues a command to open the VS1 simistor, through which the T1 autotransformer is connected to the network. After that, the MK makes control measurements of the mains voltage for another 0,5 s, and then, depending on the measurement result, opens one of the triacs VS2-VS6, thereby connecting the load to one of the five taps of the autotransformer. Galvanic isolation of triacs with MK is carried out by thyristor optocouplers U1-U6. In the process of regulation, the opening pulse is removed from the switched on triac at the end of the half-cycle of the sinusoid of the mains voltage. After that, the MK program pauses for 4 ms, and then sends an opening pulse to another triac. The duration of the delay between switching triacs can be increased by changing at the beginning of the program (in the constants description block) the corresponding value of the delay time (see comments in the source code of the program). Increasing this time to 10 ... 15 ms is necessary if an inductive load with a power factor of less than 0,7 ... 0,8 is connected to the stabilizer. If the mains voltage deviates beyond the permissible limits, the autotransformer, together with the load, is turned off by the triac VS1. LEDs HL1-HL8 indicate the state of the stabilizer and the voltage levels in the network. Depending on the value of the mains voltage U, the outputs of the additional windings of the autotransformer are switched in the following order: - U<145 V - the load is off, the red LED HL3 is on ("Low"); - 145 - 165 - 190 - 205 - 235 - 245 - 265 - U>275 V - the load is disconnected from the network, the red LED HL1 ("High") is on. To prevent random switching of triacs in case the mains voltage is at the threshold of switching the taps of the autotransformer, a certain "hysteresis" in operation has been introduced into the program. For example, if when the mains voltage increases from 189 to 190 V, the load is switched from the "+20%" tap to "+10%", Author: S. Koryakov, Shakhty, Rostov region; Publication: cxem.net
Artificial leather for touch emulation
15.04.2024 Petgugu Global cat litter
15.04.2024 The attractiveness of caring men
14.04.2024
▪ Omnidirectional speaker system Archt One ▪ Sneakers made from vegetable materials ▪ Oukitel K10000 Pro smartphone with 10100 mAh battery
▪ section of the site Normative documentation on labor protection. Article selection ▪ article All this jazz. Popular expression ▪ article Do raccoons wash their food? Detailed answer ▪ article Jaeger (senior huntsman). Job description
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: