Why is it undesirable to use ferrite magnetic cores in resonant circuits of the radio frequency path of receiving devices. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Civil radio communications
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
In any handbook on radio engineering, you can find a graph of the dependence of the magnetic induction B in a ferromagnet on the magnetic field strength H, the so-called magnetization curve (Fig. 1.a).

Fig.1.a
If a demagnetized ferrite is placed in a magnetic field, then with increasing strength, the magnetic induction will increase in accordance with the OA curve. If the ferrite is pre-magnetized, then the dependence of B on H has the form of the so-called hysteresis loop. When the field strength decreases, the value of B changes in accordance with the upper part of the curve, and with an increase, in accordance with the lower one.
If the current i flowing through the coil changes in time according to a harmonic law, i.e., along a sinusoid (Fig. 1.b), then the voltage that arises at the ends of the coil is proportional to the rate of change of the magnetic flux penetrating the section of the coil.
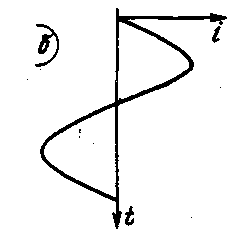
Fig.1.b
Thus, from Fig. 1c it can be seen that the U(t) graph is very different from a sinusoid, i.e., in the voltage spectrum, in addition to the first harmonic, there are also higher harmonics. Moreover, if the hysteresis loop is symmetrical, and the current through the coil does not have a constant component u. therefore, there is no permanent bias, then the spectrum contains only odd harmonics - mainly the first, third, fifth and seventh. If, however, currents of two frequencies f1 and f2 flow simultaneously through the coil, then in the frequency spectrum of the voltage, as a result of mutual modulation, not only higher harmonics will appear, but also combination frequencies 2f1-f2, 2f2-f1, 3f1-2f2, 3f2-2f2, etc. d. Therefore, the shapes of the output and input signals are very different.
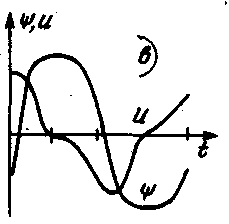
Fig.1.c
In receiving equipment, ferrite magnetic cores can be used in non-resonant current transformers and balancing devices, which must be calculated so that the magnetic fields created by currents flowing through different windings are mutually compensated.
Literature
-
Radio No. 3, 1985, p.63.
Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
 See other articles Section Civil radio communications.
See other articles Section Civil radio communications.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Wind turbine efficiency increased
08.06.2014
By changing the design of the blades, General Electric engineers were able to improve the efficiency of wind turbines.
The work was carried out by General Electric researchers as part of a $2 million renewable energy project. GE's way to improve the efficiency of old wind turbines has proven effective and low cost.
A serious problem with modern wind farms is that they are not efficient enough - to replace one coal-fired thermal power plant, it is necessary to build a wind farm consisting of thousands of turbines occupying a large area. According to experts, the efficiency of wind turbines depends on the size of the blades and the height at which the rotor is located. The larger the rotor and the higher it is, the more efficient the windmill is. For this reason, in recent years, the height of wind turbines has been increased from an average of 15,2 m to 152 m.
General Electric engineers proposed cutting a 27-meter blade in half and inserting a 7-meter part into it, the contours of which exactly match the contour of the original blade. According to the company, this operation on the blades increases the performance of the wind turbine by 20% when operating with low wind speeds.
The modified blades have surpassed International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards in both fatigue failure tests (6 million cycles completed) and static tests.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Algae will help extract gold from hot springs
▪ Multi-Voltage Power Supply Controllers for LCD Monitors
▪ Development of technology for capturing greenhouse gases
▪ cool mice
▪ Improvement of iOLED technology
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the website job descriptions. Article selection
▪ article by Bayard Taylor. Famous aphorisms
▪ article Why is white drink chilled, and red - at room temperature? Detailed answer
▪ article Pomeranian. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
▪ article Small-sized oscilloscope-probe. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Indicator for connecting electrical appliances to a 220 V network. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese




 See other articles Section
See other articles Section 